|
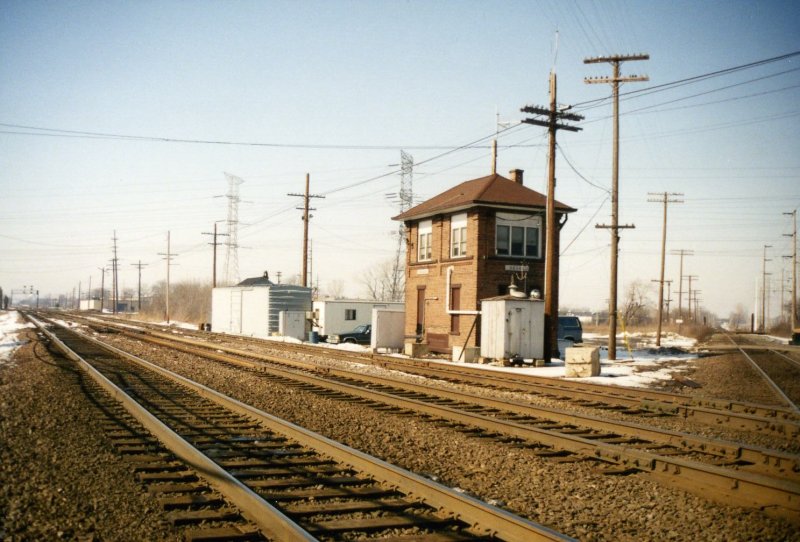
Aalen Station
Aalen Hauptbahnhof is a junction on the Stuttgart-Bad Cannstatt–Nördlingen railway from Stuttgart to and the Aalen–Ulm railway from Ulm. The station is located 200 metres northeast of the historic old town (Altstadt) of Aalen in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 3 station. Aalen station was renamed a ''Hauptbahnhof'' (main station) at the timetable change on 11 December 2016. History Despite disagreements between the countries of Württemberg and Bavaria, which did not have a common concept of a cross-border railway, the Rems Railway () was opened by the Royal Württemberg State Railways The Royal Württemberg State Railways (''Königlich Württembergische Staats-Eisenbahnen'' or ''K.W.St.E.'') were the state railways of the Kingdom of Württemberg (from 1918 the ''People's State of Württemberg'') between 1843 and 1920. Early ... on 18 July 1861. Aalen was not planned as a railway junction and the station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aalen
Aalen (; Swabian German, Swabian: ''Oole'') is a town located in the eastern part of the German state of Baden-Württemberg, about east of Stuttgart and north of Ulm. It is the seat of the Ostalbkreis district and is its largest town. It is also the largest town in the Ostwürttemberg region. Since 1956, Aalen has had the status of Große Kreisstadt (major district town). It is noted for its many half-timbered houses constructed from the 16th century through the 18th century. With an area of 146.63 km2, Aalen is ranked 7th in Baden-Württemberg and 2nd within the Stuttgart (region), Government Region of Stuttgart, after Stuttgart. With a population of about 66,000, Aalen is the 15th most-populated settlement in Baden-Württemberg. Geography Situation Aalen is situated on the upper reaches of the river Kocher, at the foot of the Swabian Jura which lies to the south and south-east, and close to the hilly landscapes of the Ellwangen Hills to the north and the ''Wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidenheim An Der Brenz
Heidenheim an der Brenz, or just Heidenheim (; Swabian language, Swabian: ''Hoidna'' or ''Hoirna''), is a town in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is located near the border with Bavaria, approximately 17 km south of Aalen and 33 km north of Ulm. Heidenheim is the largest town and the seat of the Heidenheim (district), district of Heidenheim, and ranks third behind Aalen and Schwäbisch Gmünd in size among the towns in the region of East Württemberg. Heidenheim is the economic center for all the communities in Heidenheim district and is the headquarters of the Voith industrial company. The town's population in 2021 was just below the 50,000 mark. Heidenheim collaborates with the town of Nattheim in administrative matters. The residents of Heidenheim and its surrounding area speak the distinct German dialect of Swabian German, Swabian. Geography Heidenheim is situated between Albuch and the Härtsfeld, Härtsfeld region in the northeast corner of the Swabian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwäbische Post
The ''Schwäbische Post'' is a local daily newspaper for Ostalbkreis. It is published by the media conglomerate SDZ Druck und Medien GmbH & Co. KG in Aalen. It uses the outer jacket or (the national section of a regional newspaper) composed by the editorial department of Südwest Presse in Ulm. SDZ Druck und Medien has 312 employees, including graphic designers, salesmen for both digital and print, IT systems support specialists, economists, editorial volunteers and 30 editors. History On 29 January 1837, two Schwäbisch Gmünd booksellers, Johannes Raach and Philip Jakob Andreas Buck, founded Aalen's first newspaper, the ''Bote von Aalen''. In 1853, Ludwig Gottlob Stierlin was awarded the publication rights for the ''Bote von Aalen:Amts- und Intelligenz-Blatts Oberamtsbezirk Aalen'', renamed to ''Kocherzeitung'' in 1873. In 1933, the National Socialist Press (''NS Presse'') became the majority shareholder under Gleichschaltung. They renamed the paper ''Kocher- und Nationalze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Mark
The Deutsche Mark (; "German mark (currency), mark"), abbreviated "DM" or "D-Mark" (), was the official currency of West Germany from 1948 until 1990 and later of unified Germany from 1990 until the adoption of the euro in 2002. In English, it was typically called the "Deutschmark" ( ). One Deutsche Mark was divided into 100 pfennigs. It was first issued under Bizone, Allied occupation in 1948 to replace the Reichsmark and served as the Federal Republic of Germany's official currency from its founding the following year. On 31 December 1998, the Council of the European Union fixed the irrevocable exchange rate, effective 1 January 1999, for German mark to euros as DM 1.95583 = €1. In 1999, the Deutsche Mark was replaced by the euro; its coins and banknotes remained in circulation, defined in terms of euros, until the introduction of euro notes and coins on 1 January 2002. The Deutsche Mark ceased to be legal tender immediately upon the introduction of the euro—in contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahnbetriebswerk Aalen
A ''Bahnbetriebswerk'' is the equivalent of a locomotive depot (or motive power depot) on the German and Austrian railways. It is an installation that carries out the maintenance, minor repairs, refuelling and cleaning of locomotives and other motive power. In addition it organises the deployment of locomotives and crews. In the Deutsche Bahn, a ''Bahnbetriebswerk'' is known today as a ''Betriebshof''; the ÖBB refer to it as a ''Zugförderungsstelle'' (''Zf''). Many other countries simply use the term 'depot'. The smaller facility, the ''Lokomotivstation'' (also ''Einsatzstelle'' or ''Lokbahnhof'') akin to the British sub-depot or stabling point, is affiliated to a ''Bahnbetriebswerk''. N.B. The shortened form ''Betriebswerk'' is also used and both are commonly abbreviated to Bw or BW. The plural is ''Bahnbetriebswerke''. History Beginnings On 7 January 1835 the first ''Bahnbetriebswerk'' in Germany was opened. It looked after locomotives on the first railway line in Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlocking
In railway signalling, an interlocking is an arrangement of signal apparatus that prevents conflicting movements through an arrangement of tracks such as junctions or crossings. In North America, a set of signalling appliances and tracks interlocked together are sometimes collectively referred to as an ''interlocking plant'' or just as an ''interlocking''. An interlocking system is designed so that it is impossible to display a signal to proceed unless the route to be used is proven safe. Interlocking is a safety measure designed to prevent signals and points/switches from being changed in an improper sequence. For example, interlocking would prevent a signal from being changed to indicate a diverging route, unless the corresponding points/switches had been changed first. In North America, the official railroad definition of interlocking is: "''An arrangement of signals and signal appliances so interconnected that their movements must succeed each other in proper sequence''". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
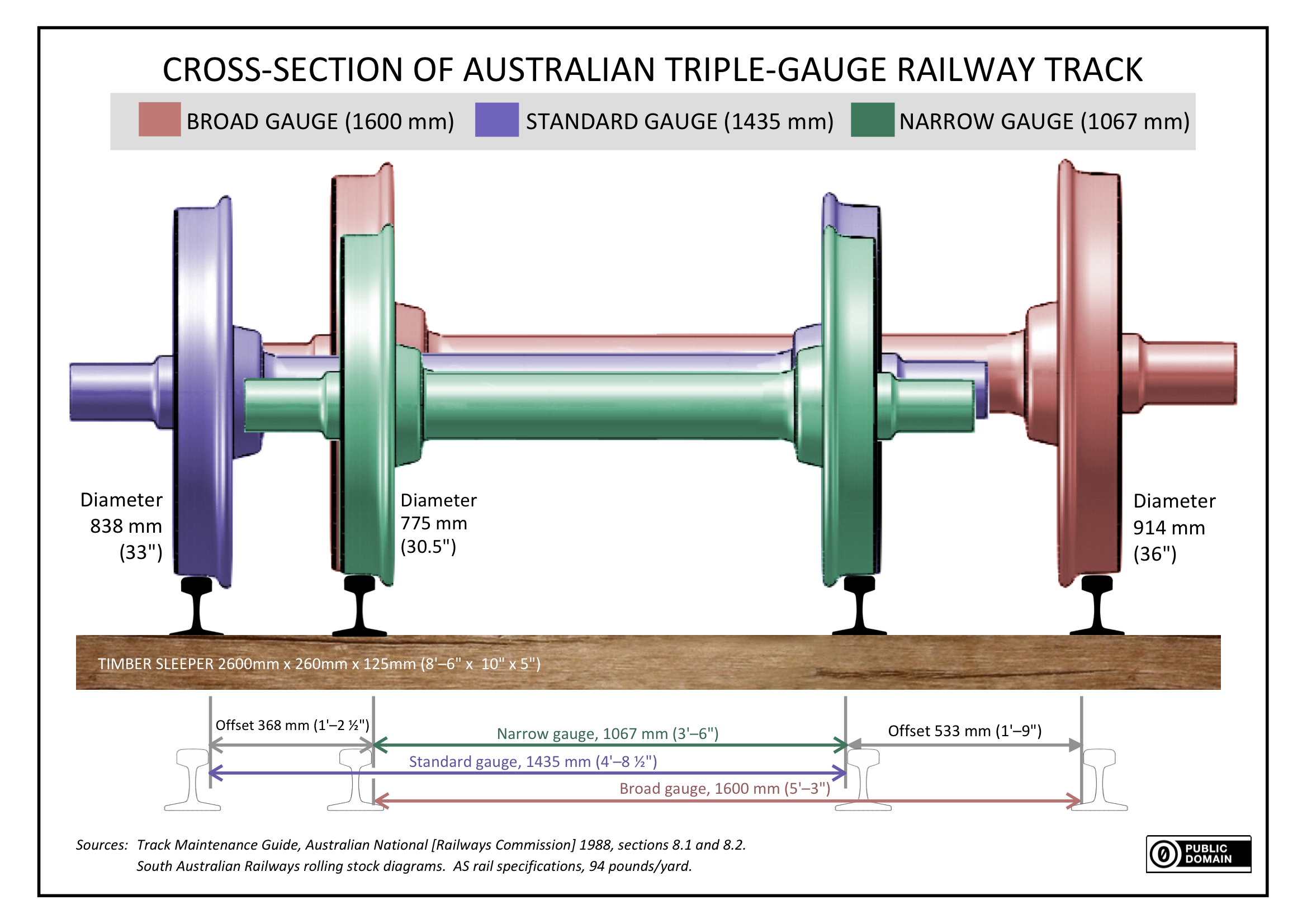
Dual Gauge
Dual gauge railroad track has three or four rails, allowing vehicles of two track gauges to run on it. Signalling and sidings are more expensive to install on dual gauge tracks than on two single gauge tracks. Dual gauge is used when there is not enough room for two single tracks or when tracks of two different gauges meet in marshalling yards or train stations. Background The rail gauge is the most fundamental specification of a railway. Rail tracks and Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets are built within engineering tolerances that allow optimum lateral movement of the wheelsets between the rails. Pairs of rails that become too wide or narrow in gauge will cause derailments, especially if in excess of normal gauge-widening on curves. Given the requirement for gauge to be within very tight limits, when the designed distance between the pair of wheels on a wheelset differs even slightly from that of others on a railway, track must be built to two specific gauges. That is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dillingen An Der Donau
Dillingen an der Donau (; officially Dillingen a.d.Donau; ) is a Town#Germany, town in Swabia (Bavaria), Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is the administrative center of the district of Dillingen (district), Dillingen. Besides the town of Dillingen proper, the municipality encompasses the villages of Donaualtheim, Fristingen, Hausen, Kicklingen, Schretzheim and Steinheim. Schretzheim is notable for its 6th to 7th century Alemannic cemetery, 630 row graves in an area of 100 by 140 metres. History The counts of Dillingen ruled from the 10th to the 13th century; in 1258 the territory was turned over to the Prince-Bishop, Prince Bishops of Augsburg. After the Protestant Reformation, Reformation, the Prince-Bishopric of Augsburg, prince-bishops of Augsburg moved to the Catholic city of Dillingen and made it one of the centers of the Catholic Reformation, Counter-Reformation. In 1800, during the War of the Second Coalition, the armies of the French First Republic, under command of Jean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neresheim
Neresheim is a town in the Ostalbkreis district, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated northeast of Heidenheim an der Brenz, Heidenheim, and southeast of Aalen. It's the home of the Neresheim Abbey, which still hosts monks, was ''Reichsfrei'' until the German Mediatisation and was built by Johann Balthasar Neumann, Balthasar Neumann. Another notable touristic attraction is the heritage railway Härtsfeldbahn. Neresheim is listed on the Arc de Triomphe in Paris, France, along with 95 other sites of battles won by the French army. on Parisrama.com 
Notable people * Oscar F. Mayer (185 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre Gauge
Metre-gauge railways ( US: meter-gauge railways) are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre. Metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by several European colonial powers including France, Britain and Germany in their colonies. In Europe, large metre-gauge networks remain in use in Switzerland, Spain and many European towns with urban trams, but most metre-gauge local railways in France, Germany and Belgium closed down in the mid-20th century, although some still remain. With the revival of urban rail transport, metre-gauge light metros were built in some cities. The slightly-wider gauge is used in Sofia, Bulgaria. Another similar gauge is . __TOC__ Examples of metre-gauge See also * Italian metre gauge * Narrow-gauge railways A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge (distance between the rails) narrower than . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and . Since narrow-gaug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Gold Mark
The German mark ( ; sign: ℳ︁) was the currency of the German Empire, which spanned from 1871 to 1918. The mark was paired with the minor unit of the pfennig (₰); 100 pfennigs were equivalent to 1 mark. The mark was on the gold standard from 1871 to 1914, but like most nations during World War I, the German Empire removed the gold backing in August 1914, and gold coins ceased to circulate. After the fall of the Empire due to the November Revolution of 1918, the mark was succeeded by the Weimar Republic's mark, derisively referred to as the Papiermark () due to hyperinflation in the Weimar Republic from 1918 to 1923. History The introduction of the German mark in 1873 was the culmination of decades-long efforts to unify the various currencies used by the German Confederation. The Zollverein unified in 1838 the Prussian and South German currencies at a fixed rate of 1 Prussian thaler = South German gulden = 16.704 g fine silver. A larger currency convention i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |