|
AD 411
__NOTOC__ Year 411 ( CDXI) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in Rome as the Year of the Consulship of Theodosius without colleague (or, less frequently, year 1164 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 411 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Honorius sends two Roman generals to deal with the usurper Constantine III in Gaul. They kill Gerontius, Constantine's rebellious general (''magister militum'') in Spain, then besiege Arles and defeat Constantine III. He is taken prisoner and put to death at Ravenna. * Following the defeat of Constantine III, the Burgundians and the Gallic nobility proclaim Jovinus, Gallo-Roman senator, emperor of the Western Roman Empire at '' Mogontiacum'' (modern Mainz). Europe * King Ataulf leads the Goths into Gaul at the instigation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siliqua Jovinus-RSC 0004
The siliqua (. siliquas or siliquae) is the modern namegiven without any ancient evidence to confirm the designationto small, thin, Roman silver coins produced in the 4th century and later. When the coins were in circulation, the Latin word was a unit of weight or value defined by one late Roman writer as one twenty-fourth of a Roman solidus (coin), solidus. The term siliqua comes from the ''siliqua graeca'', the seed of the carob tree, which in the Ancient Roman weights and measures, Roman weight system is equivalent to of a scruple ( of a Roman pound or about 0.19 grams). The term has been applied in modern times to various silver coins on the premise that the coins were valued at of the gold solidus (which weighed of a Roman pound) and therefore represented a siliqua of gold in value. Since gold was worth about 12 times as much as silver in ancient Rome (in Diocletian's Edict on Maximum Prices of 301),Bransbourg, Giles. "Inflation and monetary reforms in the fourth cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the senators for life (or until expulsion by Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutons
The Teutons (, ; ) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with the Roman Republic in the late second century BC. Some generations later, Julius Caesar compared them to the Germanic peoples of his own time, and used this term for all northern peoples located east of the Rhine. Later Roman authors followed his identification. However, there is no direct evidence about whether or not they spoke a Germanic language. Evidence such as the tribal name, and the names of their rulers, as they were written up by Roman historians, indicates a strong influence from Celtic languages. On the other hand, the indications that classical authors gave about the homeland of the Teutones is considered by many scholars to show that they lived in an area associated with early Germanic languages, and not in an area associated with Celtic languages. Name Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douro
The Douro (, , , ; ; ) is the largest river of the Iberian Peninsula by discharge. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in the Spanish Soria Province, province of Soria, meanders briefly south, then flows generally west through the northern part of the Meseta Central in Castile and León into northern Portugal. Its largest tributary (carrying more water than the Douro at their confluence) is the right-bank Esla (river), Esla. The Douro flows into the Atlantic Ocean at Porto, the second largest city of Portugal. The scenic Douro railway line runs close to the river. Adjacent areas produce port wine, port (a mildly fortification (wine), fortified wine) and other agricultural produce. A small tributary of the river has the Côa Valley Paleolithic Art site which is considered important to the archaeological pre-historic patrimony, designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Within Spain, it flows through the middle of the autonomous community of Castile and León, with the basin spanni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lusitania
Lusitania (; ) was an ancient Iberian Roman province encompassing most of modern-day Portugal (south of the Douro River) and a large portion of western Spain (the present Extremadura and Province of Salamanca). Romans named the region after the Lusitanians, an Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European tribe inhabiting the lands. The capital Emerita Augusta was initially part of the Roman Republic province of Hispania Ulterior before becoming a province of its own during the Roman Empire. After Romans arrived in the territory during the 2nd century BC, a Lusitanian War, war with Lusitanian tribes ensued between 155 and 139 BC, with the Roman province eventually established in 27 BC. In modern parlance, ''Lusitania'' is often synonymous with Portugal, despite the province's capital being located in modern Mérida, Spain. Etymology The etymology of the name of the Lusitanians, Lusitani (who gave the Roman province its name) remains unclear. Popular etymology connected the name to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
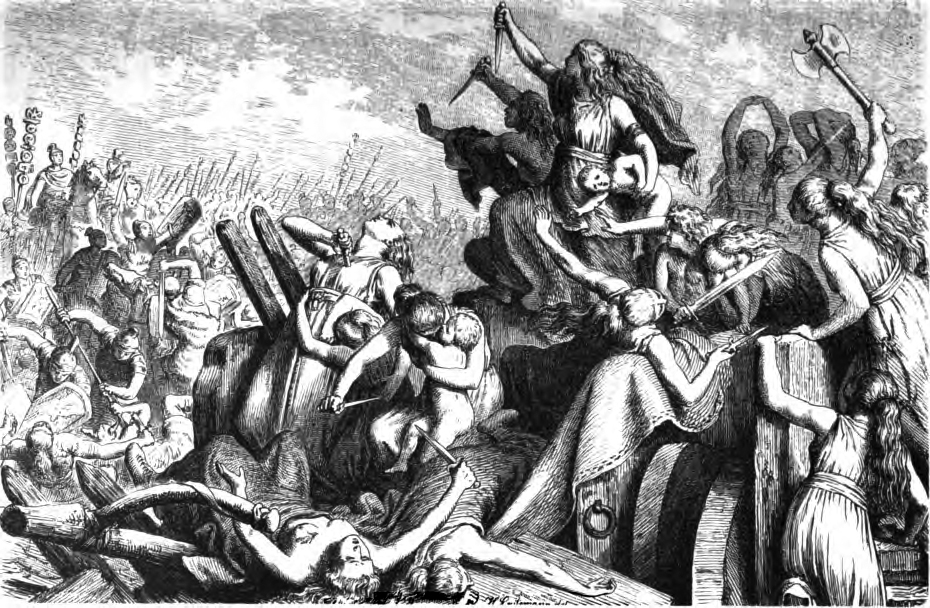
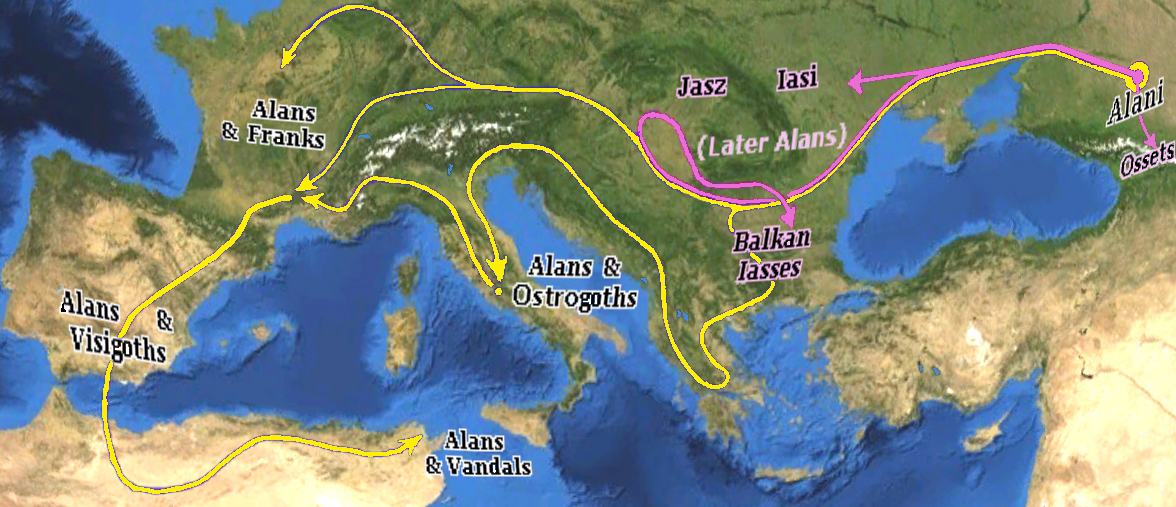
Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of China, Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Ancient Rome, Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the South Caucasus provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe, thereby assimilating a sizeable portion of the associated Alans. Upon the Huns, Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Usurper
Roman usurpers were individuals or groups of individuals who obtained or tried to obtain power by force and without legitimate legal authority. Usurpation was endemic during the Roman imperial era, especially from the crisis of the third century onwards, when political instability became the rule. Instability The first dynasty of the Roman Empire, the Julio-Claudian dynasty (27 BC – 68 AD), justified the imperial throne with familial ties through adoption. However, conflicts within the family led to the demise of the line. Nero committed suicide in 68 as an enemy of the people, resulting in a brief civil war. The Flavian dynasty started with Vespasian, only to end with the assassination of his second son, Domitian. Throughout most of the 2nd century, the empire enjoyed relative stability under the rule of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, but the next century would be characterised by endemic political instability, one of the factors that eventually contributed to the fall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic Spain or Kingdom of the Goths () was a Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic peoples, Germanic successor states to the Western Roman Empire, it was originally created by the settlement of the Visigoths under King Wallia in the province of Gallia Aquitania in southwest Gaul by the Roman government and then extended by conquest over all of Hispania. The Kingdom maintained independence from the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire, whose attempts to re-establish Roman authority in Hispania were only partially successful and short-lived. The Visigoths were Romanization (cultural), romanized central Europeans who had moved west from the Danube, Danube Valley. They became foederati of Rome, and sought to restore the Roman order against the hordes of Vandals, Alans and Suebi. The Fall of the Western Roman Empire, Western Roman Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is now Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania. From here they conducted raids into Roman territory, and large numbers of them joined the Roman military. These early Goths lived in the regions where archaeologists find the Chernyakhov culture, which flourished throughout this region during the 3rd and 4th centuries. In the late 4th century, the lands of the Goths in present-day Ukraine were overwhelmed by a significant westward movement of Alans and Huns from the east. Large numbers of Goths subsequently concentrated upon the Roman border at the Lower Danube, seeking refuge inside the Roman Empire. After they entered the Empire, violence broke out, and Goth-led forces inflicted a devastating defeat upon the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataulf
Athaulf (also ''Athavulf'', ''Atawulf'', or ''Ataulf'' and ''Adolf'', Latinized as ''Ataulphus'') ( 37015 August 415) was king of the Visigoths from 411 to 415. During his reign, he transformed the Visigothic state from a tribal kingdom to a major political power of late antiquity. Life He was unanimously elected to the throne to succeed his brother-in-law Alaric, who had been struck down by a fever suddenly in Calabria. King Athaulf's first act was to halt Alaric's southward expansion of the Goths in Italy. Meanwhile, Gaul had been separated from the Western Roman Empire by the usurper Constantine III. So in 411 Constantius, the ''magister militum'' (master of military) of the western emperor, Flavius Augustus Honorius, with Gothic auxiliaries under Ulfilas, crushed the Gallic rebellion with a siege of Arles. There Constantine and his son were offered an honorable capitulation— but were beheaded in September on their way to pay homage to Honorius at Ravenna. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |