|
ARDB
ARDB also known as Antibiotic Resistance Genes Database is a database that tracks antibiotic resistance genes with information such as mechanism of action, resistance profile, ontology, Clusters of Orthologous Genes (COG) and Conserved Domain Database (CDD) annotations. It also contains links to external databases. The database is also for the identification of new resistance genes. During the creation of ARDB in 2009, there was no comprehensive annotation system available. Thus, ontology terms for resistance profiles and mechanisms of actions were created for ARDB. Other things classified by ontology include drug target modification, drug enzymatic destruction and drug transport. Drug transporters are further subclassified by MFS Efflux pumps, SMR Efflux pumps, ABC Efflux pumps, RND Efflux pumps following conventions outlined in this paper. Currently, ARDB contains resistance information for 13,293 genes, 377 types, 257 antibiotics, 632 genomes, 933 species and 124 genera. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Biological Databases
Biological databases are stores of biological information. The journal ''Nucleic Acids Research'' regularly publishes special issues on biological databases and has a list of such databases. The 2018 issue has a list of about 180 such databases and updates to previously described databasesOmics Discovery Indexcan be used to browse and search several biological databases. Furthermore, thNIAID Data Ecosystem Discovery Portaldeveloped by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) enables searching across databases. Meta databases Meta databases are databases of databases that collect data about data to generate new data. They are capable of merging information from different sources and making it available in a new and more convenient form, or with an emphasis on a particular disease or organism. Originally, metadata was only a common term referring simply to ''data about data '' such as tags, keywords, and markup headers. * ConsensusPathDB: a molecular funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
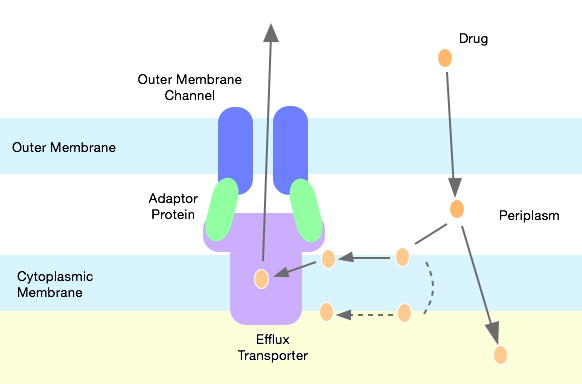
ATP-binding Cassette Transporter
The ABC transporters, ATP synthase (ATP)-binding cassette transporters are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene family, gene families. It is represented in all extant taxon, extant Phylum, phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters belong to translocases. ABC transporters often consist of multiple subunits, one or two of which are transmembrane proteins and one or two of which are membrane-associated AAA proteins, AAA ATPases. The ATPase subunits utilize the energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding and hydrolysis to provide the energy needed for the translocation of substrates across membranes, either for uptake or for export of the substrate. Most of the uptake systems also have an extracytoplasmic receptor, a solute binding protein. Some homologous ATPases function in non-transport-related processes such as RNA translation, translation of RNA and DNA repair. ABC transporters are considered to be an ABC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database
The Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD) is a biological database that collects and organizes reference information on antimicrobial resistance genes, proteins and phenotypes. The database covers all types of drug classes and resistance mechanisms and structures its data based on an ontology. The CARD database was one of the first resources that covered antimicrobial resistance genes. The resource is updated monthly and provides tools to allow users to find potential antibiotic resistance genes in newly-sequenced genomes. Ontology Each resistance determinant described by the CARD Antibiotic Resistance Ontology (ARO) must include a connection to each of three branches: Determinant of Antibiotic Resistance, Antibiotic Molecule and Mechanism of Antibiotic Resistance. CARD has recently also launched draft ontologies for both virulence and mobile genetic elements, which are in active development. Curation CARD curation occurs continuously, with monthly updates release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demonstrate both monophyly and validity as a separate lineag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistance-nodulation-cell Division Superfamily
Resistance-nodulation-division (RND) family transporters are a category of bacterial efflux pumps, especially identified in Gram-negative bacteria and located in the cytoplasmic membrane, that actively transport substrates. The RND superfamily includes seven families: the heavy metal efflux (HME), the hydrophobe/amphiphile efflux-1 (gram-negative bacteria), the nodulation factor exporter family (NFE), the SecDF protein-secretion accessory protein family, the hydrophobe/amphiphile efflux-2 family, the eukaryotic sterol homeostasis family, and the hydrophobe/amphiphile efflux-3 family. These RND systems are involved in maintaining homeostasis of the cell, removal of toxic compounds, and export of virulence determinants. They have a broad substrate spectrum and can lead to the diminished activity of unrelated drug classes if over-expressed. The first reports of drug resistant bacterial infections were reported in the 1940s after the first mass production of antibiotics. Most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Multidrug Resistance Protein
Small multidrug resistance protein (also known as Drug/Metabolite Transporter) is a family of integral membrane proteins that confer drug resistance to a wide range of toxic compounds by removing them for the cells. The efflux is coupled to an influx of protons. An example is ''Escherichia coli ''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...'' mvrC which prevents the incorporation of methyl viologen into cells and is involved in ethidium bromide efflux. References Protein domains Protein families Membrane proteins {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Database
Biological databases are libraries of biological sciences, collected from scientific experiments, published literature, high-throughput experiment technology, and computational analysis. They contain information from research areas including genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microarray gene expression, and phylogenetics. Information contained in biological databases includes gene function, structure, localization (both cellular and chromosomal), clinical effects of mutations as well as similarities of biological sequences and structures. Biological databases can be classified by the kind of data they collect (see below). Broadly, there are molecular databases (for sequences, molecules, etc.), functional databases (for physiology, enzyme activities, phenotypes, ecology etc), taxonomic databases (for species and other taxonomic ranks), images and other media, or specimens (for museum collections etc.) Databases are important tools in assisting scientists to analyze and explain a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Facilitator Superfamily
The major facilitator superfamily (MFS) is a Protein superfamily, superfamily of membrane transport proteins that facilitate movement of small solutes across cell membranes in response to chemiosmosis, chemiosmotic gradients. Function The major facilitator superfamily (MFS) are membrane proteins which are expressed ubiquitously in all kingdoms of life for the import or export of target substrates. The MFS family was originally believed to function primarily in the uptake of sugars but subsequent studies revealed that drugs, metabolites, oligosaccharides, amino acids and oxyanions were all transported by MFS family members. These proteins energetically drive transport utilizing the electrochemical gradient of the target substrate (uniporter), or act as a cotransporter where transport is coupled to the movement of a second substrate. Fold The basic fold of the MFS transporter is built around 12, or in some cases, 14 transmembrane helix, transmembrane helices (TMH), with two 6- (o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |