|
AIMA Prophecy
The AIMA prophecy was a prophecy current during the reign of the Byzantine emperor, Manuel I Komnenos () and at the same time an example of a medieval contrived acronym. It claimed to foretell that the initial letters of the names of the emperors of the Komnenos dynasty would spell ''aima'' (αἶμα), the Greek word for "blood". The emperors of the dynasty had been, in order, Alexios I Komnenos () ( alpha), Ioannes II Komnenos () (iota), and Manuel I ( mu) (whose succession was unexpected since he was the fourth son of Ioannes). Because of his belief that his successor's name would have to start with the letter alpha, Manuel had the name Alexios bestowed on Béla, the fiancé of his daughter Maria and his designated heir from 1168 to 1169, when his second wife bore Manuel a son, who was named again in accordance with the prophecy as Alexios II Komnenos (), rather than Ioannes after his paternal grandfather, as was customary among the Byzantines. Manuel also gave the name to at l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prophecy
In religion, a prophecy is a message that has been communicated to a person (typically called a '' prophet'') by a supernatural entity. Prophecies are a feature of many cultures and belief systems and usually contain divine will or law, or preternatural knowledge, for example of future events. They can be revealed to the prophet in various ways depending on the religion and the story, such as visions, divination, or direct interaction with divine beings in physical form. Stories of prophetic deeds sometimes receive considerable attention and some have been known to survive for centuries through oral tradition or as religious texts. Etymology The English noun "prophecy", in the sense of "function of a prophet" appeared from about 1225, from Old French ''profecie'' (12th century), and from ''prophetia'', Greek ''propheteia'' "gift of interpreting the will of God", from Greek ''prophetes'' (see prophet). The related meaning, "thing spoken or written by a prophet", dates from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Komnenos Of Cyprus
Isaac Doukas Komnenos (or Ducas Comnenus, c. 1155 – 1195/1196) was a claimant to the Byzantine Empire and the ruler of Cyprus from 1184 to 1191. Contemporary sources commonly refer to him as the emperor of Cyprus. He lost the island to King Richard I of England during the Third Crusade. Family At the death of Byzantine emperor John II Komnenos in 1143, the throne passed not to his third and oldest living son, Isaac Komnenos, but his youngest son, Manuel I Komnenos, who successfully claimed the throne. Isaac nevertheless served amiably as ''sebastokrator'', and his first wife Theodora Kamaterina (d. 1144) bore him a daughter, Irene Komnene, and other children. Irene Komnene married an unnamed Doukas Kamateros and gave birth to Isaac Komnenos, a minor member of the Komnenos family, . Life Byzantine historian Niketas Choniates provides most of the following account of his life. Isaac was the son of an unnamed member of the noble Byzantine family, Doukas Kamateros, and Irene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine And Modern Greek Studies
''Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies'' or BMGS is a peer reviewed British journal which contains articles that pertain to both Byzantine Studies and Modern Greek studies, i.e. the language, literature, history and archaeology of the post-classical Greek world, from Late Antiquity to the present day, and also reviews of recent books of importance to Byzantine and Modern Greek studies. It is published annually, from 1975 to the current day, by the Centre of Byzantine, Ottoman and Modern Greek Studies at the University of Birmingham The University of Birmingham (informally Birmingham University) is a Public university, public research university located in Edgbaston, Birmingham, United Kingdom. It received its royal charter in 1900 as a successor to Queen's College, Birmingha .... External links Departmental webpage European history journals Publications established in 1975 Byzantine studies journals Modern Greek studies Cambridge University Press academic journals {{h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos II Of Trebizond
Andronikos II Megas Komnenos ( el, Ανδρόνικος Κομνηνός; 1240 – 1266), or Andronicus II Grand Comnenus, was the Emperor of Trebizond from 1263 to 1266. Despite being the designated successor of his father Manuel I, Andronikos' tenure was short due to premature death from unrecorded causes. The major event of his reign was the definitive loss of Sinope to the Seljuk Turks under the regency of Mu‘in al-Din Suleyman, also known as the Pervane, in the summer or fall of 1265. The capture of Sinope by the Turks gave them the best port on the Black Sea, allowing them to create a navy and compete with the Trapezuntines for influence in the Black Sea. Andronikos was the eldest son of Manuel Komnenos by his first wife, Anna Xylaloe, a Trapezuntine noblewoman. William Miller, ''Trebizond: The last Greek Empire of the Byzantine Era: 1204-1461'', 1926 (Chicago: Argonaut, 1969), p. 27 According to the chronicler Michael Panaretos, "And so, his son by lady Anna Xyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel I Of Trebizond
Manuel I Megas Komnenos ( el, Μανουήλ Κομνηνός; died March 1263) was Emperor of Trebizond from 1238 until his death. He was the son of Emperor Alexios I and his wife, Theodora. At the time Manuel reigned, the Empire of Trebizond comprised a band of territory stretching along the southern coast of the Black Sea. Although Michael Panaretos, a 14th-century Trapezuntine chronicler, calls Manuel "the greatest general and the most fortunate" and states he ruled "virtuously in the eyes of God", the only event he documents for Manuel's reign is a catastrophic fire striking the city of Trebizond in January 1253. The major events of his reign are known from external sources, most important of which is the recovery of Sinope in 1254, which had been lost to the Sultanate of Rum forty years before. Manuel and the Mongols In 1243, a Trapezuntine army is recorded as assisting the Seljuk Turks, along with a detachment from the Nicaean Empire, against the Mongols of Persia at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I Of Trebizond
John I Komnenos Axouchos ( gr, Ιωάννης Κομνηνός Ἀξούχος, Iōannēs Komnēnos Axouchos) was Emperor of Trebizond from 1235 to 1238. One editor reads the text of the chronicle of Michael Panaretos as stating that John ruled six years; although William Miller follows Fallmerayer in assuming this was a mistake for three years, another possible solution is that John was co-ruler with his predecessor Andronikos I Gidos for three years then ruled alone for three more. Background He was the eldest son of Alexios I of Trebizond and a woman the primary sources do not identify; some writers have named her Theodora Axuchina. Miller suggests that he was perhaps a minor at the time of his father's death in 1222, for his father was succeeded by the throne passed to Alexis' son-in-law, Andronikos I Gidos. During the Siege of Sinope The siege of Sinope in 1214 was a successful siege and capture of Sinope by the Sultanate of Rum under their Sultan, Kaykaus I (r. 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos I Of Trebizond
Andronikos I Gidos ( el, Ανδρόνικος Κομνηνός Γίδος, translit=Andronikos Komnēnos Gidos), Latinisation of names, Latinized as Andronicus I Gidus or Gidon, was an Emperor of Empire of Trebizond, Trebizond (1222–1235). He is the only ruler of Trebizond who was not a blood relative of the founder of that state, Alexios I of Trebizond, Alexios I Megas Komnenos. George Finlay suggests he may be the same Andronikos who was a general of Theodore I Laskaris. During his reign, Trebizond successfully withstood a Siege of Trebizond (1222–23), siege of the city by the Seljuk Turks, and later supported the Shah of Khwarizm in the latter's Battle of Yassıçemen, unsuccessful battle with the Seljuks. Origins The Gidos family appears briefly in Byzantine history at the turn of the 12th/13th century. The etymology of the surname is uncertain, but one view considers it to be from the Greek word for "goat" ('Gida' γίδα f., γίδι), another speculative view suggest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
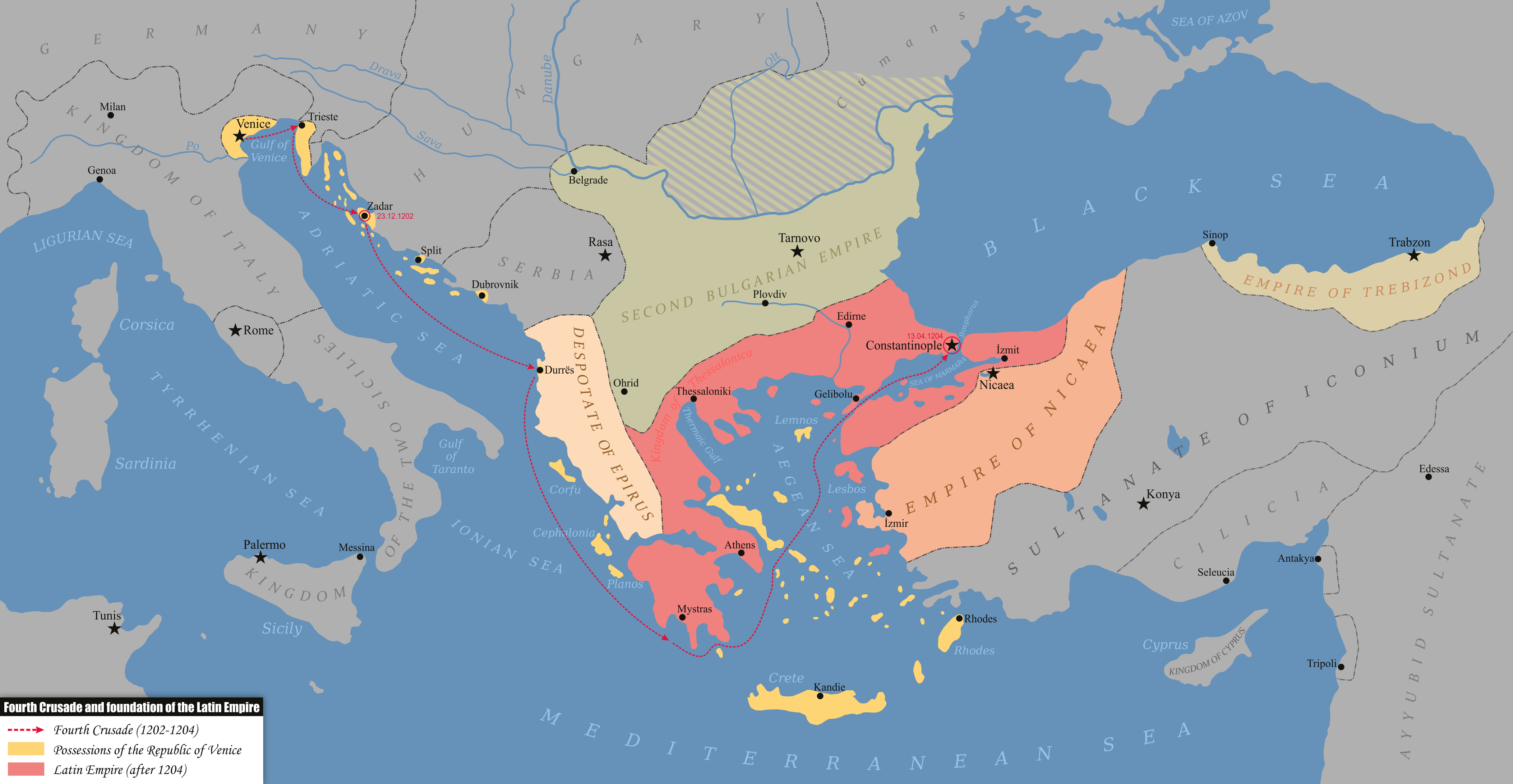
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to the 15th century, consisting of the far northeastern corner of Anatolia (the Pontus) and the southern Crimea. The empire was formed in 1204 with the help of the Georgian queen Tamar after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself Emperor and established himself in Trebizond (modern day Trabzon, Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of deposed Emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as "Roman emperors" against Byzantine Emperor Alexios V Doukas. The later Byzantine emperors, as well as Byzantine authors, such as George Pachymeres, Nicephorus Gregoras and to some ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexios I Of Trebizond
Alexios I Megas Komnenos ( el, Αλέξιος Κομνηνός; c. 1182 – 1 February 1222) or Alexius I Megas Comnenus was, with his brother David, the founder of the Empire of Trebizond and its ruler from 1204 until his death in 1222. The two brothers were the only male descendants of the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos I, who had been dethroned and killed in 1185, and thus claimed to represent the legitimate government of the Empire following the conquest of Constantinople by the Fourth Crusade in 1204. Although his rivals governing the Nicaean Empire succeeded in becoming the de facto successors, and rendered his dynastic claims to the imperial throne moot, Alexios' descendants continued to emphasize both their heritage and connection to the Komnenian dynasty by later referring to themselves as ''Megas Komnenos'' ("grand Komnenos"). While his brother David conquered a number of Byzantine provinces in northwestern Anatolia, Alexios defended his capital Trebizond from an un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperors Of Trebizond
The Trapezuntine emperors were the rulers of the Empire of Trebizond, one of the successor states of the Byzantine Empire founded after the Fourth Crusade in 1204, until its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1461. All but two of the Trapezuntine rulers belonged to the Komnenos dynasty, which had previously ruled the Byzantine Empire from 1081 to 1185, and they initially claimed to represent the legitimate line of Roman emperors, in opposition to the Latin Empire in Constantinople, the Laskaris dynasty of the Nicene Empire, and the Komnenos Doukas family of Epirus and Thessalonica. To emphasize their dynastic claim, Trapezuntine emperors from the late 13th century onwards styled themselves as (, ). Out of the Byzantine claimants that emerged in 1204 and thereafter, the Trapezuntine emperors, despite their illustrious descent, had perhaps the worst position. Not only were they far away from Constantinople in a peripheral province of the empire, but the reputation of the Komnenoi had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Orthodox Church, Greek Orthodox church which lasted from 360 AD until the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople by the Ottoman Empire in 1453. It served as a mosque until 1935, when it became a museum. In 2020, the site once again became a mosque. The current structure was built by the eastern Roman emperor Justinian I as the Christian cathedral of Constantinople for the state church of the Roman Empire between 532 and 537, and was designed by the Greeks, Greek geometers Isidore of Miletus and Anthemius of Tralles. It was formally called the Church of the Holy Wisdom () and upon completion became the world's largest interior space and among History of Roman and Byzantine domes, the first to employ a fully pendentive dome. It is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis (Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_at_Cyprus.jpg)


.jpg)
