|
Absolute Income Hypothesis
In economics, the absolute income hypothesis concerns how a consumer divides their disposable income between consumption and saving. It is part of the theory of consumption proposed by economist John Maynard Keynes. The hypothesis was subject to further research in the 1960s and 70s, most notably by American economist James Tobin (1918–2002)."", wisdomsupreme.com. Retrieved 2019-03-01 Background Keynes' ''General Theory'' in 1936 identified the relationship between income and consumption as a key macroeconomic relationship. Keynes asserted that real consumption (i.e. adjusted for inflation) is a function of real disposable income, which is total income net of taxes. As income rises, the theory asserts that consumption will also rise, but not necessarily at the same rate. When applied to a cross section of a population, rich people are expected to consume a lower proportion of their income than poor people. The marginal propensity to consume is present in Keynes' consumpti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory Of Consumption
Consumption refers to the use of resources to fulfill present needs and desires. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of ''future'' income. Consumption is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences. Different schools of economists define consumption differently. According to mainstream economists, only the final purchase of newly produced goods and services by individuals for immediate use constitutes consumption, while other types of expenditure — in particular, fixed investment, intermediate consumption, and government spending — are placed in separate categories (see consumer choice). Other economists define consumption much more broadly, as the aggregate of all economic activity that does not entail the design, production and marketing of goods and services (e.g., the selection, adoption, use, disposal and recycling of goods and services). Economists are particularly interested in the relationship b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Maynard Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist and philosopher whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originally trained in mathematics, he built on and greatly refined earlier work on the causes of business cycles. One of the most influential economists of the 20th century, he produced writings that are the basis for the schools of economic thought, school of thought known as Keynesian economics, and its various offshoots. His ideas, reformulated as New Keynesianism, are fundamental to mainstream economics, mainstream macroeconomics. He is known as the "father of macroeconomics". During the Great Depression of the 1930s, Keynes spearheaded Keynesian Revolution, a revolution in economic thinking, challenging the ideas of neoclassical economics that held that free markets would, in the short to medium term, automatically provide full employment, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Tobin
James Tobin (March 5, 1918 – March 11, 2002) was an American economist who served on the Council of Economic Advisers and consulted with the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, and taught at Harvard University, Harvard and Yale University, Yale Universities. He contributed to the development of key ideas in the Keynesian economics of his generation and advocated government intervention in particular to stabilize output and avoid recessions. His academic work included pioneering contributions to the study of investment (macroeconomics), investment, monetary and fiscal policy and financial markets. He also proposed an econometric model for Censoring (statistics), censored dependent variables, the well-known tobit model. Along with fellow Neo-Keynesian economics, neo-Keynesian economist James Meade in 1977, Tobin proposed Nominal income target, nominal GDP targeting as a Discretionary policy, monetary policy rule in 1980. Tobin received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The General Theory Of Employment, Interest And Money
''The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money'' is a book by English economist John Maynard Keynes published in February 1936. It caused a profound shift in economic thought, giving macroeconomics a central place in economic theory and contributing much of its terminology – the "Keynesian Revolution". It had equally powerful consequences in economic policy, being interpreted as providing theoretical support for government spending in general, and for budgetary deficits, monetary intervention and counter-cyclical policies in particular. It is pervaded with an air of mistrust for the rationality of free-market decision-making. Keynes denied that an economy would automatically adapt to provide full employment even in equilibrium, and believed that the volatile and ungovernable psychology of markets would lead to periodic booms and crises. The ''General Theory'' is a sustained attack on the classical economics orthodoxy of its time. It introduced the concepts of the consu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. For example, a person's income in an economic sense may be different from their income as defined by law. An extremely important definition of income is Haig–Simons income, which defines income as ''Consumption + Change in net worth'' and is widely used in economics. For households and individuals in the United States, income is defined by tax law as a sum that includes any wage, salary, profit, interest payment, rent, or other form of earnings received in a calendar year.Case, K. & Fair, R. (2007). ''Principles of Economics''. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. p. 54. Discretionary income is often defined as gross income minus taxes and other deductions (such as mandatory pension contributions), and is widely used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumption (economics)
Consumption refers to the use of resources to fulfill present needs and desires. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of ''future'' income. Consumption is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences. Different schools of economists define consumption differently. According to mainstream economics, mainstream economists, only the final purchase of newly produced Good (economics), goods and Service (economics), services by individuals for immediate use constitutes consumption, while other types of expenditure — in particular, fixed investment, intermediate consumption, and government spending — are placed in separate categories (see consumer choice). Other economists define consumption much more broadly, as the aggregate of all economic activity that does not entail the design, production and marketing of goods and services (e.g., the selection, adoption, use, disposal and recycling of goods and services). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroeconomic
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomists study topics such as output/ GDP (gross domestic product) and national income, unemployment (including unemployment rates), price indices and inflation, consumption, saving, investment, energy, international trade, and international finance. Macroeconomics and microeconomics are the two most general fields in economics. The focus of macroeconomics is often on a country (or larger entities like the whole world) and how its markets interact to produce large-scale phenomena that economists refer to as aggregate variables. In microeconomics the focus of analysis is often a single market, such as whether changes in supply or demand are to blame for price increases in the oil and automotive sectors. From introductory classes in "principles of economics" through doctora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Propensity To Consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending ( consumption) occurs with an increase in disposable income (income after taxes and transfers). The proportion of disposable income which individuals spend on consumption is known as propensity to consume. MPC is the proportion of additional income that an individual consumes. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.65, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Obviously, the household cannot spend ''more'' than the extra dollar (without borrowing or using savings). If the extra money accessed by the individual gives more economic confidence, then the MPC of the individual may well exceed 1, as they may borrow or utilise savings. According to John Maynard Keynes, marginal propensity to consume is less than one. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Consumption
Autonomous consumption (also exogenous consumption, autonomous spending) is the consumption expenditure that occurs when income levels are zero. Such consumption is considered autonomous of income only when expenditure on these consumables does not vary with changes in income; generally, it may be required to fund necessities and debt obligations. If income levels are actually zero, this consumption counts as dissaving, because it is financed by borrowing or using up savings. Autonomous consumption contrasts with induced consumption, in that it does not systematically fluctuate with income, whereas induced consumption does. The two are related, for all households, through the consumption function: :C = c_0 + c_1 Y_d where * ''C'' = total consumption, * ''c0'' = autonomous consumption (''c0'' > 0), * ''c1'' = the marginal propensity to consume (the gradient of induced consumption) (0 < ''c1'' < 1), and * ''Yd'' = disposable income (income after government t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Consumption
Induced consumption is the portion of Consumption (economics), consumption that varies with Disposable and discretionary income, disposable income. When a change in disposable income “induces” a change in consumption on goods and services, then that changed consumption is called “induced consumption”. In contrast, expenditures for autonomous consumption do not vary with income. For instance, expenditure on a consumable that is considered a normal good would be considered to be induced. In the simple linear consumption function, C = a + b \times Y_ induced consumption is represented by the term b \times Y_, where Y_ denotes disposable income and b is called the marginal propensity to consume. See also * Lifestyle creep * Diderot effect * Induced demand References Consumption (macroeconomics) {{Econ-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
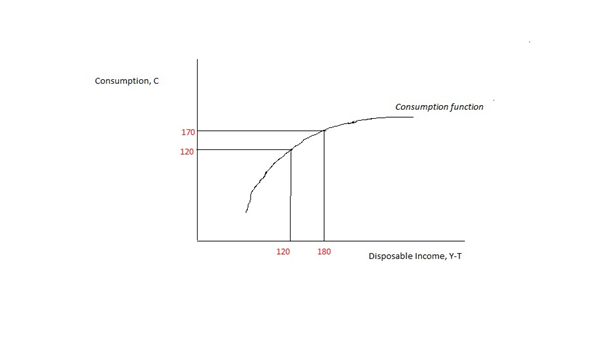
Consumption Function
In economics, the consumption function describes a relationship between consumption and disposable income. The concept is believed to have been introduced into macroeconomics by John Maynard Keynes in 1936, who used it to develop the notion of a government spending multiplier. Details Its simplest form is the ''linear consumption function'' used frequently in simple Keynesian models: :C = a + b \cdot Y_ where a is the autonomous consumption that is independent of disposable income; in other words, consumption when disposable income is zero. The term b \cdot Y_ is the induced consumption that is influenced by the economy's income level Y_. The parameter b is known as the marginal propensity to consume, i.e. the increase in consumption due to an incremental increase in disposable income, since \partial C / \partial Y_ = b. Geometrically, b is the slope of the consumption function. Keynes proposed this model to fit three stylized facts: * People typically spend a part, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |