|
AV Valve
A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Heart valves are opened or closed by a difference in blood pressure on each side. The mammalian heart has two atrioventricular valves separating the upper atria from the lower ventricles: the mitral valve in the left heart, and the tricuspid valve in the right heart. The two semilunar valves are at the entrance of the arteries leaving the heart. These are the aortic valve at the aorta, and the pulmonary valve at the pulmonary artery. The heart also has a coronary sinus valve and an inferior vena cava valve, not discussed here. Structure The heart valves and the chambers are lined with endocardium. Heart valves separate the atria from the ventricles, or the ventricles from a blood vessel. Heart valves are situated around the fibrous rin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
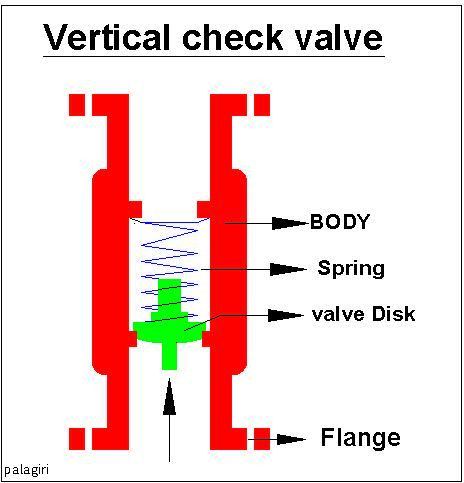
Check Valve
A check valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve, foot valve, or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid (liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction. Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have two openings in the body, one for fluid to enter and the other for fluid to leave. There are various types of check valves used in a wide variety of applications. Check valves are often part of common household items. Although they are available in a wide range of sizes and costs, check valves generally are very small, simple, and inexpensive. Check valves work automatically and most are not controlled by a person or any external control; accordingly, most do not have any valve handle or stem. The bodies (external shells) of most check valves are made of plastic or metal. An important concept in check valves is the cracking pressure which is the minimum differential upstream pressure between inlet and outlet at which the valve will operate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Diagram-en
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the thorax, chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right Atrium (heart), atria and lower left and right Ventricle (heart), ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent cardiac regurgitation, backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Valve
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) is a valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, and has three cusps. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the aortic valve. Similar to the aortic valve, the pulmonary valve opens in ventricular systole when the pressure in the right ventricle rises above the pressure in the pulmonary artery. At the end of ventricular systole, when the pressure in the right ventricle falls rapidly, the pressure in the pulmonary artery closes the pulmonary valve. The closure of the pulmonary valve contributes to the P2 component of the second heart sound (S2). Structure The pulmonary orifice lies nearly in the horizontal plane, and is situated at a superior level than the aortic orifice. Cusps File:Lunules of semilunar leaflets of pulmonary valve.png File:Anterior semilunar leaflet of pulmonary valve.png File:Right semilunar le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semilunar Valves
A heart valve is a biological Check valve, one-way valve that allows blood flow, blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Heart valves are opened or closed by a difference in blood pressure on each side. The mammalian heart has two atrioventricular valves separating the upper Atrium (heart), atria from the lower Ventricle (heart), ventricles: the mitral valve in the left heart, and the tricuspid valve in the right heart. The two semilunar valves are at the entrance of the arteries leaving the heart. These are the aortic valve at the aorta, and the pulmonary valve at the pulmonary artery. The heart also has a coronary sinus valve and an inferior vena cava valve, not discussed here. Structure The heart valves and the heart chamber, chambers are lined with endocardium. Heart valves separate the Atrium (heart), atria from the Ventricle (he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitral Valve
The mitral valve ( ), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two Cusps of heart valves, cusps or flaps and lies between the atrium (heart), left atrium and the ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-way valves allowing blood flow in just one direction. The mitral valve and the tricuspid valve are known as the Heart valve#Atrioventricular valves, atrioventricular valves because they lie between the atria and the ventricles. In normal conditions, blood flows through an open mitral valve during diastole with contraction of the left atrium, and the mitral valve closes during systole with contraction of the left ventricle. The valve opens and closes because of pressure differences, opening when there is greater pressure in the left atrium than ventricle and closing when there is greater pressure in the left ventricle than atrium. In abnormal conditions, blood may flow backward thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricuspid Valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle during diastole, and to close to prevent backflow (Regurgitation (circulation), regurgitation) from the right ventricle into the right atrium during right ventricular contraction (systole). Structure The tricuspid valve usually has three Cusps of heart valves, cusps or leaflets, named the anterior, posterior, and septal cusps. Each leaflet is connected via chordae tendineae to the anterior, posterior, and septal papillary muscles of the right ventricle, respectively. Tricuspid valves may also occur with two or four leaflets; the number may change over a lifetime. Function The tricuspid valve functions as a one-way valve that closes during ventricular systole to prevent regurgitation of blood from the right ventricle back into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrioventricular Valves
A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Heart valves are opened or closed by a difference in blood pressure on each side. The mammalian heart has two atrioventricular valves separating the upper atria from the lower ventricles: the mitral valve in the left heart, and the tricuspid valve in the right heart. The two semilunar valves are at the entrance of the arteries leaving the heart. These are the aortic valve at the aorta, and the pulmonary valve at the pulmonary artery. The heart also has a coronary sinus valve and an inferior vena cava valve, not discussed here. Structure The heart valves and the chambers are lined with endocardium. Heart valves separate the atria from the ventricles, or the ventricles from a blood vessel. Heart valves are situated around the fibrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flutter Valve
In respiratory medicine, a flutter valve (also Pneumostat valve, and Heimlich valve) is a one-way check valve used to prevent airflow back into a chest tube, and usually is applied to drain air from a pneumothorax. The design of the flutter valve features a rubber sleeve in a plastic case, where the rubber sleeve is arranged so that when air flows through the valve the sleeve opens and allows the outwards airflow from the body of the patient; however, when the airflow is reversed, the rubber sleeve closes and halts backwards airflow into the body of the patient. The construction of the flutter valve enables it to function as a one-way valve allowing airflow, or the flow of a fluid, in only one direction along the drainage tube. The end of the drainage tube is placed inside the chest cavity of the patient — into the air mass or into the fluid mass to be drained from the thorax. The flutter valve is placed in the appropriate orientation (designed so that the valve can only be c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duckbill Valve
A duckbill valve is a check valve, usually manufactured from rubber or synthetic elastomer, and has two or more flaps, usually shaped like the beak of a duck. It is commonly used in medical applications to prevent contamination due to backflow. One end of the valve is stretched over the outlet of a supply line, conforming itself to the shape of the line, usually round. The other end, the duckbill, retains its natural flattened shape. When a fluid is pumped through the supply line and therefore the duckbill, the flattened end opens to permit the pressurized fluid to pass. When pressure is removed, however, the duckbill end returns to its flattened shape, preventing backflow. The duckbill valve is similar in function to the mitral valve in the heart. See also Heimlich valve. A trifold form of this valve, known as a joker valve, is used in one popular marine toilet. Also known as a spear valve or flutter valve, this automatic device serves as a gas exhaust valve on the insi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Skeleton
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through them. The cardiac skeleton separates and partitions the atria (the smaller, upper two chambers) from the ventricles (the larger, lower two chambers). The heart's cardiac skeleton comprises four dense connective tissue rings that encircle the mitral and tricuspid atrioventricular (AV) canals and extend to the origins of the pulmonary trunk and aorta. This provides crucial support and structure to the heart while also serving to electrically isolate the atria from the ventricles. The unique matrix of connective tissue within the cardiac skeleton isolates electrical influence within these defined chambers. In normal anatomy, there is only one conduit for electrical conduction from the upper chambers to the lower chambers, known as the atriov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |