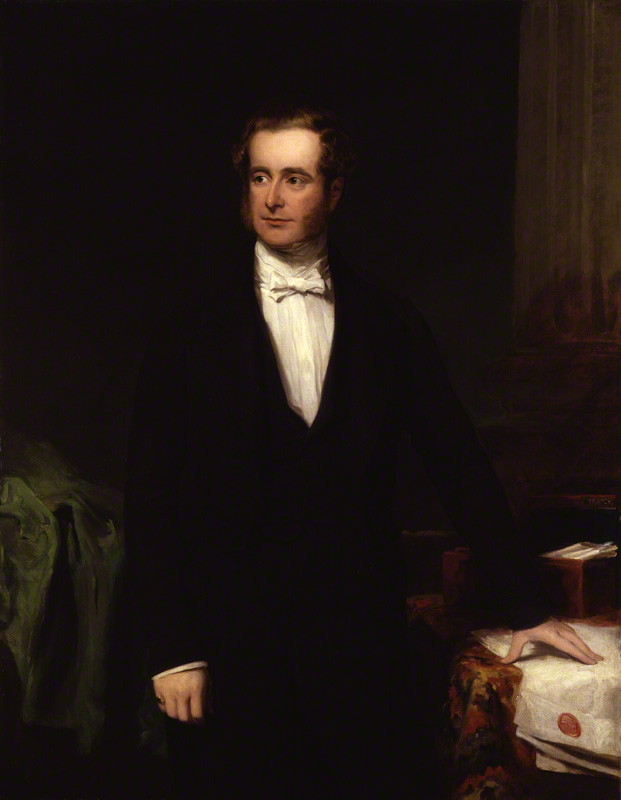|
ANZAC Oval
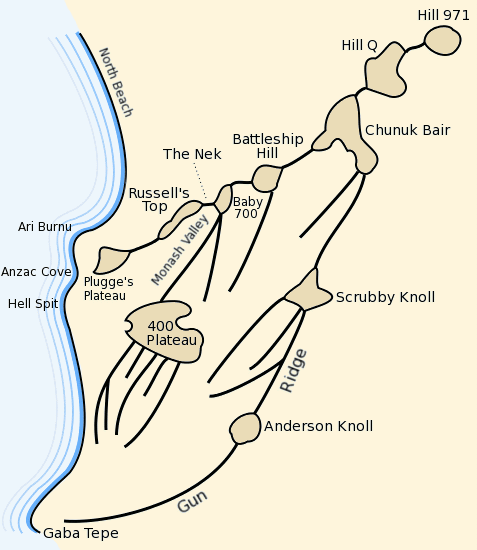
The Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) was originally a First World War army corps of the British Empire under the command of the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force. It was formed in Egypt in December 1914, and operated during the Gallipoli campaign. General William Birdwood commanded the corps, which primarily consisted of troops from the First Australian Imperial Force and 1st New Zealand Expeditionary Force, although there were also British and Indian units attached at times throughout the campaign. The corps disbanded in 1916, following the Allied evacuation of the Gallipoli peninsula and the formation of I ANZAC Corps and II ANZAC Corps. The corps was re-established, briefly, in the Second World War during the Battle of Greece in 1941. The term 'ANZAC' has been used since for joint Australian–New Zealand units of different sizes. History Original formation and the Gallipoli disaster Plans for the formation began in November 1914 while the first contingent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by possessing an army aviation component. Within a national military force, the word army may also mean a field army. Definition In some countries, such as France and China, the term "army", especially in its plural form "armies", has the broader meaning of armed forces as a whole, while retaining the colloquial sense of land forces. To differentiate the colloquial army from the formal concept of military force, the term is qualified, for example in France the land force is called , meaning Land Army, and the air and space force is called , meaning Air and Space Army. The naval force, although not using the term "army", is also included in the broad sense of the term "armies" — thus the French Navy is an integral component of the collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Greece
The German invasion of Greece or Operation Marita (), were the attacks on Greece by Italy and Germany during World War II. The Italian invasion in October 1940, which is usually known as the Greco-Italian War, was followed by the German invasion in April 1941. German landings on the island of Crete (May 1941) came after Allied forces had been defeated in mainland Greece. These battles were part of the greater Balkans Campaign of the Axis powers and their associates. Following the Italian invasion on 28 October 1940, Greece, with British air and material support, repelled the initial Italian attack and a counter-attack in March 1941. When the German invasion, known as Operation Marita, began on 6 April, the bulk of the Greek Army was on the Greek border with Albania, then a vassal of Italy, from which the Italian troops had attacked. German troops invaded from Bulgaria, creating a second front. Greece received a small reinforcement from British, Australian and New Zealand fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade
The New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was a brigade of the New Zealand Army during the First World War. Raised in 1914 as part of the New Zealand Expeditionary Force, it was one of the first New Zealand units to sail for service overseas. The brigade was formed from three regiments – the Auckland Mounted Rifles, the Canterbury Mounted Rifles, the Wellington Mounted Rifles – and smaller support units. Altogether the brigade had an establishment of 1,940 men and 2,032 horses and by the end of the war over 17,700 men had served in the brigade. However, the entire brigade's dismounted rifle strength was the equivalent of only a battalion of infantry. By the end of 1914, the brigade had arrived in British Egypt and was assigned to the New Zealand and Australian Division. Its first active service was, in a dismounted role, during the Gallipoli Campaign, where they fought against the forces of the Ottoman Turkish Empire. Seven months later, after the evacuation from Gall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Infantry Brigade
The New Zealand and Australian Division was a composite army division raised for service in the First World War under the command of Major General Alexander Godley. Consisting of several mounted and standard infantry brigades from both New Zealand and Australia, it served in the Gallipoli Campaign between April and December 1915. At Gallipoli, the division landed at Anzac Cove on 25 April 1915, coming ashore as follow-on troops to the initial assault force that had made it ashore earlier in the day, and later occupied the northern areas of the Allied lodgement. After the initial Allied assault at Anzac Cove, elements of the division were sent to Cape Helles in early May, where they participated in the Second Battle of Krithia, launching an unsuccessful attack towards the Achi Baba peak. The division's mounted units were sent to Gallipoli in mid-May without their horses, to serve as dismounted infantry, making up for previous losses. Later that month, the division helped rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand And Australian Division
The New Zealand and Australian Division was a composite army Division (military), division raised for service in the First World War under the command of Major General Alexander Godley. Consisting of several Mounted infantry, mounted and standard infantry brigades from both New Zealand and Australia, it served in the Gallipoli Campaign between April and December 1915. At Gallipoli, the division Landing at Anzac Cove, landed at Anzac Cove on 25 April 1915, coming ashore as follow-on troops to the initial assault force that had made it ashore earlier in the day, and later occupied the northern areas of the Allies of World War I, Allied lodgement. After the initial Allied assault at Anzac Cove, elements of the division were sent to Cape Helles in early May, where they participated in the Second Battle of Krithia, launching an unsuccessful attack towards the Achi Baba peak. The division's mounted units were sent to Gallipoli in mid-May without their horses, to serve as dismounted infa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Division (Australia)
The 1st Division, also known as the 1st (Australian) Division, is a division headquartered in Enoggera Barracks in Brisbane. The division was first formed in 1914 for service during the First World War as a part of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF). It was initially part of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) and served with that formation during the Gallipoli campaign, before later serving on the Western Front. After the war, the division became a part-time unit based in New South Wales. During the Second World War it undertook defensive duties in Australia. It was disbanded in 1945. After the Second World War, the division remained off the Australian Army's order of battle until the 1960s, when it was reformed in New South Wales. In 1965 it adopted a certification role, determining the operational readiness of units deploying to Vietnam. It was re-formed in 1973 as a full division based in Queensland and in the decades that followed it formed the Australia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
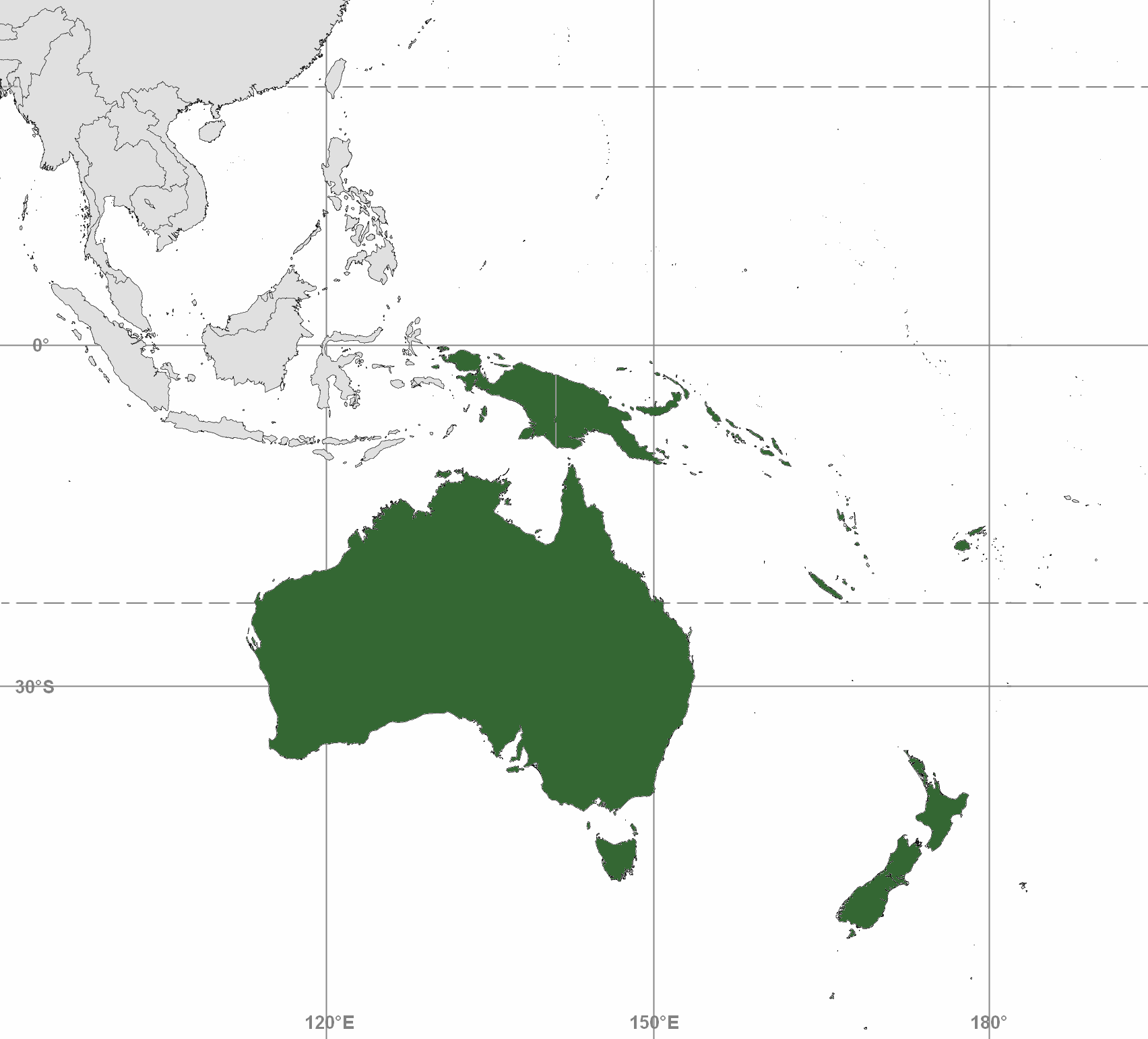
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of largest cities in the Arab world, the Arab world, and List of largest metropolitan areas of the Middle East, the Middle East. The Greater Cairo metropolitan area is List of largest cities, one of the largest in the world by population with over 22.1 million people. The area that would become Cairo was part of ancient Egypt, as the Giza pyramid complex and the ancient cities of Memphis, Egypt, Memphis and Heliopolis (ancient Egypt), Heliopolis are near-by. Located near the Nile Delta, the predecessor settlement was Fustat following the Muslim conquest of Egypt in 641 next to an existing ancient Roman empire, Roman fortress, Babylon Fortress, Babylon. Subsequently, Cairo was founded by the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid dynasty in 969. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Indian Army
The Indian Army was the force of British Raj, British India, until Indian Independence Act 1947, national independence in 1947. Formed in 1895 by uniting the three Presidency armies, it was responsible for the defence of both British India and the princely states, which could also have their own Imperial Service Troops, armies. As stated in the ''Imperial Gazetteer of India'', the "British Government has undertaken to protect the dominions of the Native princes from invasion and even from rebellion within: its army is organized for the defence not merely of British India, but of all possessions under the suzerainty of the Emperor of India, King-Emperor." The Indian Army was a vital part of the British Empire's military forces, especially in World War I and World War II. The Indian Presidencies and provinces of British India, Presidency armies were originally under East India Company command, and comprised the Bengal Army, Madras Army, and Bombay Army. After the Indian Rebellion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horatio Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener Of Khartoum
Field Marshal Horatio Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener (; 24 June 1850 – 5 June 1916) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator. Kitchener came to prominence for his imperial campaigns, his involvement in the Second Boer War, and his central role in the early part of the First World War. Kitchener was credited in 1898 for having won the Battle of Omdurman and securing control of the Sudan, for which he was made Baron Kitchener of Khartoum. As Chief of Staff (1900–1902) in the Second Boer WarAnon."Kitchener of Khartoum, Viscount" in ''Debrett's peerage, baronetage, knightage, and companionage'', London: Dean & Son, 1903, p. 483-484. he played a key role in Lord Roberts' conquest of the Boer Republics, then succeeded Roberts as commander-in-chief – by which time Boer forces had taken to guerrilla fighting and British forces imprisoned Boer and African civilians in concentration camps. His term as commander-in-chief (1902–1909) of the Army in India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretary Of State For War
The secretary of state for war, commonly called the war secretary, was a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, which existed from 1794 to 1801 and from 1854 to 1964. The secretary of state for war headed the War Office and was assisted by a parliamentary under-secretary of state for war, a parliamentary private secretary who was also a member of parliament (MP), and a military Secretary, who was a general. History The position of ''secretary of state for war'' was first held by Henry Dundas who was appointed in 1794. In 1801, the post became that of secretary of state for war and the colonies. The position of secretary of state for war was re-instated in 1854 when the secretary of state for the colonies was created as a separate position. In the nineteenth century, the post was twice held by future prime minister Henry Campbell-Bannerman. At the outset of the First World War, prime minister H. H. Asquith was filling the role, but he quickly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War I)
The Western Front was one of the main Theatre (warfare), theatres of war during World War I. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the Imperial German Army, German Army opened the Western Front by German invasion of Belgium (1914), invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in Third Republic of France, France. The German advance was halted with the First Battle of the Marne, Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both sides dug in along a meandering line of fortified trench warfare, trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France, the position of which changed little except during early 1917 and again in 1918. Between 1915 and 1917 there were several offensives along this Front (military), front. The attacks employed massive artillery bombardments and massed infantry advances. Entrenchments, machine gun emplacements, barbed wire, and artillery repeatedly inflicted severe casualties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |