|
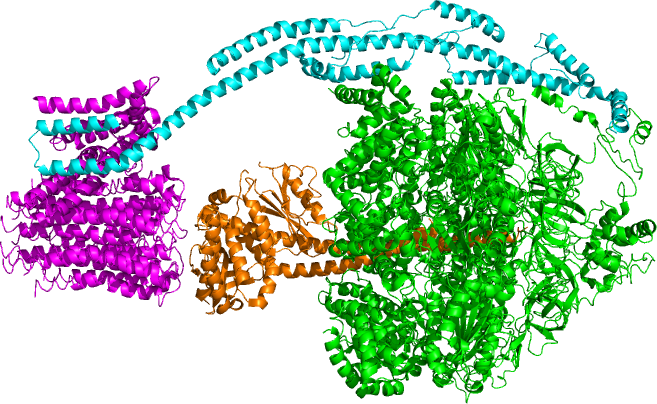
ATP5H
The human gene ATP5PD encodes subunit d of the peripheral stalk part of the enzyme mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. It is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, F0, which comprises the proton channel. The F1 complex consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled in a ratio of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and a single representative of the other 3. The Fo seems to have nine subunits (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, F6 and 8). This gene encodes the d subunit of the Fo complex. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. In addition, three pseudogene Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Pseudogenes can be formed from both prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATP Synthase
ATP synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). ATP synthase is a molecular machine. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is: * ADP + Pi + 2H+out ATP + H2O + 2H+in ATP synthase lies across a cellular membrane and forms an aperture that hydron (chemistry), protons can cross from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, imparting energy for the synthesis of ATP. This electrochemical gradient is generated by the electron transport chain and allows cells to store energy in ATP for later use. In prokaryote, prokaryotic cells ATP synthase lies across the plasma membrane, while in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells it lies across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Organisms capable of photosynthesis also have ATP synthase across the thylakoid membrane, which in plants is located in the chloroplast and in cyanobacteria is located in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cell (biology), cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'', meaning a thread-like granule, was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase popularized by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 ''Scientific American'' article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). The multicellular animal ''Henneguya zschokkei, Henneguya salminicola'' is known to have retained mitochondrion-related organelles despite a complete loss of their mitochondrial genome. A large number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in a Metabolism, metabolic process, ATP converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. It is also a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. An average adult human processes around 50 kilograms (about 100 mole (unit), moles) daily. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of three parts: a sugar, an amine base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
The inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) is the mitochondrial membrane which separates the mitochondrial matrix from the intermembrane space. Structure The structure of the inner mitochondrial membrane is extensively folded and compartmentalized. The numerous invaginations of the membrane are called cristae, separated by crista junctions from the inner boundary membrane juxtaposed to the outer membrane. Cristae significantly increase the total membrane surface area compared to a smooth inner membrane and thereby the available working space for oxidative phosphorylation. The inner membrane creates two compartments. The region between the inner and outer membrane, called the intermembrane space, is largely continuous with the cytosol, while the more sequestered space inside the inner membrane is called the matrix. Cristae For typical liver mitochondria, the area of the inner membrane is about 5 times as large as the outer membrane due to cristae. This ratio is variable and mitocho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis. The energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose is released by the cell in the citric acid cycle, producing carbon dioxide and the energetic reducing agent, electron donors NADH and FADH. Oxidative phosphorylation uses these molecules and O2 to ATP synthase, produce ATP, which is used throughout the cell whenever energy is needed. During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from the electron donors to a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Pump
A proton pump is an integral membrane protein pump that builds up a proton gradient across a biological membrane. Proton pumps catalyze the following reaction: : n one side of a biological membrane/sub> + energy n the other side of the membrane/sub> Mechanisms are based on energy-induced conformational changes of the protein structure or on the Q cycle. During evolution, proton pumps have arisen independently on multiple occasions. Thus, not only throughout nature, but also within single cells, different proton pumps that are evolutionarily unrelated can be found. Proton pumps are divided into different major classes of pumps that use different sources of energy, exhibiting different polypeptide compositions and evolutionary origins. Function Transport of the positively charged proton is typically electrogenic, i.e.: it generates an electric field across the membrane also called the membrane potential. Proton transport becomes electrogenic if not neutralized electrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Splicing
RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcription (biology), transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA (Messenger RNA, mRNA). It works by removing all the introns (non-coding regions of RNA) and ''splicing'' back together exons (coding regions). For nuclear genes, nuclear-encoded genes, splicing occurs in the cell nucleus, nucleus either during or immediately after Transcription (biology), transcription. For those eukaryotic transcription, eukaryotic genes that contain introns, splicing is usually needed to create an mRNA molecule that can be translation (biology), translated into protein. For many eukaryotic introns, splicing occurs in a series of reactions which are catalyzed by the spliceosome, a complex of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). There exist self-splicing introns, that is, ribozymes that can catalyze their own excision from their parent RNA molecule. The process of transcription, spli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (biology)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression. Some segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, called messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, Antiparallel (biochemistry), antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. In virology, the term transcription is used when referring to mRNA synthesis from a viral RNA molecule. The genome of many Orthornavirae, RNA viruses is composed of Sense (molecular biology), negative-sense RNA which acts as a template for positive sense viral messenger RNA - a necessary step in the synthesis of viral proteins needed for viral replication. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments ( exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions of genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different proteins e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Pseudogenes can be formed from both protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. In the case of protein-coding genes, most pseudogenes arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by gene duplication or indirectly by Reverse transcriptase, reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences or are incapable of producing a functional product. Pseudogenes are a type of junk DNA. Most non-bacterial genomes contain many pseudogenes, often as many as functional genes. This is not surprising, since various biological processes are expected to accidentally create pseudogenes, and there are no specialized mechanisms to remove them from genomes. Eventually pseudogenes may be deleted from their genomes by chance of DNA replication or DNA repair errors, or they may accumulate so many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 9 (human)
Chromosome 9 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome, as they normally do with all chromosomes. Chromosome 9 spans about 138 million base pairs of nucleic acids (the building blocks of DNA) and represents between 4.0 and 4.5% of the total DNA in cells. Genes Number of genes These are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 9. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation, their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 9. For a complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. Diseases and disorders The follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |