|
A Key Into The Language Of America
''A Key into the Language of America'' or ''An help to the Language of the Natives in that part of America called New England'' is a book written by Roger Williams in 1643 describing the Native American languages in New England in the 17th century, largely Narragansett, an Algonquian language. The book is the first published colonial study of a Native American language in English. History Author Roger Williams was a Puritan who was banished from Massachusetts Bay Colony and founded Providence Plantations which grew into the Colony of Rhode Island. He believed that the king had no right to grant title to Indian land without paying for it. He interacted extensively with the Narragansett and Wampanoag tribes as a missionary, friend, and trader. He extolled some elements of Indian culture as superior to European culture, and he wrote a complementary poem at the end of each chapter within the book. According to J. Patrick Cesarini, Williams also published the book to rebut Massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
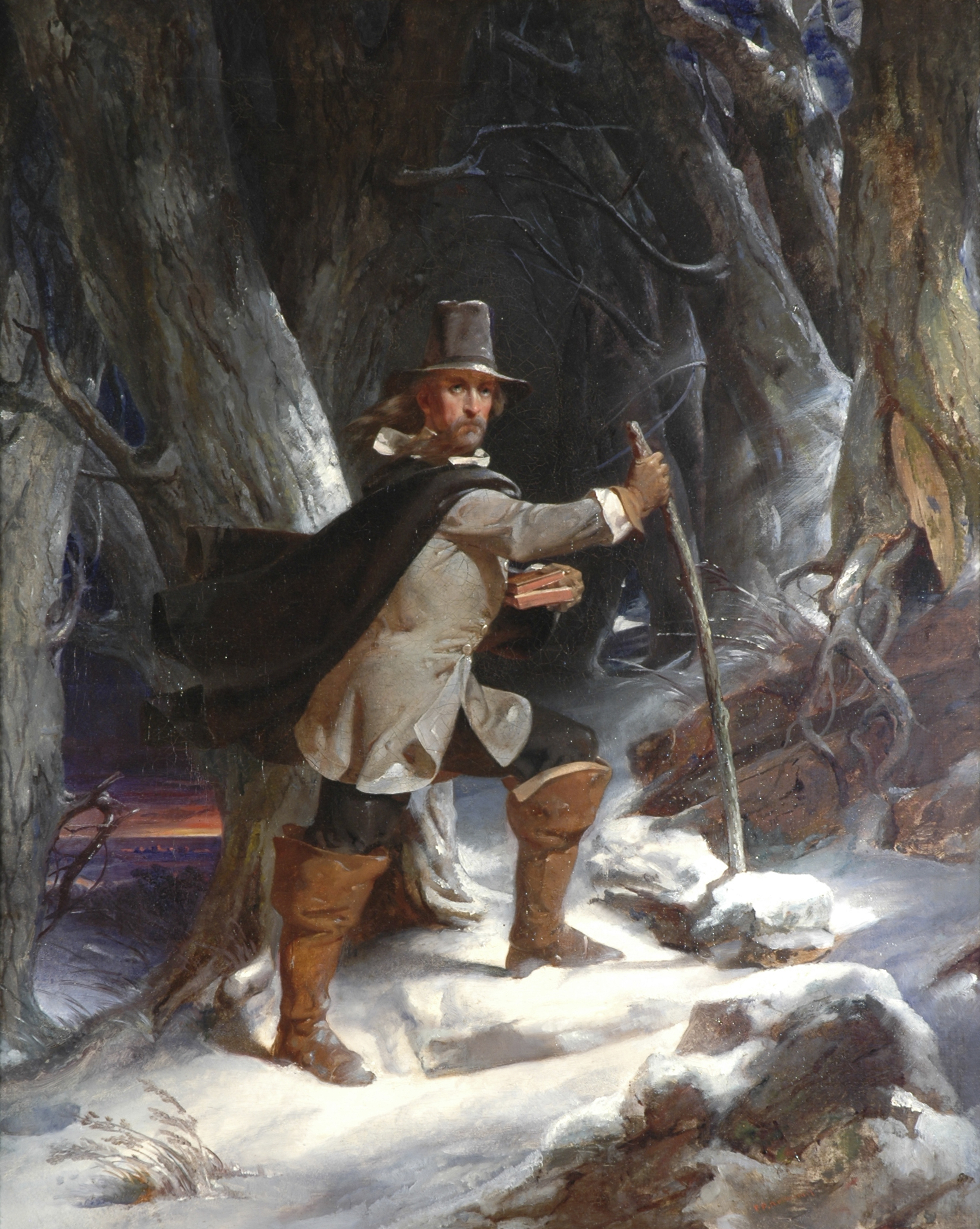
Roger Williams
Roger Williams (March 1683) was an English-born New England minister, theologian, author, and founder of the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Providence Plantations, which became the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations and later the Rhode Island, State of Rhode Island. He was a staunch advocate for religious liberty, separation of church and state, and fair dealings with the Native Americans. Initially a Puritan minister, his beliefs evolved and he questioned the authority of the Puritan church in enforcing religious conformity. He was expelled by the Puritan leaders from the Massachusetts Bay Colony, and he established Providence Plantations in 1636 as a refuge offering what he termed "liberty of conscience" making Rhode Island the first government in the Western civilization, Western world to guarantee Freedom of religion, religious freedom in its founding charter. His ideas on religious tolerance and civil government directly influenced the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London, England
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. London stands on the River Thames in southeast England, at the head of a tidal estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for nearly 2,000 years. Its ancient core and financial centre, the City of London, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as Londinium and has retained its medieval boundaries. The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has been the centuries-long host of Government of the United Kingdom, the national government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. London grew rapidly 19th-century London, in the 19th century, becoming the world's List of largest cities throughout history, largest city at the time. Since the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Carter Brown Library
The John Carter Brown Library is an independently funded research library of history and the humanities on the campus of Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island. The library's rare book, manuscript, and map collections encompass a variety of topics related to the history of European exploration and colonization of the New World until circa 1825. The library was the first independent private library placed within the context of a university campus in the United States. History The John Carter Brown Library began as the private collection of John Carter Brown. Beginning in 1845, Brown began traveling throughout Europe in search of books and materials related European exploration and colonization of the New World. Brown acquired a number of rare books from prominent libraries, including those of Henri Ternaux-Compans and Maximilian I of Mexico.Mitchell, Martha"John Carter Brown Library"in ''Encyclopedia Brunoniana'' (Providence, Rhode Island: Brown University Library, 1993) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Bloudy Tenent Of Persecution For Cause Of Conscience
''The Bloudy Tenent of Persecution, for Cause of Conscience, Discussed in a Conference between Truth and Peace'' is a 1644 book about government force written by Roger Williams, the founder of Providence Plantations in New England and the co-founder of the First Baptist Church in America. ''Tenent'' is an obsolete variant of ''tenet'', and the book argues for a "wall of separation" between church and state and for state toleration of various Christian denominations, including Catholicism, and also "paganish, Jewish, Turkish or anti-Christian consciences and worships." The book takes the form of a dialogue between Truth and Peace and is a response to correspondence by Boston minister John Cotton regarding Cotton's support for state enforcement of religious uniformity in Massachusetts Bay Colony. Williams argues that Christianity requires the existence of a separate civil authority which may not generally infringe upon liberty of conscience, which Williams interpreted to be a Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
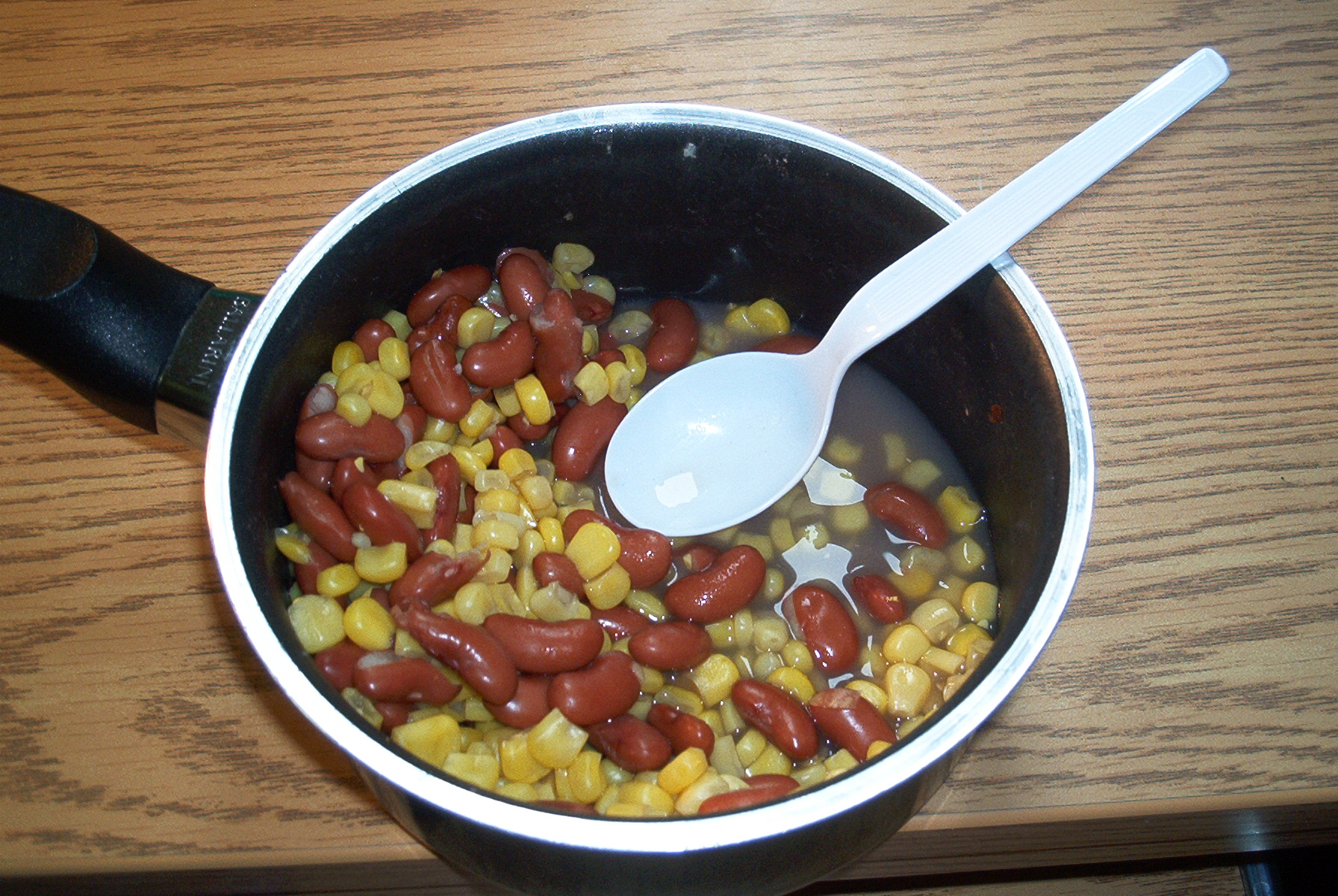
Succotash
Succotash is a North American vegetable dish consisting primarily of sweet corn with lima beans or other shell beans. The name ''succotash'' is derived from the Narragansett word , which means "broken corn kernels". Other ingredients may be added, such as onions, potatoes, turnips, tomatoes, bell peppers, corned beef, salt pork, or okra. Combining a grain with a legume provides a dish that is high in all essential amino acids. History Succotash has a long history. It is believed to have been an invention of indigenous peoples in what is now known as New England, though English soldier and explorer Jonathan Carver attributed it to numerous tribes of eastern North America:One dish however, which answers nearly the same purpose as bread, is in use among the Ottagaumies, the Saukies, and the more eastern nations, where Indian corn grows, which is not only much esteemed by them, but it is reckoned extremely palatable by all the Europeans who enter their dominions. This is comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squaw
The English word squaw is an ethnic and sexual slur, historically used for Indigenous North American women. Contemporary use of the term, especially by non-Natives, is considered derogatory, misogynist, and racist.King, C. Richard,De/Scribing Squ*w: Indigenous Women and Imperial Idioms in the United States in the ''American Indian Culture and Research Journal'', v27 n2 p1-16 2003. Accessed October 9, 2015 While ''squaw'' (or a close variant) is found in several Eastern and Central Algonquian languages, primarily spoken in the northeastern United States and in eastern and central Canada, these languages only make up a small minority of the Indigenous languages of North America. The word "squaw" is not used among Native American, First Nations, Inuit, or Métis peoples. Even in Algonquian, the words used are not the English-language word. Status The term ''squaw'' is considered offensive by Indigenous peoples in America and Canada due to its use for hundreds of years in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squash (plant)
is a genus of Herbaceous plant, herbaceous fruits in the gourd family (biology), family, Cucurbitaceae (also known as ''cucurbits'' or ''cucurbi''), native to the Andes and Mesoamerica. Five edible species are grown and consumed for their flesh and seeds. They are variously known as squash, pumpkin, or gourd, depending on species, Variety (botany), variety, and local parlance. Other kinds of gourd, also called bottle-gourds, are native to Africa and belong to the genus ''Lagenaria'', which is in the same family and subfamily as ''Cucurbita'', but in a different Tribe (biology), tribe; their young fruits are eaten much like those of the ''Cucurbita'' species. Most ''Cucurbita'' species are herbaceous vines that grow several meters in length and have tendrils, but non-vining "bush" cultivars of ''C. pepo'' and ''C. maxima'' have also been developed. The yellow or orange flowers on a ''Cucurbita'' plant are of two types: female and male. The female flowers produce the fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
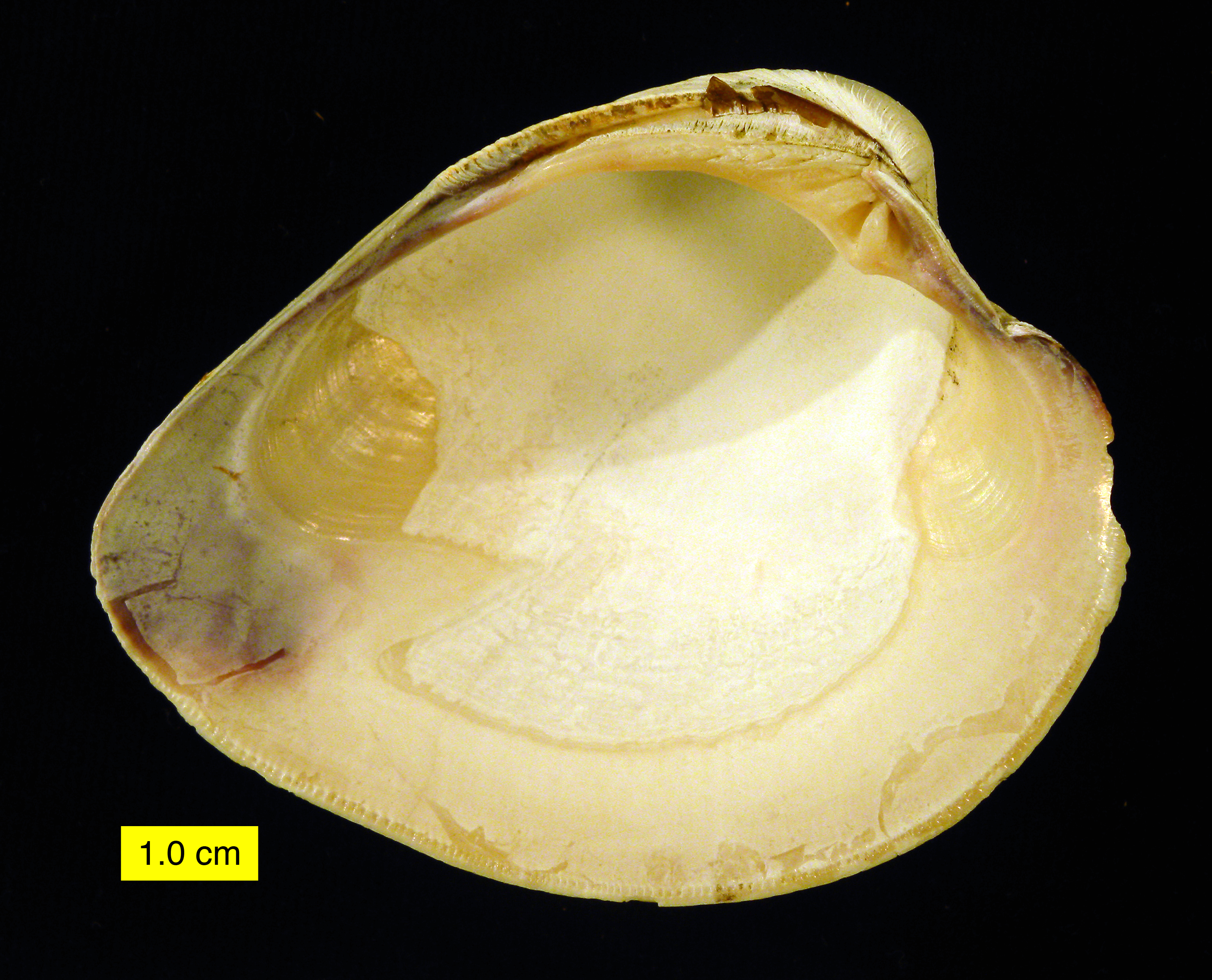
Quahog
The hard clam (''Mercenaria mercenaria''), also known as the round clam, hard-shell (or hard-shelled) clam, or the quahog, is an edible marine bivalve mollusk that is native to the eastern shores of North America and Central America from Prince Edward Island to the Yucatán Peninsula. It is one of many unrelated edible bivalves that in the United States are frequently referred to simply as clams. Older literature sources may use the systematic name ''Venus mercenaria''; this species is in the family Veneridae, the venus clams. Confusingly, the "ocean quahog" is a different species, ''Arctica islandica'', which, although superficially similar in shape, is in a different family of bivalves: it is rounder than the hard clam, usually has a black periostracum, and there is no pallial sinus in the interior of the shell. Alternative names The hard clam has many alternative common names. It is also known as the Northern quahog, round clam, or chowder clam. In fish markets, there ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powwow
A powwow (also pow wow or pow-wow) is a gathering with dances held by many Native Americans in the United States, Native American and First Nations in Canada, First Nations communities. Inaugurated in 1923, powwows today are an opportunity for Indigenous people to socialize, dance, sing, and honor their cultures. Powwows may be private or public, indoors or outdoors. Dancing events can be competitive with monetary prizes. Powwows vary in length from single-day to weeklong events. In mainstream American culture, such as 20th-century Western movies or by military personnel, the term ''powwow'' was used to refer to any type of meeting. This usage is now considered by some Native Americans to be an offensive case of Cultural appropriation, appropriation because of the cultural significance powwows hold. History The word ''powwow'' is derived from the Narragansett language, Narragansett word ''powwaw'', meaning "spiritual leader." The term has variants, including ''Powaw'', ''Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papoose
Papoose (from the Narragansett ''papoos'', meaning "child") is an American English word whose present meaning is "a Native American child" (regardless of tribe) or, even more generally, any child, usually used as a term of endearment, often in the context of the child's mother. In 1643, Roger Williams Roger Williams (March 1683) was an English-born New England minister, theologian, author, and founder of the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Providence Plantations, which became the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Pl ... recorded the word in his '' A Key into the Language of America'', helping to popularize it. Papoose carrier Cradle boards and other child carriers used by Native Americans are known by various names. In Algonquin history, the term ''papoose'' is sometimes used to refer to a child carrier. However, there are many different terms among the 573 federally recognized tribes, nations, and communities. References External links * Chil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tallest, and the second-largest, land animal in North America, falling short only to the American bison in body mass. Most adult male moose have broad, palmate ("open-hand shaped") antlers; other members of the deer family have pointed antlers with a dendritic ("twig-like") configuration. Moose inhabit the circumpolar boreal forests or temperate broadleaf and mixed forests of the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in cooler, temperate areas as well as subarctic climates. Hunting shaped the relationship between moose and humans, both in Eurasia and North America. Prior to the colonial era (around 1600–1700 CE), moose were one of many valuable sources of sustenance for certain tribal groups and First Nations. Hunting and habitat loss hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |