|
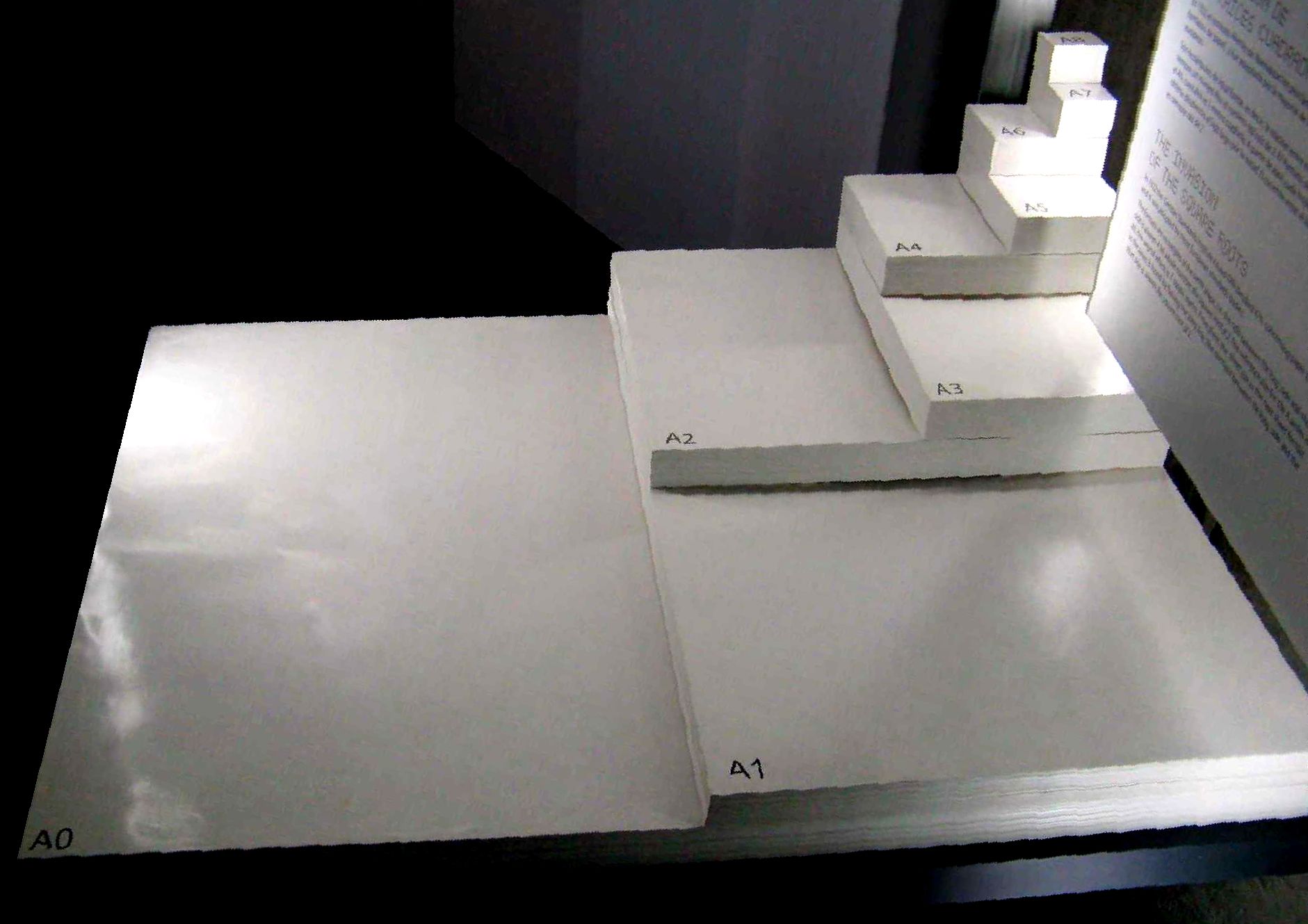
A4 Paper
ISO 216 is an International Organization for Standardization, international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, which includes the A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, square root of 2, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of \sqrt is found in a letter writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Paper Sizes
Comparison or comparing is the act of evaluating two or more things by determining the relevant, comparable characteristics of each thing, and then determining which characteristics of each are similar to the other, which are different, and to what degree. Where characteristics are different, the differences may then be evaluated to determine which thing is best suited for a particular purpose. The description of similarities and differences found between the two things is also called a comparison. Comparison can take many distinct forms, varying by field: To compare things, they must have characteristics that are similar enough in relevant ways to merit comparison. If two things are too different to compare in a useful way, an attempt to compare them is colloquially referred to in English as "comparing apples and oranges." Comparison is widely used in society, in science and the arts. General usage Comparison is a natural activity, which even animals engage in when decidin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Metre
The square metre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures) or square meter ( American spelling) is the unit of area in the International System of Units (SI) with symbol m2. It is the area of a square with sides one metre in length. Adding and subtracting SI prefixes creates multiples and submultiples; however, as the unit is exponentiated, the quantities grow exponentially by the corresponding power of 10. For example, 1 kilometre is 103 (one thousand) times the length of 1 metre, but 1 square kilometre is (103)2 (106, one million) times the area of 1 square metre, and 1 cubic kilometre is (103)3 (109, one billion) cubic metres. SI prefixes applied The square metre may be used with all SI prefixes used with the metre. Unicode characters Unicode has several characters used to represent metric area units, but these are for compatibility with East Asian character encodings and are meant to be used in new documents. * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a Physical unit, unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth of a kilogram. Originally defined in 1795 as "the absolute Mass versus weight, weight of a volume of pure water equal to Cube (algebra), the cube of the hundredth part of a metre [1 Cubic centimetre, cm3], and at Melting point of water, the temperature of Melting point, melting ice", the defining temperature (0 °C) was later changed to the temperature of maximum density of water (approximately 4 °C). Subsequent redefinitions agree with this original definition to within 30 Parts-per notation, parts per million (0.003%), with the maximum density of water remaining very close to 1 g/cm3, as shown by modern measurements. By the late 19th century, there was an effort to make the Base unit (measurement), base unit the kilogram and the gram a derived unit. In 1960, the new International System of Units defined a '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammage
Grammage and basis weight, in the pulp and paper industry, are the area density of a paper product, that is, its mass per unit of area. Two ways of expressing the area density of a paper product are commonly used: * Expressed in grams (g) per square metre (g/m2), regardless of its thickness ( caliper)International Standard ISO 536: Paper and board – Determination of grammage. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva. (known as ''grammage''). This is the measure used in most parts of the world. It is often notated as ''gsm'' on paper product labels and spec sheets. * Expressed in terms of the mass per number of sheets of a specific paper size (known as ''basis weight''). The convention used in the United States and a few other countries using US-standard paper sizes is pounds (lb) per ream of 500 (or in some cases 1000) sheets of a given (raw, still uncut) basis size. The traditional British practice is pounds per ream of 480, 500, 504, or 516 sheets of a give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 536
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Article 3 of the ISO Statutes. ISO was founded on 23 February 1947, and () it has published over 25,000 international standards covering almost all aspects of technology and manufacturing. It has over 800 technical committees (TCs) and subcommittees (SCs) to take care of standards development. The organization develops and publishes international standards in technical and nontechnical fields, including everything from manufactured products and technology to food safety, transport, IT, agriculture, and healthcare. More specialized topics like electrical and electronic engineering are instead handled by the International Electrotechnical Commission.Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. 3 June 2021.Internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photocopier
A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called '' xerography'', a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles (a powder) onto paper in the form of an image. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, pressure, or a combination of both. Copiers can also use other technologies, such as inkjet, but xerography is standard for office copying. Commercial xerographic office photocopying gradually replaced copies made by verifax, photostat, carbon paper, mimeograph machines, and other duplicating machines. Photocopying is widely used in the business, education, and government sectors. While there have been predictions that photocopiers will eventually become obsol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brochure
A brochure is an promotional document primarily used to introduce a company, organization, products, or services and inform prospective customers or members of the public of the benefits. Although, initially, a paper document that can be folded into a template, pamphlet, or Folded leaflet, leaflet, a brochure can also be a set of related unfolded papers put into a pocket folder or packet or can be in digital format. A brochure is a corporate marketing instrument to promote a product or service. It is a tool used to circulate information about the product or service. A brochure is like a magazine but with pictures of the product or the service which the brand is promoting. Depending on various aspects there are different types of brochures: Gate Fold Brochures, Trifold Brochures, and Z-Fold Brochures. Brochures are distributed in many ways: as newspaper inserts, handed out personally, by mail, or placed in brochure racks in high-traffic locations, especially in tourist precincts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectangle
In Euclidean geometry, Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a Rectilinear polygon, rectilinear convex polygon or a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram containing a right angle. A rectangle with four sides of equal length is a ''square''. The term "wikt:oblong, oblong" is used to refer to a non-square rectangle. A rectangle with Vertex (geometry), vertices ''ABCD'' would be denoted as . The word rectangle comes from the Latin ''rectangulus'', which is a combination of ''rectus'' (as an adjective, right, proper) and ''angulus'' (angle). A #Crossed rectangles, crossed rectangle is a crossed (self-intersecting) quadrilateral which consists of two opposite sides of a rectangle along with the two diagonals (therefore only two sides are parallel). It is a special case of an antiparallelogram, and its angles are not right angles an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and international security, security, to develop friendly Diplomacy, relations among State (polity), states, to promote international cooperation, and to serve as a centre for harmonizing the actions of states in achieving those goals. The United Nations headquarters is located in New York City, with several other offices located in United Nations Office at Geneva, Geneva, United Nations Office at Nairobi, Nairobi, United Nations Office at Vienna, Vienna, and The Hague. The UN comprises six principal organizations: the United Nations General Assembly, General Assembly, the United Nations Security Council, Security Council, the United Nations Economic and Social Council, Economic and Social Council, the International Court of Justice, the United Nations Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rounding Error
In computing, a roundoff error, also called rounding error, is the difference between the result produced by a given algorithm using exact arithmetic and the result produced by the same algorithm using finite-precision, rounded arithmetic. Rounding errors are due to inexactness in the representation of real numbers and the arithmetic operations done with them. This is a form of quantization error. When using approximation equations or algorithms, especially when using finitely many digits to represent real numbers (which in theory have infinitely many digits), one of the goals of numerical analysis is to estimate computation errors. Computation errors, also called numerical errors, include both truncation errors and roundoff errors. When a sequence of calculations with an input involving any roundoff error are made, errors may accumulate, sometimes dominating the calculation. In ill-conditioned problems, significant error may accumulate. In short, there are two major facets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsches Institut Für Normung
' (DIN; in English language, English, the German Institute for Standardisation) is a Germany, German non-profit organization and acting as national organization for standardization. DIN is the German International Organization for Standardization, ISO member body. DIN is headquartered in Berlin. There are around thirty thousand DIN Technical standard, Standards, covering nearly every field of technology. History Founded in 1917 as the ' (NADI, "Standardisation Committee of German Industry"), the NADI was renamed ' (DNA, "German Standardisation Committee") in 1926 to reflect that the organization now dealt with standardization issues in many fields; viz., not just for industrial products. In 1975 it was renamed again to ', or 'DIN' and is recognised by the German government as the official national-standards body, representing German interests at the international and European levels. The acronym, 'DIN' is often incorrectly expanded as ' ("German Industry Standard"). This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |