|
ACBI3
ACBI3 is an experimental anticancer drug which is one of the first examples of a proteolysis targeting chimera or PROTAC. It is a bifunctional molecule with two halves joined by a linker; one half binds to a protein found in various forms of cancer cell called Kirsten rat sarcoma virus or KRAS, while the other half binds E3 ligase which triggers the cell's natural protein degradation mechanisms so that the entire complex is broken down. In early stage testing, it was able to target 13 of the 17 most common mutated forms of KRAS found in cancer cells, allowing selective targeting of a wide range of cancer types. While this particular molecule is still at an early developmental stage and may be unlikely to be approved as a medicine itself, it is an important proof of concept which is likely to lead to the development of a range of related PROTAC type anticancer drugs. See also * Adagrasib * K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 6 * MRTX1133 * Olomorasib * RMC-9805 * Sotorasib Sotorasib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olomorasib
Olomorasib (LY3537982) is an experimental anticancer drug which acts as an inhibitor of the G12C mutant form of Kirsten rat sarcoma virus (KRAS), an oncogene commonly present in several forms of cancer. It is in early stage clinical trials against lung and colorectal cancers and advanced solid tumors. See also * ACBI3 * Adagrasib * Divarasib * MRTX1133 * RMC-9805 * Sotorasib Sotorasib, sold under the brand names Lumakras and Lumykras, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat non-small-cell lung cancer. It targets a specific mutation, G12C, in the protein K-Ras encoded by gene KRAS which is responsible for vario ... References {{reflist Experimental cancer drugs Benzothiophenes Pyrazines Oxazocines Nitriles Fluoroarenes Chloroarenes Amines Carboxamides Cyclic ketones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRTX1133
MRTX1133 is an investigational drug that targets the G12D mutation in KRAS dependent cancers. MRTX1133 was in a phase 1/2 clinical trial for the treatment of solid tumors, however the study was terminated in Q1 2025. MRTX1133 is considered to be harmful from direct skin or eye exposure other than transient irritation. It may cause irritation of the respiratory system if inhaled. See also * ACBI3 * Adagrasib * Olomorasib * RMC-9805 * Sotorasib Sotorasib, sold under the brand names Lumakras and Lumykras, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat non-small-cell lung cancer. It targets a specific mutation, G12C, in the protein K-Ras encoded by gene KRAS which is responsible for vario ... References {{antineoplastic-drug-stub Antineoplastic drugs Pyridopyrimidines Pyrrolizidines Fluoroarenes Ethynyl compounds Naphthols Aromatic ethers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RMC-9805
RMC-9805 is an investigational drug that selectively targets the G12D mutation in KRAS dependent cancers. RMC-9805 functions as molecular glue that forms a non-covalent ligand-mediated protein-protein interaction between cyclophilin A and GTP-bound RAS. Subsequent covalent modification of the mutant Asp12 residue affords selectivity over wild-type RAS. RMC-9805 is currently in a phase 1/1b clinical trial for the treatment of KRAS G12D-mutant solid tumors. Preliminary data indicated that KRAS G12D–mutant PDAC patients dosed at 1200 mg daily or 600 mg twice daily achieved a 30% objective response rate (n = 12) and 80% disease control rate (n = 32). See also * ACBI3 * Adagrasib * MRTX1133 * Olomorasib * Sotorasib Sotorasib, sold under the brand names Lumakras and Lumykras, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat non-small-cell lung cancer. It targets a specific mutation, G12C, in the protein K-Ras encoded by gene KRAS which is responsible for vario ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticancer
An anticarcinogen (also known as a carcinopreventive agent) is a substance that counteracts the effects of a carcinogen or inhibits the development of cancer. Anticarcinogens are different from anticarcinoma agents (also known as anticancer or anti-neoplastic agents) in that anticarcinoma agents are used to selectively destroy or inhibit cancer cells ''after'' cancer has developed. Interest in anticarcinogens is motivated primarily by the principle that it is preferable to prevent disease ( preventive medicine) than to have to treat it ( rescue medicine). In theory, anticarcinogens may act via different mechanisms including enhancement of natural defences against cancer, deactivation of carcinogens, and blocking the mechanisms by which carcinogens act (such as free radical damage to DNA). Confirmation that a substance possesses anticarcinogenic activity requires extensive ''in vitro'', '' in vivo'', and clinical investigation. Health claims for anticarcinogens are regulated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzothiophenes
The substituted benzothiophenes are a class of chemical compounds based on benzothiophene. They are closely related to the substituted benzofurans, substituted tryptamines, and to other chemical class, chemical groups such as the substituted benzodioxoles (or methylenedioxyphenyl group, phenyl compounds). Substituted benzothiophenes include the (2-aminopropyl)benzo[β]thiophenes (APBTs) 2-APBT, 3-APBT (SKF-6678), 4-APBT, 5-APBT, 5-MAPBT, 6-APBT, 6-MAPBT, and 7-APBT. These drugs have been found to act as serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agents (SNDRAs) and, in some cases, as potency (pharmacology), potent serotonin 5-HT2 receptor, 5-HT2 receptor agonists, analogously to the entactogen MDMA. They do not produce hyperlocomotion in rodents, suggesting that they lack psychostimulant effects. However, those acting as serotonin 5-HT2 receptor agonists have been found to induce the head-twitch response, a behavioral proxy of psychedelic drug, psychedelic effects, in rodents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitriles
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The name of the compound is composed of a base, which includes the carbon of the , suffixed with "nitrile", so for example is called "propionitrile" (or propanenitrile). The prefix ''cyano-'' is used interchangeably with the term ''nitrile'' in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex, latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons. Inorganic compounds containing the group are not called nitriles, but cyanides instead. Though both nitriles and cyanides can be derived from cyanide salts, most nitriles are not nearly as toxic. Structure and basic properties The N−C−C geome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiazoles
Thiazole (), or 1,3-thiazole, is a 5-membered heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen. The term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS. The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1). Molecular and electronic structure Thiazoles are members of the azoles, heterocycles that include imidazoles and oxazoles. Thiazole can also be considered a functional group when part of a larger molecule. Being planar thiazoles are characterized by significant pi-electron delocalization and have some degree of aromaticity, more so than the corresponding oxazoles. This aromaticity is evidenced by the 1H NMR chemical shift of the ring protons, which absorb between 7.27 and 8.77 ppm, indicating a strong diamagnetic ring current. The calculated pi-electron density marks C5 as the primary site for electrophilic substitution, and C2-H a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrolidines
Pyrrolidine, also known as tetrahydropyrrole, is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)4NH. It is a cyclic secondary amine, also classified as a saturated heterocycle. It is a colourless liquid that is miscible with water and most organic solvents. It has a characteristic odor that has been described as "ammoniacal, fishy, shellfish-like". In addition to pyrrolidine itself, many substituted pyrrolidines are known. Production and synthesis Industrial production Pyrrolidine is prepared industrially by the reaction of 1,4-butanediol and ammonia at a temperature of 165–200 °C and a pressure of 17–21 MPa in the presence of a cobalt- and nickel oxide catalyst, which is supported on alumina. : The reaction is carried out in the liquid phase in a continuous tube- or tube bundle reactor, which is operated in the cycle gas method. The catalyst is arranged as a fixed-bed and the conversion is carried out in the downflow mode. The product is obtained after m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
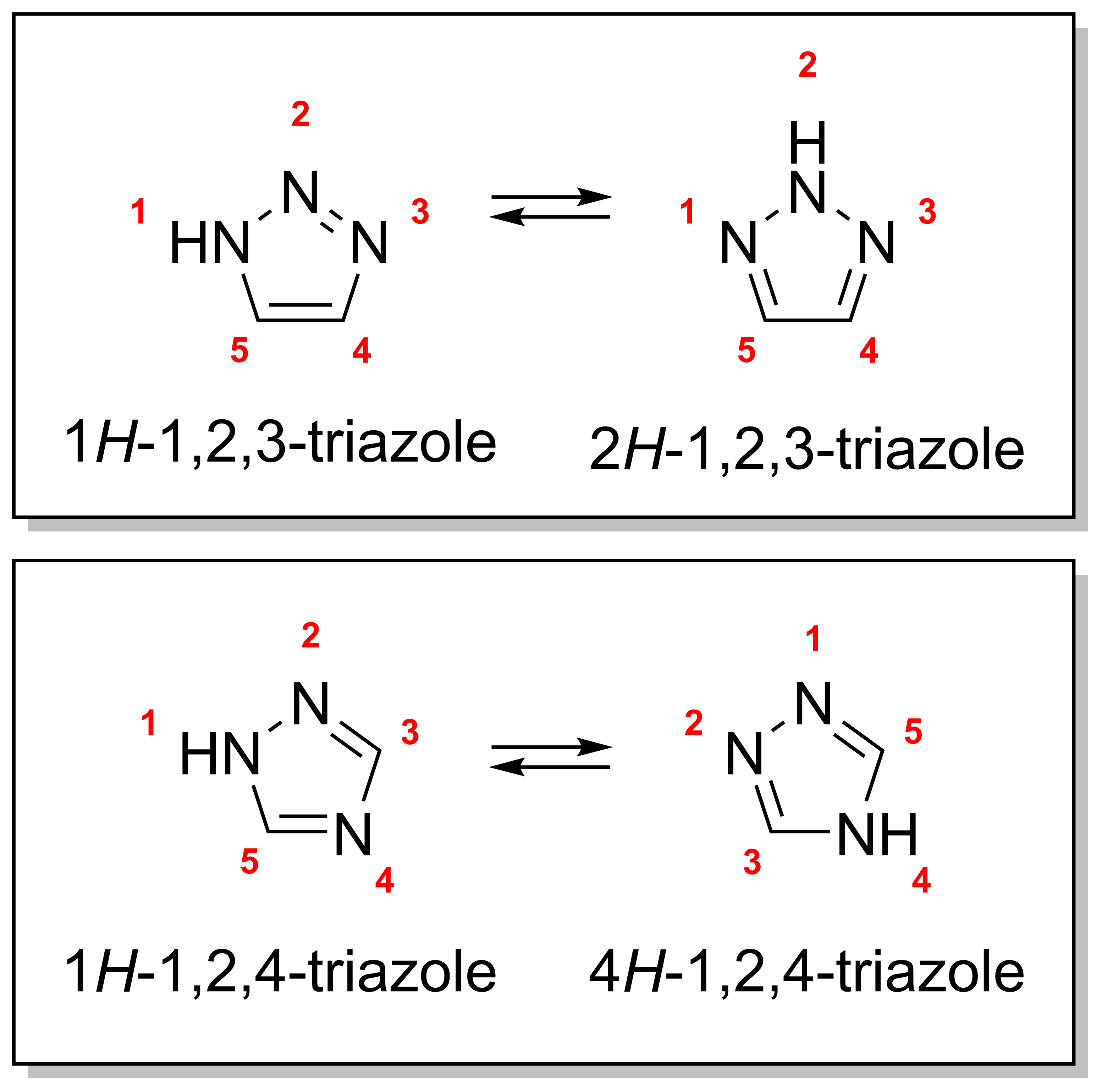
Triazoles
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial Isomer, isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to Azide, azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as Piano stool complex, haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of Tautomer, tautomers. In the 1,2,3-Triazole, 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-Triazole, 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidines
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux reported the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |