|
A4 Processor
The Apple A4 is a 32-bit package on package (PoP) system on a chip (SoC) designed by Apple Inc., part of the Apple silicon series, and manufactured by Samsung. It was the first SoC Apple designed in-house. The first product to feature the A4 was the iPad (1st generation), first-generation iPad, followed by the iPhone 4, IPod Touch (4th generation), fourth-generation iPod Touch, and Apple TV, second-generation Apple TV. The last operating system update Apple provided for a mobile device containing an A4 (iPhone 4) was iOS 7, iOS 7.1.2, which was released on June 30, 2014 as it was discontinued with the release of iOS 8 in September 2014. The iPad (1st generation) was discontinued earlier than the iPhone 4 with the release of IOS 5, iOS 5.1.1 on May 7, 2012 because it only had 256 MB of RAM compared to 512 MB on the iPhone, and the fact that applications would crash more frequently with the graphics using a large portion of the RAM. The last operating system update Apple provided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple A5
The Apple A5 is a 32-bit system on a chip (SoC) designed by Apple Inc., part of the Apple silicon series, and manufactured by Samsung. The first product Apple featured an A5 in was the iPad 2. Apple claimed during their media event on March 2, 2011, that the ARM Cortex-A9 central processing unit (CPU) in the A5 is up to two times faster than the CPU in the Apple A4, and the PowerVR#Series5XT (SGX), PowerVR SGX543MP2 graphics processing unit (GPU) in the A5 is up to nine times faster than the GPU in the A4. Apple also claimed that the A5 uses the same amount of power as the A4. The last operating system update Apple provided for a mobile device containing an A5 (iPad 2 CDMA, iPhone 4S, and IPad Mini (1st generation), first-generation iPad Mini cellular models) was IOS 9#9.3.6, iOS 9.3.6, which was released on July 22, 2019, as they were discontinued with the release of iOS 10 in 2016. The latest operating system update Apple has provided for an Apple TV containing an A5 (Apple TV# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IOS 7
iOS 7 is the seventh major release of the iOS mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc., being the successor to iOS 6. It was announced at the company's Worldwide Developers Conference on June 10, 2013, and was released on September 18 of that year. It was succeeded by iOS 8 on September 17, 2014. iOS 7 introduced a completely redesigned user interface, a design credited to a team led by Apple's former senior vice president of design, Jony Ive. The new look, featuring flatter icons, a new slide-to-unlock function, and new animations, was described by Ive as "profound and enduring beauty in simplicity." The new design was implemented throughout the operating system, including the Notification Center, which was updated with three tabs offering different views of information, notifications visible on the lock screen; a redesigned Siri voice assistant offering visual indicators, and a Control Center offering easy access to the most commonly used features. iOS 7 also int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
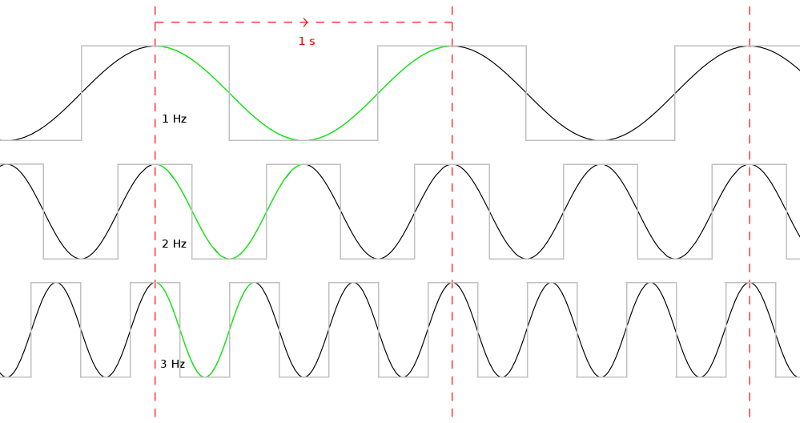
Clock Rate
Clock rate or clock speed in computing typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses used to synchronize the operations of its components. It is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. Clock rate is measured in the SI unit of frequency hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers from the 1970s through the 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz). In the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Determining factors Binning Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge higher prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called binning. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at the end of the manufact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Processing Unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. GPUs were later found to be useful for non-graphic calculations involving embarrassingly parallel problems due to their parallel structure. The ability of GPUs to rapidly perform vast numbers of calculations has led to their adoption in diverse fields including artificial intelligence (AI) where they excel at handling data-intensive and computationally demanding tasks. Other non-graphical uses include the training of neural networks and cryptocurrency mining. History 1970s Arcade system boards have used specialized graphics circuits since the 1970s. In early video game hardware, RAM for frame buffers was expensive, so video chips composited data together as the display was being scann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PC World (magazine)
''PC World'' (stylized as PCWorld) is a global computer magazine published monthly by IDG. Since 2013, it has been an online-only publication. It offers advice on various aspects of PCs and related items, the Internet, and other personal technology products and services. In each publication, ''PC World'' reviews and tests hardware and software products from a variety of manufacturers, as well as other technology related devices such as still and video cameras, audio devices and televisions. The current editorial director of ''PC World'' is Jon Phillips, formerly of '' Wired''. In August 2012, he replaced Steve Fox, who had been editorial director since the December 2008 issue of the magazine. Fox replaced the magazine's veteran editor Harry McCracken, who resigned that spring, after some rocky times, including quitting and being rehired over editorial control issues in 2007. ''PC World'' is published under other names such as PC Advisor and PC Welt in some countries. ''PC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arm Holdings
Arm Holdings plc (formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a British semiconductor and software design company based in Cambridge, England, whose primary business is the design of central processing unit (CPU) cores that implement the ARM architecture family of instruction sets. It also designs other chips, provides software development tools under the DS-5, RealView and Keil brands, and provides systems and platforms, system-on-a-chip (SoC) infrastructure and software. As a "holding" company, it also holds shares of other companies. Since 2016, it has been majority owned by Japanese conglomerate SoftBank Group. While ARM CPUs first appeared in the Acorn Archimedes, a desktop computer, today's systems include mostly embedded systems, including ARM CPUs used in virtually all modern smartphones. Processors based on designs licensed from Arm, or designed by licensees of one of the ARM instruction set architectures, are used in all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samsung Hummingbird
The Samsung Exynos (stylized as SΛMSUNG Exynos), formerly Hummingbird (), is a series of Arm-based system-on-chips developed by Samsung Electronics' System LSI division and manufactured by Samsung Foundry. It is a continuation of Samsung's earlier S3C, S5L and S5P line of SoCs. The first debut of Samsung's indigenously developed SoC is Samsung Hummingbird (S5PC110/111), later renamed as Exynos 3 Single 3110. Samsung announce it on July 27, 2009. In 2011, Samsung announced Exynos 4 Dual 4210 that was later equipped on Samsung Galaxy S II. Since then, Samsung has used Exynos as a representative brand name of their SoC, based on Arm Cortex cores. In 2017, Samsung launched their proprietary Arm ISA-based customized core designs, codenamed "Exynos M". Exynos M series core made a debut with Exynos M1 nicknamed "Mongoose", which was used for Exynos 8 Octa 8890. The Exynos M-series have been implemented throughout the flagship lineup of Samsung Exynos 9 series, until Exynos 990. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EE Times
''EE Times'' (''Electronic Engineering Times'') is an electronics industry magazine published in the United States since 1972. EE Times is currently owned by AspenCore, a division of Arrow Electronics since August 2016. Ownership and status ''EE Times'' was launched in 1972 by Gerard G. Leeds of CMP Publications Inc. In 1999, the Leeds family sold CMP to United Business Media for $900 million. After 2000, ''EE Times'' moved more into web publishing. The shift in advertising from print to online began to accelerate in 2007, and the periodical shed staff to adjust to the downturn in revenue. In July 2013, the digital edition migrated to UBM TechWeb's DeusM community platform. On June 3, 2016, UBM announced that ''EE Times'', along with the rest of its electronics media portfolio ( EDN, Embedded.com, TechOnline, and Datasheets.com), was being sold to AspenCore Media, a company owned by Arrow Electronics, for $23.5 million. The acquisition was completed on August 1, 2016. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrinsity
Intrinsity, Inc. was a privately held Austin, Texas based fabless semiconductor company; it was founded in 1997 as EVSX on the remnants of Exponential Technology and changed its name to Intrinsity in 2000. It had around 100 employees and supplied tools and services for highly efficient semiconductor logic design, enabling high performance microprocessors with fewer transistors and low power consumption. The acquisition of the firm by Apple Inc. was confirmed on April 27, 2010. Products Intrinsity's main selling point was its Fast14 technology, a set of design tools implemented in custom EDA software, for using dynamic logic and novel signal encodings to permit greater processor speeds in a given process than naive static design can offer. Concepts used in Fast14 are described in a white paper: and include the use of multi-phase clocks so that synchronisation is not required at every cycle boundary (that is, a pipelined design does not require latches at every clock cycle); '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometre
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling), is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth ( short scale) or one thousand million (long scale) of a meter (0.000000001 m) and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as 1 × 10−9 m and as m. History The nanometre was formerly known as the "''millimicrometre''" – or, more commonly, the "''millimicron''" for short – since it is of a micrometer. It was often denoted by the symbol ''mμ'' or, more rarely, as ''μμ'' (however, ''μμ'' should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron). Etymology The name combines the SI prefix '' nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the parent unit name ''metre'' (from Greek , ', "unit of measurement"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, CPU design, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic operation, arithmetic and Bitwise operation, logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the #Fetch, fetching (from memory), #Decode, decoding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Glass
The history of glass-making dates back to at least 3,600 years ago in Mesopotamia. However, most writers claim that they may have been producing copies of glass objects from Egypt. Other archaeological evidence suggests that the first true glass was made in coastal north Syria, Mesopotamia or Egypt. The earliest known glass objects, of the mid 2,000 BCE, were beads, perhaps initially created as the accidental by-products of metal-working (slags) or during the production of faience, a pre-glass vitreous material made by a process similar to glazing. Glass products remained a luxury until the disasters that overtook the late Bronze Age civilizations seemingly brought glass-making to a halt. Development of glass technology in India may have begun in 1,730 BCE. From across the former Roman Empire, archaeologists have recovered glass objects that were used in domestic, industrial and funerary contexts. Anglo-Saxon glass has been found across England during archaeological excava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |