|
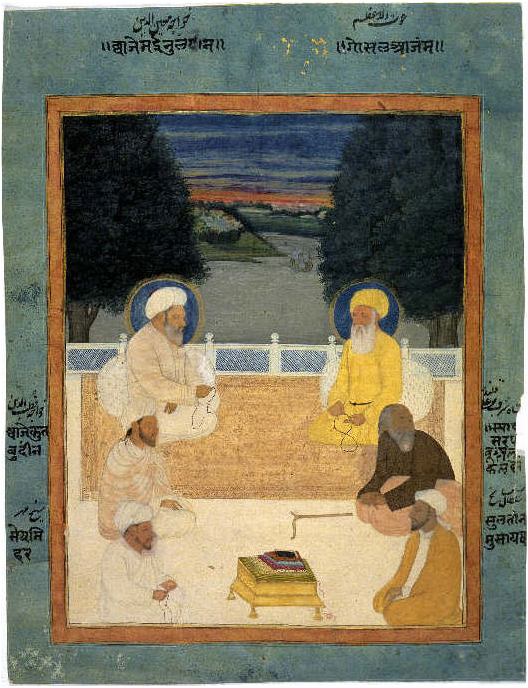
Abu Uthman Al-Hiri
Abu 'Uthman al-Hiri, also known as Sa’id ibn Isma’il ibn Sa’id ibn al-Mansur, was a Sufi master from Khurasan in the 9th century. He played a significant role in the formation of the Malamatiyya, a Muslim mystic group that emphasized self-blame and the concealment of one's piety. Born in Rayy, he was also referred to as al-Razi Razi () or al-Razi () is a name that was historically used to indicate a person coming from Ray, Iran. People It most commonly refers to: * Muhammad ibn Zakariya al-Razi (865–925), influential physician, alchemist and philosopher, also known b .... References 9th-century Muslim scholars of Islam Sufi saints People from Ray, Iran 9th-century Iranian people 9th-century Sufis {{Islam-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray, Iran
Shahre Ray, Shahr-e Ray, Shahre Rey, or Shahr-e Rey (, ) or simply Ray or Rey (), is the capital of Ray County, Iran, Rey County in Tehran Province, Iran. Formerly a distinct city, it has now been absorbed into the metropolitan area of Greater Tehran as the 20th district of municipal Tehran, the capital city of the country. In historical sources also known as Rhages (), Rhagae, and Arsacia, Ray is the oldest existing city in Tehran Province. In the Classical antiquity, classical era, it was a prominent city belonging to Media (region), Media, the political and cultural base of the Medes. Old Persian cuneiform, Ancient Persian inscriptions and the Avesta (Zoroastrianism, Zoroastrian Religious text, scriptures), among other sources, attest to the importance of ancient Ray. Ray is mentioned several times in the Biblical apocrypha, Apocrypha. It is also shown on the fourth-century Tabula Peutingeriana, Peutinger Map. The city was subject to severe destruction during the Middle Ages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malamatiyya
The Malāmatiyya (), or Malamatis, were an early Muslim organization and associated Islamic mystical movement active in 9th-century Greater Khorasan. The root word of their name is the Arabic word ''malāmah'' () "blame". The Malamatiyya believed in the value of self-blame, that piety should be a private matter and that being held in good esteem would lead to worldly attachment. They concealed their knowledge and made sure their faults would be known, reminding them of their imperfection. The Malamati is one for whom the doctrine of "spiritual states" is fraught with subtle deceptions of the most despicable kind; he despises personal piety, not because he is focused on the perceptions or reactions of people, but as a consistent involuntary witness of his own "pious hypocrisy". "Malamati" can also refer to a method of teaching within Sufism based on taking blame. Malamatiyyas and Sufis According to scholar Sara Sviri, the Malamati originated in Nishapur in the 9th-10th centurie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign of the Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid (786 to 809) with the inauguration of the House of Wisdom, which saw Ulama, scholars from all over the Muslim world flock to Baghdad, the world's largest city at the time, to translate the known world's classical knowledge into Arabic and Persian language, Persian. The period is traditionally said to have ended with the collapse of the Abbasid caliphate due to Mongol invasions and conquests, Mongol invasions and the Siege of Baghdad (1258), Siege of Baghdad in 1258. There are a few alternative timelines. Some scholars extend the end date of the golden age to around 1350, including the Timurid Renaissance within it, while others place the end of the Islamic Golden Age as late as the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khurasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses western and northern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, the eastern halves of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, and portions of Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan. The extent of the region referred to as ''Khorasan'' varied over time. In its stricter historical sense, it comprised the present territories of Khorasan Province, northeastern Iran, parts of Afghanistan and southern parts of Central Asia, extending as far as the Amu Darya (Oxus) river. However, the name has often been used in a loose sense to include a wider region that included most of Transoxiana (encompassing Bukhara and Samarqand in present-day Uzbekistan), extended westward to the Caspian Sea, Caspian coast and to the Dasht-e Kavir southward to Sistan, and eastward to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufism
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism. Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and historically typically belonged to "orders" known as (pl. ) — congregations formed around a grand (saint) who would be the last in a Silsilah, chain of successive teachers linking back to Muhammad, with the goal of undergoing (self purification) and the hope of reaching the Maqam (Sufism), spiritual station of . The ultimate aim of Sufis is to seek the pleasure of God by endeavoring to return to their original state of purity and natural disposition, known as . Sufism emerged early on in Islamic history, partly as a reaction against the expansion of the early Umayyad Caliphate (661–750) and mainly under the tutelage of Hasan al-Basri. Although Sufis were opposed to dry legalism, they strictly obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayy
Shahre Ray, Shahr-e Ray, Shahre Rey, or Shahr-e Rey (, ) or simply Ray or Rey (), is the capital of Rey County in Tehran Province, Iran. Formerly a distinct city, it has now been absorbed into the metropolitan area of Greater Tehran as the 20th district of municipal Tehran, the capital city of the country. In historical sources also known as Rhages (), Rhagae, and Arsacia, Ray is the oldest existing city in Tehran Province. In the classical era, it was a prominent city belonging to Media, the political and cultural base of the Medes. Ancient Persian inscriptions and the Avesta (Zoroastrian scriptures), among other sources, attest to the importance of ancient Ray. Ray is mentioned several times in the Apocrypha. It is also shown on the fourth-century Peutinger Map. The city was subject to severe destruction during the medieval invasions by the Arabs, Turks, and Mongols. Its position as a capital city was revived during the reigns of the Buyid Daylamites and the Seljuk Turks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Razi (other)
Razi () or al-Razi () is a name that was historically used to indicate a person coming from Ray, Iran. People It most commonly refers to: * Muhammad ibn Zakariya al-Razi (865–925), influential physician, alchemist and philosopher, also known by his Latinized name Rhazes or Rasis * Abu Hatim Ahmad ibn Hamdan al-Razi (died c. 934), Isma'ili philosopher * Fakhr al-Din al-Razi (1150–1210), influential polymath and theologian It may also refer to: * Shapur of Rey, also known as Sabur al-Razi, Sasanian military officer from the Mihran family, Marzban of Persian Armenia 483–4 * Mihran Razi (died 637), military officer from the Mihran family * Abu Zur’a al-Razi (died 878), Sunni hadith scholar * Abu Hatim Muhammad ibn Idris al-Razi (811–890), Sunni hadith scholar * Muhammad ibn Ya'qub al-Kulayni al-Razi (864–941), Shia compiler of hadith * Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad ibn Mūsa al-Rāzī (888–955), historian * ʿĪsā al-Rāzī (died 980), historian * Najm al-Din Razi, 13th-cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century Muslim Scholars Of Islam
The 9th century was a period from 801 (represented by the Roman numerals DCCCI) through 900 (CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. In America, the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfare, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufi Saints
Sufi saints or wali (, plural ʾawliyāʾ أولياء) played an instrumental and foregrounding role in spreading Islam throughout the world. In the traditional Islamic view, a saint is portrayed as someone "marked by pecialdivine favor ... ndholiness", and who is specifically "chosen by God and endowed with exceptional gifts, such as the ability to work miracles."Radtke, B., "Saint", in: ''Encyclopaedia of the Qurʾān'', General Editor: Jane Dammen McAuliffe, Georgetown University, Washington, D.C. List A * Abul Hasan ash-Shadhili * Ali Hisam-ad-Din Naqshbandi * Ameer Muhammad Akram Awan (1934–2017, 12th Sheikh of Silsila Naqshbandia Owaisiah and writer of several books and 03 Tafaseer of the Holy Qur'an) * Abdallah ibn Alawi al-Haddad (1634–1720, buried in Hadhramaut, author on several books on Dhikr) * Abdullah Ansari * Abdullah Shah Ghazi (d. 720, buried in Karachi) * Abdul Khaliq Ghajadwani (d. 1179, buried in Bukhara, one of the Khwajagan of the Naqshb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Ray, Iran
The term "the people" refers to the public or Common people, common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of Person, persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independence, independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century Iranian People
The 9th century was a period from 801 (represented by the Roman numerals DCCCI) through 900 (CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and Imprisonment, imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan Kingdom, Pagan. Tang china, Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong of Tang, Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao#Rebellions, Huang Chao rebellions. In America, the Maya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |