|
ALPHA Experiment
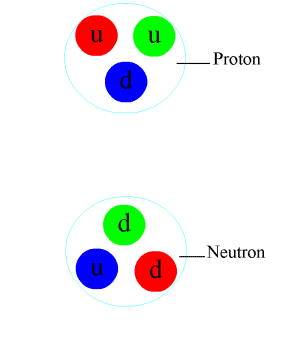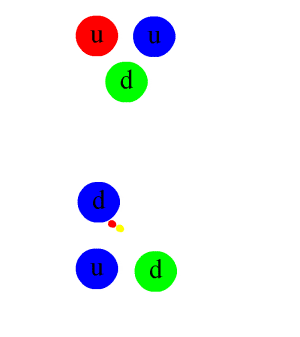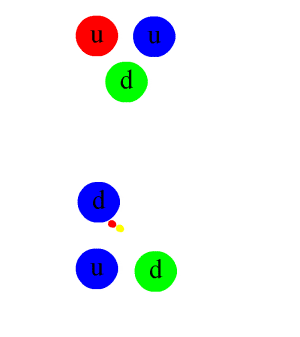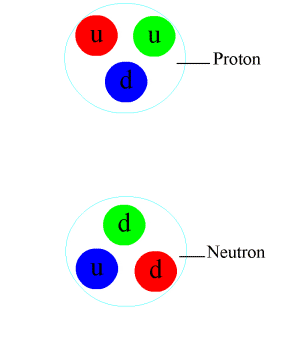
The Antihydrogen Laser Physics Apparatus (ALPHA), also known as AD-5, is an experiment at CERN's Antiproton Decelerator, designed to trap antihydrogen in a magnetic trap in order to study its atomic spectra. The ultimate goal of the experiment is to test CPT symmetry through comparing the respective spectra of hydrogen and antihydrogen. Scientists taking part in ALPHA include former members of the ATHENA experiment (AD-1), the first to produce cold antihydrogen in 2002. On 27 September 2023, ALPHA collaborators published findings suggesting that antimatter interacts with gravity in a way similar to regular matter, supporting a prediction of the weak equivalence principle. Experimental setup Working with antimatter presents several experimental challenges. Magnetic traps—wherein neutral atoms are trapped using their magnetic moments—are required to keep antimatter from annihilating with matter, but are notoriously weak. Only atoms with kinetic energies equivalent to less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN Antimatter Factory - Alpha Experiment
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in Meyrin, western suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises 24 member states. Israel, admitted in 2013, is the only full member geographically out of Europe. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2023, it had 2,666 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,370 users from institutions in more than 80 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research – consequently, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN through international collaborations. CERN is the site of the Large Hadron Collid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () is a state of matter characterized by the presence of a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. It is the most abundant form of ordinary matter in the universe, mostly in stars (including the Sun), but also dominating the rarefied intracluster medium and Outer space#Intergalactic space, intergalactic medium. Plasma can be artificially generated, for example, by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field. The presence of charged particles makes plasma electrically conductive, with the dynamics of individual particles and macroscopic plasma motion governed by collective electromagnetic fields and very sensitive to externally applied fields. The response of plasma to electromagnetic fields is used in many modern devices and technologies, such as plasma display, plasma televisions or plasma etching. Depending on temperature and density, a certain number of neutral particles may also be present, in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh less than it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of knowledge of physics. It publishes more than a dozen scientific journals, including the prestigious '' Physical Review'' and ''Physical Review Letters'', and organizes more than twenty science meetings each year. It is a member society of the American Institute of Physics. Since January 2021, it is led by chief executive officer Jonathan Bagger. History The American Physical Society was founded on May 20, 1899, when thirty-six physicists gathered at Columbia University for that purpose. They proclaimed the mission of the new Society to be "to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics", and in one way or another the APS has been at that task ever since. In the early years, virtually the sole activity of the APS was to hold scientific m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporative Cooling (atomic Physics)
Evaporative cooling is an atomic physics technique to achieve high phase space densities which optical cooling techniques alone typically can not reach. Atoms trapped in optical or magnetic traps can be evaporatively cooled via two primary mechanisms, usually specific to the type of trap in question: in magnetic traps, radiofrequency (RF) fields are used to selectively drive warm atoms from the trap by inducing transitions between trapping and non-trapping spin states; or, in optical traps, the depth of the trap itself is gradually decreased, allowing the most energetic atoms in the trap to escape over the edges of the optical barrier. In the case of a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution for the velocities of the atoms in the trap, these atoms which escape/are driven out of the trap lie in the highest velocity tail of the distribution, meaning that their kinetic energy (and therefore temperature) is much higher than the average for the trap. The net result is that while the total trap p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenics
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th International Institute of Refrigeration's (IIR) International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington, DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of "cryogenics" and "cryogenic" by accepting a threshold of to distinguish these terms from conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120 K, while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120 K. Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low-cost methods of producing high-temperature cryogenic refrigeration. The term "high temperature cryogenic" describes temperatures ranging from above the boili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk are deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pion
In particle physics, a pion (, ) or pi meson, denoted with the Greek alphabet, Greek letter pi (letter), pi (), is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often particle decay, decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual particle, virtual pions, along with vector meson, vector, rho meson, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the nuclear force, residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, electric currents, and electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, called a vector field (more precisely, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconducting
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete cancellation of the magnetic field in the interior of the superconductor during its transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penning Trap
A Penning trap is a device for the storage of charged particles using a homogeneous magnetic field and a quadrupole electric field. It is mostly found in the physical sciences and related fields of study for precision measurements of properties of ions and stable subatomic particles, like for example mass, fission yields and isomeric yield ratios. One initial object of study was the so-called geonium atoms, which represent a way to measure the electron magnetic moment by storing a single electron. These traps have been used in the physical realization of quantum computation and quantum information processing by trapping qubits. Penning traps are in use in many laboratories worldwide, including CERN, to store and investigate anti-particles such as antiprotons. The main advantages of Penning traps are the potentially long storage times and the existence of a multitude of techniques to manipulate and non-destructively detect the stored particles. This makes Penning traps versa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground State
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. In quantum field theory, the ground state is usually called the vacuum. If more than one ground state exists, they are said to be degenerate. Many systems have degenerate ground states. Degeneracy occurs whenever there exists a unitary operator that acts non-trivially on a ground state and commutes with the Hamiltonian of the system. According to the third law of thermodynamics, a system at absolute zero temperature exists in its ground state; thus, its entropy is determined by the degeneracy of the ground state. Many systems, such as a perfect crystal lattice, have a unique ground state and therefore have zero entropy at absolute zero. It is also possible for the highest excited state to have absolute zero temperature for sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |