|
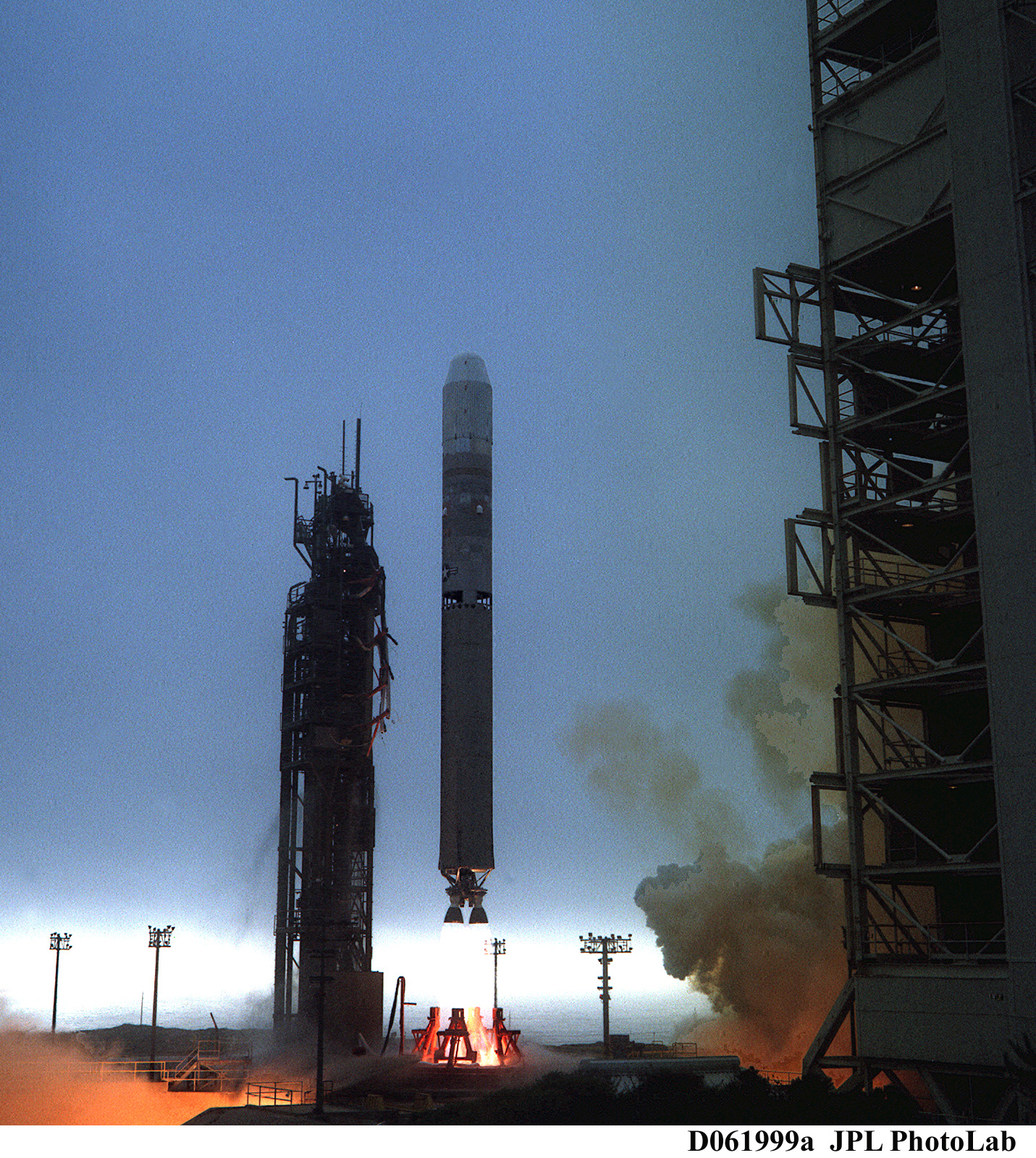
ADEOS II
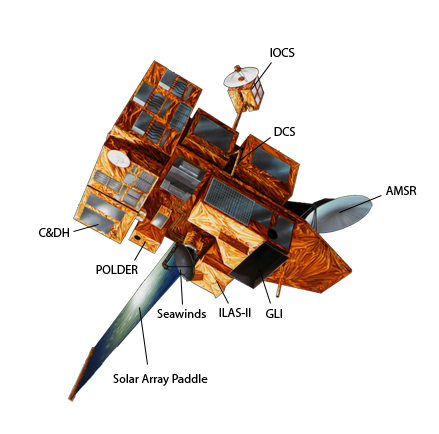
ADEOS II (Advanced Earth Observing Satellite 2) was an Earth observation satellite (EOS) launched by NASDA, with contributions from NASA and CNES, in December 2002. and it was the successor to the 1996 mission ADEOS I. The mission ended in October 2003 after the satellite's solar panels failed. Mission overview The three primary objectives of the mission, as identified by NASDA, were to: * Regularly monitor the water and energy cycle as a part of the global climate system * Quantitatively estimate the biomass and fundamental productivity as a part of the carbon cycle * Detect trends in long term climate change as a result of continuing the observations started by ADEOS I The project had a proposed minimum life of three years, with a five-year goal. Instruments The satellite was equipped with five primary instruments: Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR), Global Imager (GLI), Improved Limb Atmospheric Spectrometer-II (ILAS-II), Polarization and Directionalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Observation Satellite
An Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, cartography and others. The most common type are Earth imaging satellites, that take satellite images, analogous to aerial photographs; some EO satellites may perform remote sensing without forming pictures, such as in GNSS radio occultation. The first occurrence of satellite remote sensing can be dated to the launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957. Sputnik 1 sent back radio signals, which scientists used to study the ionosphere. The United States Army Ballistic Missile Agency launched the first American satellite, Explorer 1, for NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on January 31, 1958. The information sent back from its radiation detector led to the discovery of the Earth's Van ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Cycle
The water cycle (or hydrologic cycle or hydrological cycle) is a biogeochemical cycle that involves the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth across different reservoirs. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time. However, the partitioning of the water into the major reservoirs of ice, fresh water, Saline water, salt water and Atmosphere, atmospheric water is variable and depends on Climate, climatic variables. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere due to a variety of physical and chemical processes. The processes that drive these movements, or Flux (biology), fluxes, are evaporation, transpiration, condensation, Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, Sublimation (phase transition), sublimation, Infiltration (hydrology), infiltration, surface runoff, and subsurface flow. In doing so, the water goes through different phases: liquid, solid (ice) and W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
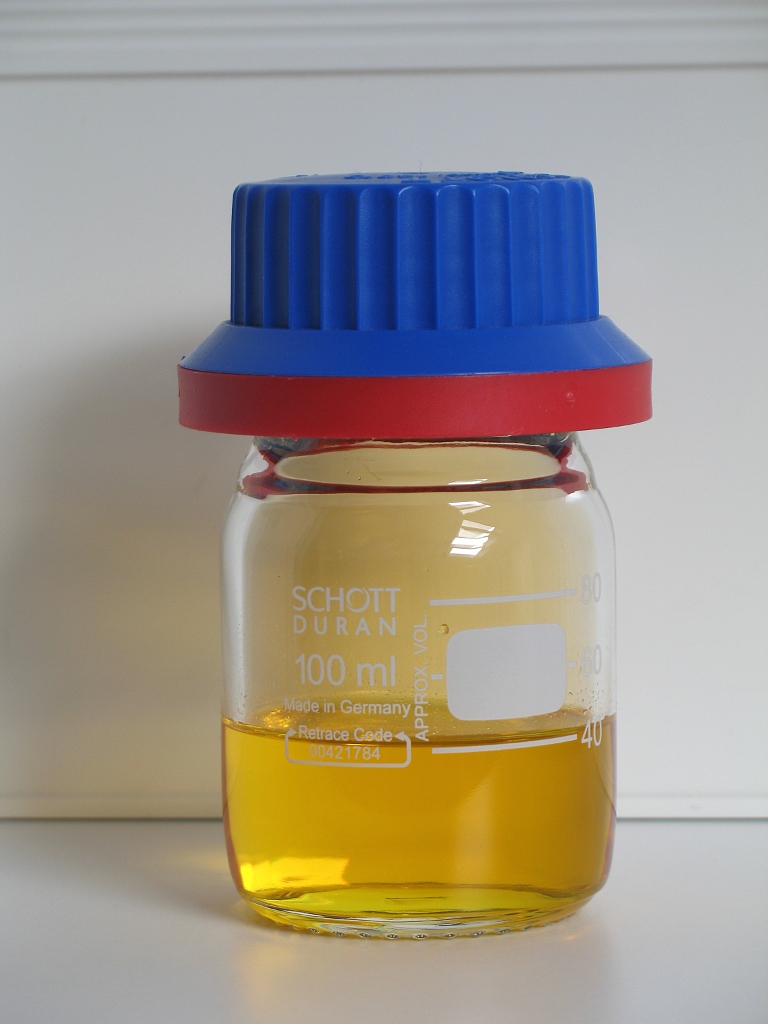
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as synthetic dyes and medicines (e.g. metronidazole). Nitric acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . One of several nitrogen oxides, nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas. It is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. Industrially, is an intermediate in the synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year, primarily for the production of fertilizers. Nitrogen dioxide is poisonous and can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities. Cooking with a gas stove produces nitrogen dioxide which causes poorer indoor air quality. Combustion of gas can lead to increased concentrations of nitrogen dioxide throughout the home environment which is linked to respiratory issues and diseases. The LC50 ( median lethal dose) for humans has been estimated to be 174 ppm for a 1-hour exposure. It is also included in the NOx family of atmospheric pollutants. Properties Nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent, acrid odor above and becomes a yellowish-brown liquid below . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the atmosphere, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odor is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 chemical structure, structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetism, diamagnetic. At standard temperature and pressure, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
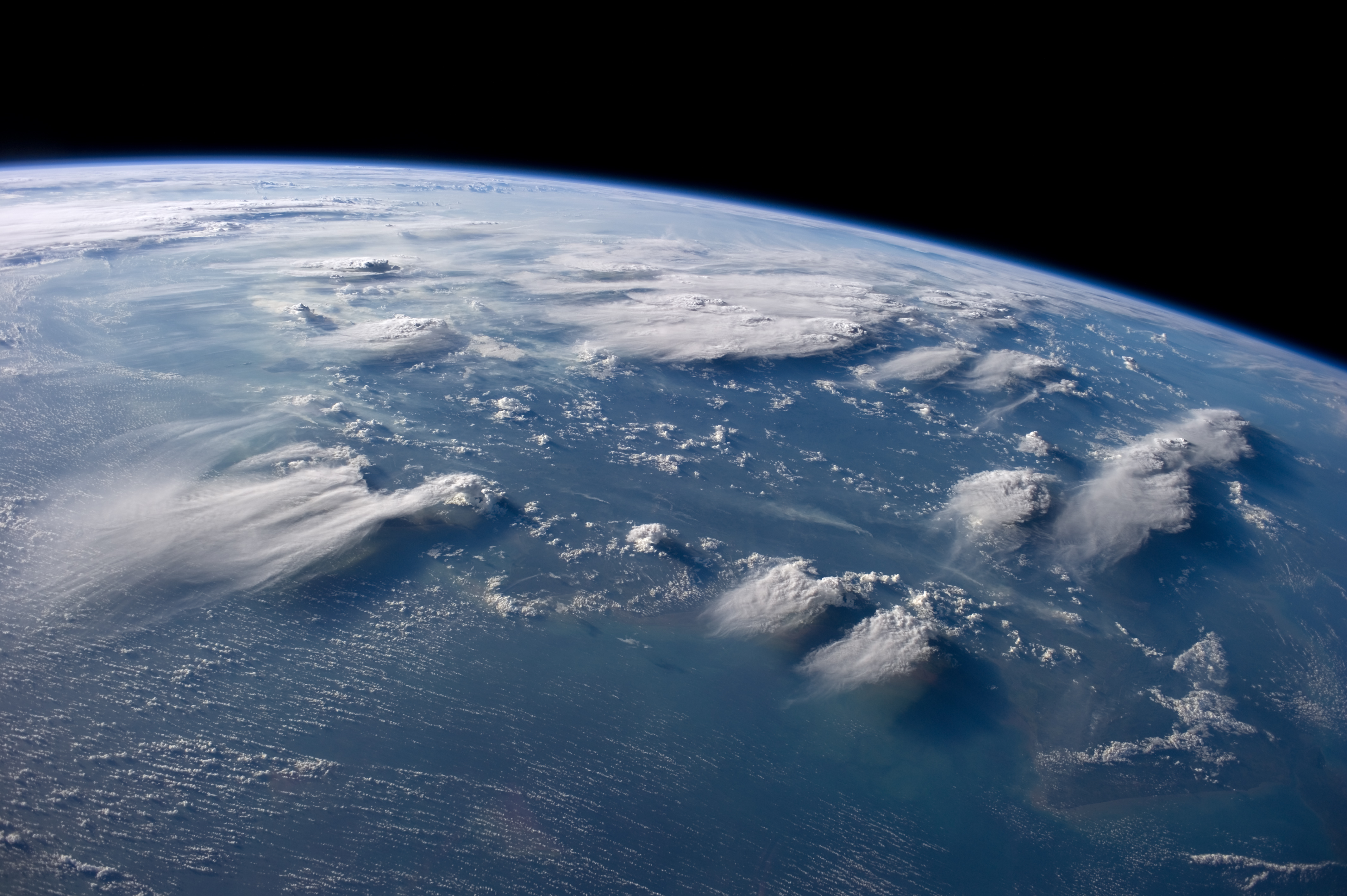
Cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles, suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. Clouds are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. The World Meteorological Organization uses two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plants and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular Taxon, taxa, life forms, structure, Spatial ecology, spatial extent, or any other specific Botany, botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader than the term ''Flora (plants), flora'' which refers to species richness, species composition. Perhaps the closest synonym is ''plant community'', but "vegetation" can, and often does, refer to a wider range of spatial scales than that term does, including scales as large as the global. Primeval redwood forests, coastal mangrove stands, sphagnum bogs, desert soil crusts, Road verge, roadside weed patches, wheat fields, cultivated gardens and lawns; all are encompassed by the term "vegetation". The vegetation type is defined by characteristic dominant species, or a common aspect of the assemblage, such as an elevation range or environmental commonality. The contemporary use of "vegetation" app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Irradiance
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m2) in SI units. Solar irradiance is often integrated over a given time period in order to report the radiant energy emitted into the surrounding environment (joule per square metre, J/m2) during that time period. This integrated solar irradiance is called solar irradiation, solar radiation, solar exposure, solar insolation, or insolation. Irradiance may be measured in space or at the Earth's surface after atmospheric absorption and scattering. Irradiance in space is a function of distance from the Sun, the solar cycle, and cross-cycle changes.Michael Boxwell, ''Solar Electricity Handbook: A Simple, Practical Guide to Solar Energy'' (2012), pp. 41–42. Irradiance on the Earth's surface additionally depends on the tilt of the measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is Scientific consensus on climate change, driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, Deforestation and climate change, deforestation, and some Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, agricultural and Environmental impact of concrete, industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases greenhouse effect, absorb some of the heat that the Earth Thermal radiation, radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, has increased in concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how biomass is defined, e.g., only from plants, from plants and algae, from plants and animals. The vast majority of biomass used for bioenergy does come from plants and fecal matter. Bioenergy is a type of renewable energy that the bioenergy industry claims has the potential to assist with climate change mitigation. Uses in different contexts Ecology * Biomass (ecology), the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. This can be the biomass of particular species or the biomass of a particular community or habitat. Energy * Biomass (energy), biomass used for energy production or in other words: biological mass used as a renewable energy source (usually produced through agriculture, forestry or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuikSCAT
The NASA QuikSCAT (Quick Scatterometer) was an Earth observation satellite carrying the SeaWinds scatterometer. Its primary mission was to measure the surface wind speed and direction over the ice-free global oceans via its effect on water waves. Observations from QuikSCAT had a wide array of applications, and contributed to climatological studies, weather forecasting, meteorology, oceanographic research, marine safety, commercial fishing, tracking large icebergs, and studies of land and sea ice, among others. This SeaWinds scatterometer is referred to as the QuikSCAT scatterometer to distinguish it from the nearly identical SeaWinds scatterometer flown on the ADEOS-2 satellite. Mission description QuikSCAT was launched on 19 June 1999 with an initial 3-year mission requirement. QuikSCAT was a "quick recovery" mission replacing the NASA Scatterometer (NSCAT), which failed prematurely in June 1997 after just 9.5 months in operation. QuikSCAT, however, far exceeded these design expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |