|
A News
A News, or Netnews Version A, originally known simply as news, was the first widely distributed program for serving and reading Usenet newsgroups. The program, written at Duke University by Steve Daniel and Tom Truscott, was released on a tape given out at the June 1980 USENIX conference held at the University of Delaware. Steve Daniel from Duke offered a presentation on the then-new Usenet network and invited attendees to join. Seventh Edition Unix included a " message of the day" facility, which allowed the system operator to cause messages to be displayed to the user at login. A News (so called because each message began with "A" as a marker character) was an expansion of this facility that allowed news messages to be distributed across an arbitrary number of systems using the new uucp service. In addition to the login display, news articles could be read at any time from the command line. A user could also post new messages to the local machine (by posting to a special defa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usenet
Usenet () is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980.''From Usenet to CoWebs: interacting with social information spaces'', Christopher Lueg, Danyel Fisher, Springer (2003), , Users read and post messages (called ''articles'' or ''posts'', and collectively termed ''news'') to one or more topic categories, known as newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to the Internet forums that have become widely used. Discussions are threaded, as with web forums and BBSs, though posts are stored on the server sequentially.The jargon file v4.4.7 , Jargon File Archive. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
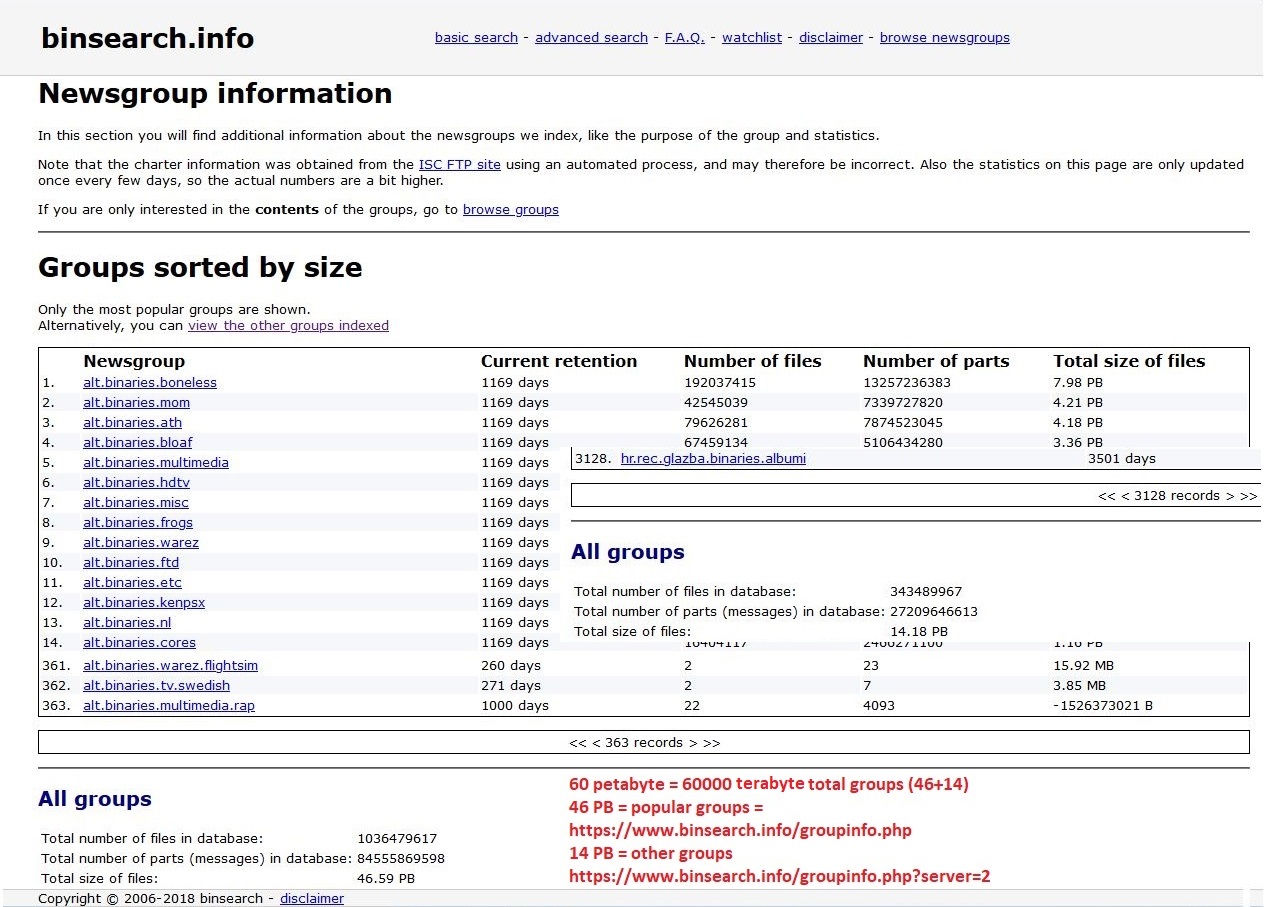
Newsgroups
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system, for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are discussion groups and are not devoted to publishing news. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption of the World Wide Web, Usenet newsgroups were among the most popular Internet services, and have retained their noncommercial nature in contrast to the increasingly ad-laden web. In recent years, this form of open discussion on the Internet has lost considerable ground to individually-operated browser-accessible forums and big media social networks such as Facebook and Twitter. Communication is facilitated by the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) which allows connection to Usenet servers and data transfer over the internet. Similar to another early (yet still used) prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke University
Duke University is a private research university in Durham, North Carolina. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1892. In 1924, tobacco and electric power industrialist James Buchanan Duke established The Duke Endowment and the institution changed its name to honor his deceased father, Washington Duke. The campus spans over on three contiguous sub-campuses in Durham, and a marine lab in Beaufort. The West Campus—designed largely by architect Julian Abele, an African American architect who graduated first in his class at the University of Pennsylvania School of Design—incorporates Gothic architecture with the Duke Chapel at the campus' center and highest point of elevation, is adjacent to the Medical Center. East Campus, away, home to all first-years, contains Georgian-style architecture. The university administers two concurrent schools in Asia, Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Truscott
Tom Truscott is an American computer scientist best known for creating Usenet with Jim Ellis, when both were graduate students at Duke University. He is also a member of ACM ACM or A.C.M. may refer to: Aviation * AGM-129 ACM, 1990–2012 USAF cruise missile * Air chief marshal * Air combat manoeuvring or dogfighting * Air cycle machine * Arica Airport (Colombia) (IATA: ACM), in Arica, Amazonas, Colombia Computing * ..., IEEE, and Sigma Xi. One of his first endeavors into computers was writing a computer chess program and then later working on a global optimizer for C at Bell Labs. This computer chess program competed in multiple computer chess tournaments such as the Toronto chess tournament in 1977 (2nd place) and the Linz tournament in 1980 (3rd place). Today, Truscott works on tools that analyze software as a software developer for the SAS Institute. Truscott received the USENIX Lifetime Achievement Award for Usenet. Further reading * References External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Delaware
The University of Delaware (colloquially UD or Delaware) is a public land-grant research university located in Newark, Delaware. UD is the largest university in Delaware. It offers three associate's programs, 148 bachelor's programs, 121 master's programs (with 13 joint degrees), and 55 doctoral programs across its eight colleges. The main campus is in Newark, with satellite campuses in Dover, Wilmington, Lewes, and Georgetown. It is considered a large institution with approximately 18,200 undergraduate and 4,200 graduate students. It is a privately governed university which receives public funding for being a land-grant, sea-grant, and space-grant state-supported research institution. UDel is ranked among the top 150 universities in the U.S. UD is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". According to the National Science Foundation, UD spent $186 million on research and development in 2018, ranking it 119th in the nation. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Edition Unix
Seventh Edition Unix, also called Version 7 Unix, Version 7 or just V7, was an important early release of the Unix operating system. V7, released in 1979, was the last Bell Laboratories release to see widespread distribution before the commercialization of Unix by AT&T Corporation in the early 1980s. V7 was originally developed for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-11 minicomputers and was later ported to other platforms. Overview Unix versions from Bell Labs were designated by the edition of the user's manual with which they were accompanied. Released in 1979, the Seventh Edition was preceded by Sixth Edition, which was the first version licensed to commercial users. Development of the Research Unix line continued with the Eighth Edition, which incorporated development from 4.1BSD, through the Tenth Edition, after which the Bell Labs researchers concentrated on developing Plan 9. V7 was the first readily portable version of Unix. As this was the era of minicomputers, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motd (Unix)
Many computer systems display a message of the day or welcome message when a user first connects to them, logs in to them, or starts them. It is a way of sending a common message to all users, and may include information about system changes, system availability, and so on. More recently, systems have displayed personalized messages of the day. On many time-sharing systems, the contents of the message of the day are fetched from a system file: * Compatible Time-Sharing System; * Multics: the motd info segment;A.K. Bhushan, "Scenarios for using ARPANET computers", Request for Comments 254, Network Working Group, IETF https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc254.txt * TOPS-10 * Incompatible Timesharing System (ITS) * Unix-like systems: the /etc/motd file, though most modern Linux distributions do not support the file. * Univac VS/9 * CP/CMS Usage The contents of the special file are displayed after the user logs in successfully, typically before the login shell is started. Newer Unix-lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uucp
UUCP is an acronym of Unix-to-Unix Copy. The term generally refers to a suite of computer programs and protocols allowing remote execution of commands and transfer of files, email and netnews between computers. A command named is one of the programs in the suite; it provides a user interface for requesting file copy operations. The UUCP suite also includes (user interface for remote command execution), (the communication program that performs the file transfers), (reports statistics on recent activity), (execute commands sent from remote machines), and (reports the UUCP name of the local system). Some versions of the suite include / (convert 8-bit binary files to 7-bit text format and vice versa). Although UUCP was originally developed on Unix in the 1970s and 1980s, and is most closely associated with Unix-like systems, UUCP implementations exist for several non-Unix-like operating systems, including DOS, OS/2, OpenVMS (for VAX hardware only), AmigaOS, classic Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-mail
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant only physical mail (hence '' e- + mail''). Email later became a ubiquitous (very widely used) communication medium, to the point that in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries. ''Email'' is the medium, and each message sent therewith is also called an ''email.'' The term is a mass noun. Email operates across computer networks, primarily the Internet, and also local area networks. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bang Path
UUCP is an acronym of Unix-to-Unix Copy. The term generally refers to a suite of computer programs and protocols allowing remote execution of commands and transfer of files, email and netnews between computers. A command named is one of the programs in the suite; it provides a user interface for requesting file copy operations. The UUCP suite also includes (user interface for remote command execution), (the communication program that performs the file transfers), (reports statistics on recent activity), (execute commands sent from remote machines), and (reports the UUCP name of the local system). Some versions of the suite include / (convert 8-bit binary files to 7-bit text format and vice versa). Although UUCP was originally developed on Unix in the 1970s and 1980s, and is most closely associated with Unix-like systems, UUCP implementations exist for several non-Unix-like operating systems, including DOS, OS/2, OpenVMS (for VAX hardware only), AmigaOS, classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARPAnet
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first wide-area packet-switched network with distributed control and one of the first networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite. Both technologies became the technical foundation of the Internet. The ARPANET was established by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the United States Department of Defense. Building on the ideas of J. C. R. Licklider, Robert Taylor (computer scientist), Bob Taylor initiated the ARPANET project in 1966 to enable access to remote computers. Taylor appointed Lawrence Roberts (scientist), Larry Roberts as program manager. Roberts made the key decisions about the network design. He incorporated Donald Davies' concepts and designs for packet switching, and sought input from Paul Baran. ARPA awarded the contract to build the network to Bolt Beranek & Newman who developed the first Communication protocol, protocol for the network. Roberts engaged Leonard Kleinrock at Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |