|
Abell 2199
Abell 2199 is a galaxy cluster in the Abell catalogue featuring the brightest cluster galaxy NGC 6166, a cD galaxy. Abell 2199 is the definition of a Bautz-Morgan type I cluster due to NGC 6166. See also * Hercules (Chinese astronomy) * List of Abell clusters * List of largest galaxies * List of nearest galaxies * List of NGC objects (6001–7000) * X-ray astronomy X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ... References 2199 Galaxy clusters Hercules (constellation) Abell richness class 2 Hercules Superclusters {{galaxy-cluster-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Clusters
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. Clusters consist of galaxies, heated gas, and dark matter. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after superclusters. They were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. Together, galaxy groups and clusters form superclusters. Basic properties Galaxy clusters typically have the following properties: * They contain 100 to 1,000 galaxies, hot X-ray emitting gas and large amounts of dark matter. Details are described in the "Composition" section. * They have total masses of 1014 to 1015 solar masses. * They typically have diameters from 1 to 5 Mpc ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abell Objects
Abell may refer to: People *Abell (surname) *George O. Abell, of the astronomical catalogues fame Places ;United States * Abell, Maryland, a location in St. Mary's County, Maryland * Abell, Baltimore, Abell, a neighborhood in Baltimore, Maryland * Abells Corners, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community Astronomy *Abell catalogue of rich clusters of galaxies (ACO) *Abell Catalog of Planetary Nebulae (A) Bibliographical database *ABELL, the ''Annual Bibliography of English Language and Literature'' See also *Abel (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abell 2199
Abell 2199 is a galaxy cluster in the Abell catalogue featuring the brightest cluster galaxy NGC 6166, a cD galaxy. Abell 2199 is the definition of a Bautz-Morgan type I cluster due to NGC 6166. See also * Hercules (Chinese astronomy) * List of Abell clusters * List of largest galaxies * List of nearest galaxies * List of NGC objects (6001–7000) * X-ray astronomy X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ... References 2199 Galaxy clusters Hercules (constellation) Abell richness class 2 Hercules Superclusters {{galaxy-cluster-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
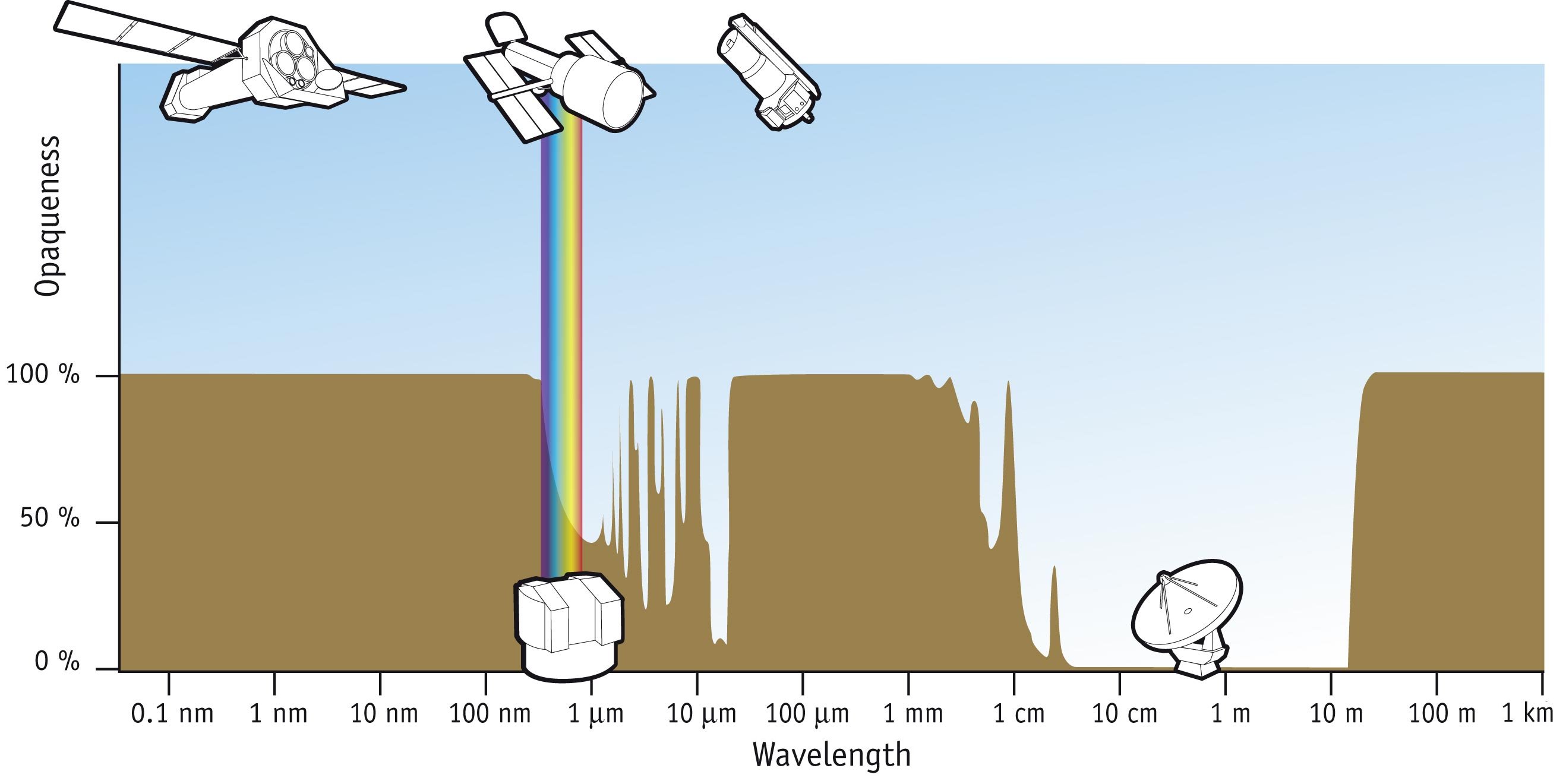
X-ray Astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by Balloon-borne telescope, balloons, sounding rockets, and X-ray astronomy satellite, satellites. X-ray astronomy uses a type of space telescope that can see x-ray radiation which standard optical telescopes, such as the Mauna Kea Observatories, cannot. X-ray generation, X-ray emission is expected from astronomical objects that contain extremely hot gases at temperatures from about a million kelvin (K) to hundreds of millions of kelvin (MK). Moreover, the maintenance of the E-layer of ionized gas high in the Earth's thermosphere also suggested a strong extraterrestrial source of X-rays. Although theory predicted that the Sun and the stars would be prominent X-ray sources, there was no way to verify this because Earth's atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of NGC Objects (6001–7000)
This is a list of NGC objects 6001–7000 from the New General Catalogue (NGC). The astronomical catalogue is composed mainly of star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies. Other objects in the catalogue can be found in the other subpages of the list of NGC objects. The constellation information in these tables is taken from ''The Complete New General Catalogue and Index Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters by J. L. E. Dreyer'', which was accessed using the "VizieR Service". Galaxy types are identified using the ''NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database''. The other data of these tables are from the SIMBAD Astronomical Database unless otherwise stated. 6001–6100 6101–6200 6201–6300 6301–6400 6401–6500 6501–6600 6601–6700 6701–6800 6801–6900 6901–7000 See also * Lists of astronomical objects This is a list of lists, grouped by type of astronomical object. Solar System * List of Solar System objects * List of gravitational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nearest Galaxies
This is a list of known galaxies within 3.8 Parsec, megaparsecs (12.4 million light-years) of the Solar System, in ascending order of heliocentric distance, or the distance to the Sun. This encompasses about 50 major Local Group galaxies, and some that are members of neighboring galaxy groups, the M81 Group and the Centaurus A/M83 Group, and some that are currently not in any defined galaxy group. The list aims to reflect current knowledge: not all galaxies within the 3.8 Mpc radius have been discovered. Nearby dwarf galaxies are still being discovered, and galaxies located behind the central plane of the Milky Way are extremely difficult to discern. It is possible for any galaxy to mask another located beyond it. Intergalactic distance measurements are subject to large uncertainties. Figures listed are composites of Cosmic distance ladder, many measurements, some of which may have had their individual error bars tightened to the point of no longer overlapping with each other. Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Largest Galaxies
This is a list of largest galaxies known, sorted by order of increasing major axis diameters. The unit of measurement used is the light-year (approximately 9.46 kilometers). Overview Galaxies are vast collections of stars, planets, nebulae and other objects that are surrounded by an interstellar medium and held together by gravity. They do not have a definite boundary by nature, and are characterized with gradually decreasing stellar density as a function of increasing distance from its center. Because of this, measuring the sizes of galaxies can often be difficult and have a wide range of results depending on the sensitivity of the detection equipment and the methodology being used. Some galaxies emit more strongly in wavelengths outside the visible spectrum, depending on its stellar population, whose stars may emit more strongly in other wavelengths that are beyond the detection range. It is also important to consider the morphology of the galaxy when attempting to measure i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Abell Clusters
The Abell catalogue is a catalogue of approximately 4,000 galaxy clusters with at least 30 members, almost complete to a redshift of ''z'' = 0.2. It was originally compiled by the American astronomer George O. Abell in 1958 using plates from National Geographic Society – Palomar Observatory Sky Survey, POSS, and extended to the southern hemisphere by Abell, Harold Corwin, Corwin and Ronald Olowin, Olowin in 1987. The name "Abell" is also commonly used as a designation for objects he compiled in a catalogue of 86 planetary nebulae in 1966. The proper designation for the galaxy clusters is ACO, as in "ACO 13", while the planetary-nebula designation is the single letter A, as in "A 39". 1–1999 2000–4076 Southern catalogue S1–S1174 See also * Lists of astronomical objects * List of galaxy groups and clusters References External linksAbell's 1958 paper and catalog [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules (Chinese Astronomy)
According to traditional Chinese uranography, the modern constellation Hercules is located in Three Enclosures (三垣, ''Sān Yuán'') The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is 武仙座 (''wǔ xiān zuò''), which means "the immortal martial constellation". Stars The map of Chinese constellation in constellation Hercules area consists of : See also *Traditional Chinese star names *Chinese constellations Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" ( Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenisti ... References {{Reflist External linksHercules – Chinese associations香港太空館https://web.archive.org/web/20120813070951/http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Space/Research/c_index.htm 研究資源] *中國星區、星官及星名英譯表*台灣自然科學博物館http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/ 天文教育資訊 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD Galaxy
The type-cD galaxy (also cD-type galaxy, cD galaxy) is a galaxy morphology classification, a subtype of type-D galaxy, type-D Elliptical galaxy#Sizes and shapes, giant elliptical galaxy. Characterized by a large galactic halo, halo of stars, they can be found near the centres of some rich galaxy clusters. They are also known as supergiant ellipticals or central dominant galaxies. Characteristics The cD-type is a classification in the Galaxy morphological classification, Yerkes galaxy classification scheme, one of two Yerkes classifications still in common use, along with D-type. The "c" in "cD" refers to the fact that the galaxies are very large, hence the adjective supergiant, while the "D" refers to the fact that the galaxies appear diffuse. A backformation of "cD" is frequently used to indicate "central Dominant galaxy"."Uncertainties on Clusters of Galaxies Distances", C. Adami, M.P. Ulmer, 18 July 2000, (accessed 14 April 2010) cDs are also frequently considered the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |