|
ANAIS-112
ANAIS (Annual modulation with NaI Scintillators) is a dark matter direct detection experiment located at the Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc, Canfranc Underground Laboratory (LSC), in Spain, operated by a team of researchers of the CAPA at the University of Zaragoza. ANAIS' goal is to confirm or refute in a model independent way the :en:DAMA/LIBRA, DAMA/LIBRA experiment positive result: an annual modulation in the low-energy detection rate having all the features expected for the signal induced by weakly interacting dark matter particles (:en:Weakly interacting massive particles, WIMPs) in a standard galactic :en:Galactic halo, halo. This modulation is produced as a result of the Earth rotation around the Sun. A modulation with all the characteristic of a :en:Dark matter, Dark Matter (DM) signal has been observed for about 20 years by DAMA/LIBRA, but it is in strong tension with the negative results of other DM direct detection experiments. Compatibility among the different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:en:DAMA/LIBRA
The DAMA/LIBRA experiment is a particle detector experiment designed to detect dark matter using the direct detection approach, by using a matrix of NaI(Tl) scintillation detectors to detect dark matter particles in the galactic halo. The experiment aims to find an annual modulation of the number of detection events, caused by the variation of the velocity of the detector relative to the dark matter halo as the Earth orbits the Sun. It is located underground at the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso (LNGS) in Italy. It is a follow-on to the DAMA/NaI experiment which observed an annual modulation signature over 7 annual cycles (1995-2002). The experiment was first proposed by Dr. Pierluigi Belli, who is now the research director of the Italian National Institute of Nuclear Physics. While DAMA/LIBRA has published exciting results, the validity of those results has been widely disputed; they have not made their data or practices publicly available, and their methods of backgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:en:Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs) are hypothetical particles that are one of the proposed candidates for dark matter. There exists no formal definition of a WIMP, but broadly, it is an elementary particle which interacts via gravity and any other force (or forces) which is as weak as or weaker than the weak nuclear force, but also non-vanishing in strength. Many WIMP candidates are expected to have been produced thermally in the early Universe, similarly to the particles of the Standard Model according to Big Bang cosmology, and usually will constitute cold dark matter. Obtaining the correct abundance of dark matter today via thermal production requires a self-annihilation cross section of \langle \sigma v \rangle ≃ , which is roughly what is expected for a new particle in the 100 GeV/''c''2 mass range that interacts via the electroweak force. Experimental efforts to detect WIMPs include the search for products of WIMP annihilation, including gamma rays, neutrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canfranc Underground Laboratory
The Canfranc Underground Laboratory ( or LSC) is an underground scientific facility located in the former railway tunnel of Somport under Monte Tobazo (Pyrenees) in Canfranc. The laboratory, 780 m deep and protected from cosmic radiation, is mainly devoted to study rarely occurring natural phenomena such as the interactions of neutrinos of cosmic origin or dark matter with Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. Access to the tunnel containing the laboratory is at the ''Estación Internacional de Canfranc'', a former international railway station in the village of Canfranc. Experiments As of 2023, the following experiments are ongoing in Canfranc: * ANAIS-112, ANAIS, Weakly interacting massive particles, WIMP dark matter search experiment * DArT (experiment), DArT, experiment to measure the radioactive activation of argon * TREX-DM, WIMP dark matter search experiment * NEXT (experiment), NEXT, neutrinoless double beta decay experiment * CROSS, Cryogenic Rare-event Observatory with Surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
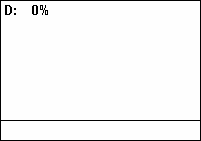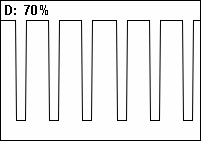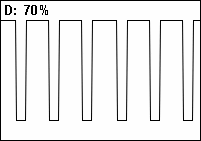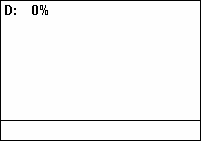
Duty Cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as: :D = \frac \times 100\% Equally, a duty cycle (ratio) may be expressed as: :D = \frac where D is the duty cycle, PW is the pulse width (pulse active time), and T is the total period of the signal. Thus, a 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time and off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period. Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply or the firing of action potentials by a living system such as a neuron. Some publications use \alpha as the symbol for duty cycle. As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:en:Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nuclear fission in 1938, the first self-sustaining nuclear reactor (Chicago Pile-1, 1942) and the first nuclear weapon (Trinity, 1945). Neutrons are found, together with a similar number of protons in the nuclei of atoms. Atoms of a chemical element that differ only in neutron number are called isotopes. Free neutrons are produced copiously in nuclear fission and fusion. They are a primary contributor to the nucleosynthesis of chemical elements within stars through fission, fusion, and neutron capture processes. Neutron stars, formed from massive collapsing stars, consist of neutrons at the density of atomic nuclei but a total mass more than the Sun. Neutron properties and interactions are described by nuclear physics. Neutrons are not elementary particles; each is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |