|
A-paper
In the mortgage industry of the United States, A-paper is a term to describe a mortgage loan (or a Prime loan) for which the asset and borrower meet the following criteria: * In the United States, the borrower has a credit score of 680 or higher * The borrower fully documents their income and assets * The borrower's debt to income ratio does not exceed 35% * The borrower retains 2 months of mortgage payments in reserves after closing * The borrower injects at least 20% equity Furthermore, there are some criteria that are guiding factors, such as the borrower having stability in the line of work and/or living in the same property for two or more years. See also * Alt-A paper * Subprime lending In finance, subprime lending (also referred to as near-prime, subpar, non-prime, and second-chance lending) is the provision of loans to people in the United States who may have difficulty maintaining the repayment schedule. Historically, subpr ... References Mortgage industry of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alt-A
An Alt-A mortgage, short for Alternative A-paper, is a type of U.S. Mortgage loan, mortgage that, for various reasons, is considered riskier than A-paper, or "prime", and less risky than "subprime lending, subprime," the riskiest category. For these reasons, as well as in some cases their size, Alt-A loans are not eligible for purchase by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac. Alt-A interest rates, which are determined by credit risk, therefore tend to be between those of prime and subprime home loans, although there is no single accepted definition of Alt-A. Typically Alt-A mortgages are characterized by borrowers with less than full documentation, average credit scores, higher Loan-to-value ratio, loan-to-values, and more Investment property, investment properties and secondary homes. A-minus is related to Alt-A, with some lenders categorizing them the same, but A-minus is traditionally defined as mortgage borrowers with a FICO score of below 680 while Alt-A is traditionally defined as loans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subprime Lending
In finance, subprime lending (also referred to as near-prime, subpar, non-prime, and second-chance lending) is the provision of loans to people in the United States who may have difficulty maintaining the repayment schedule. Historically, subprime borrowers were defined as having FICO scores below 600, although this threshold has varied over time. These loans are characterized by higher interest rates, poor quality collateral, and less favorable terms in order to compensate for higher credit risk. During the early to mid-2000s, many subprime loans were packaged into mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and ultimately defaulted, contributing to the 2008 financial crisis.Lemke, Lins and Picard, ''Mortgage-Backed Securities'', Chapter 3 (Thomson West, 2013 ed.). Defining subprime risk The term ''subprime'' refers to the credit quality of particular borrowers, who have weakened credit histories and a greater risk of loan default than prime borrowers. As people become economically ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortgage Industry Of The United States
The mortgage industry of the United States is a major financial sector. The federal government created several programs, or government sponsored entities, to foster mortgage lending, construction and encourage home ownership. These programs include the Government National Mortgage Association (known as Ginnie Mae), the Federal National Mortgage Association (known as Fannie Mae) and the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (known as Freddie Mac). The subprime mortgage crisis was one of the first indication of the 2008 financial crisis, characterized by a rise in subprime mortgage delinquencies and foreclosures, and the resulting decline of securities backing said mortgages. The earlier savings and loan crisis of the 1980s and 1990s and the national mortgage crisis of the 1930s also arose primarily from unsound mortgage lending. The mortgage crisis has led to a rise in foreclosures, leading to the 2010 United States foreclosure crisis. Mortgage lenders Mortgage lending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortgage Loan
A mortgage loan or simply mortgage (), in civil law (legal system), civil law jurisdictions known also as a hypothec loan, is a loan used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or by existing property owners to raise funds for any purpose while putting a lien on the property being mortgaged. The loan is "collateral (finance), secured" on the borrower's property through a process known as mortgage origination. This means that a Mortgage law, legal mechanism is put into place which allows the lender to take possession and sell the secured property ("foreclosure" or "repossession") to pay off the loan in the event the borrower defaults on the loan or otherwise fails to abide by its terms. The word ''mortgage'' is derived from a Law French term used in Legal professions in England and Wales, Britain in the Middle Ages meaning "death pledge" and refers to the pledge ending (dying) when either the obligation is fulfilled or the property is taken throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Loan
The prime rate or prime lending rate is an interest rate used by banks, typically representing the rate at which they lend to their most creditworthy customers. Some variable interest rates may be expressed as a percentage above or below prime rate. Use in different banking systems United States and Canada Historically, in North American banking, the prime rate represented actual interest rate charged to borrowers, although this is no longer universally true. The prime rate varies little among banks and adjustments are generally made by banks at the same time, although this does not happen frequently. , the prime rate was 7.50% in the United States and 5.20% in Canada. In the United States, the prime rate runs approximately 300 basis points (or 3 percentage points) above the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans made to fulfill reserve funding requirements. The federal funds rate plus a much smaller increment is frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Credit Score (United States)
A credit score is a number that provides a comparative estimate of an individual's creditworthiness based on an analysis of their credit report. It is an inexpensive and main alternative to other forms of consumer loan underwriting. Lenders, such as banks and credit card companies, use credit scores to evaluate the risk of lending money to consumers. Lenders contend that widespread use of credit scores has made credit more widely available and less expensive for many consumers. Under the Dodd-Frank Act passed in 2010, a consumer is entitled to receive a free report of the specific credit score used if they are denied a loan, credit card or insurance due to their credit score. History Before credit scores, credit was evaluated using credit reports from credit bureaus. During the late 1950s, banks started using computerized credit scoring to redefine creditworthiness as abstract statistical risk. The Equal Credit Opportunity Act banned denying credit on gender or marital s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt-to-income Ratio
In the consumer mortgage industry, debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is the percentage of a consumer's monthly gross income that goes toward paying debts. (Speaking precisely, DTIs often cover more than just debts; they can include principal, taxes, fees, and insurance premiums as well. Nevertheless, the term is a set phrase that serves as a convenient, well-understood shorthand.) There are two main kinds of DTI, as discussed below. Two main kinds of DTI The two main kinds of DTI are expressed as a pair using the notation x/y (for example, 28/36). # The first DTI, known as the ''front-end ratio'', indicates the percentage of income that goes toward housing costs, which for renters is the rent amount and for homeowners is PITI (mortgage principal and interest, mortgage insurance premium hen applicable hazard insurance premium, property taxes, and homeowners' association dues hen applicable. # The second DTI, known as the ''back-end ratio'', indicates the percentage of income that g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
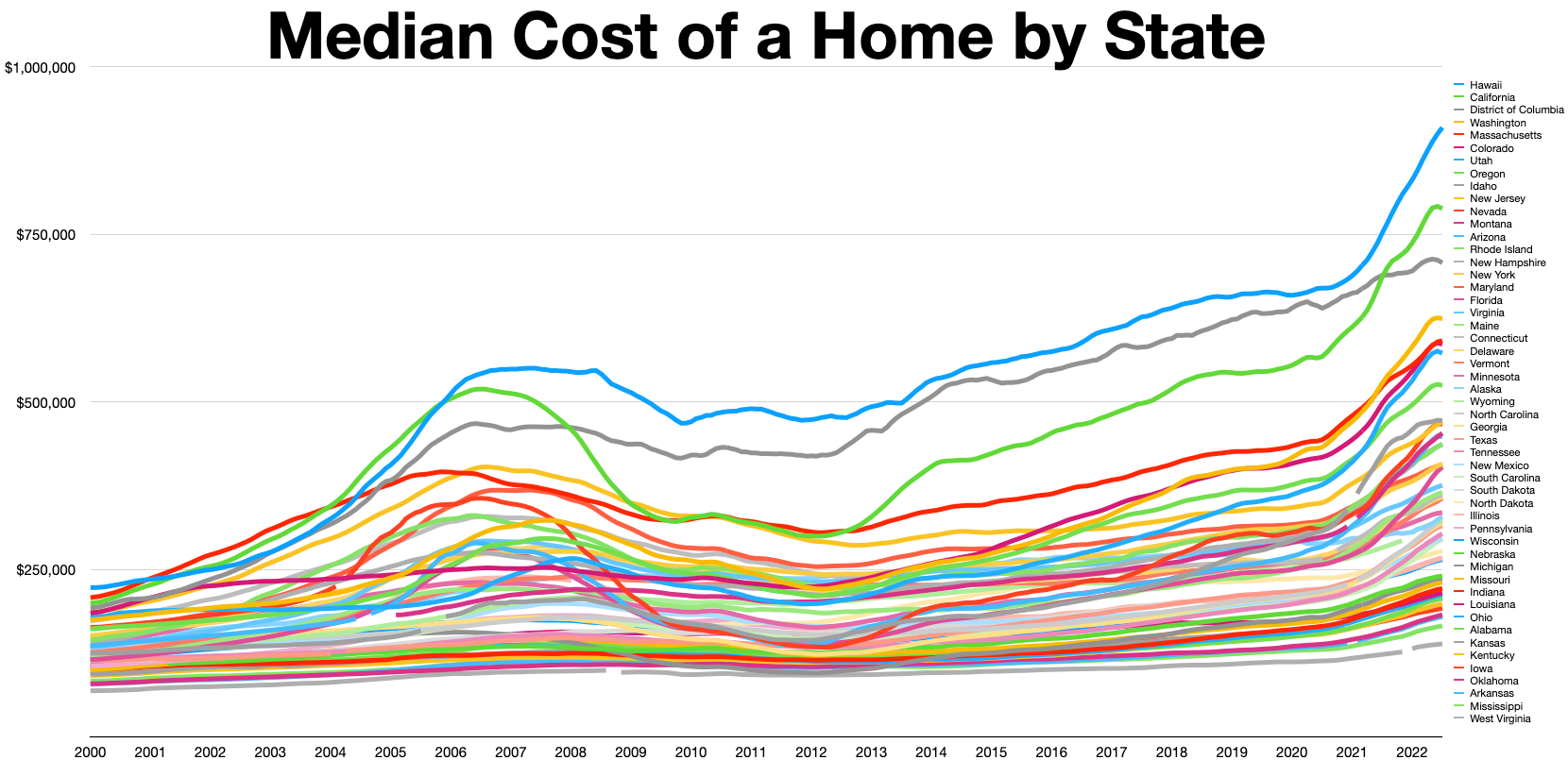
United States Housing Bubble
The 2000s United States housing bubble or house price boom or 2000s housing cycle was a sharp run up and subsequent collapse of house asset prices affecting over half of the U.S. states. In many regions a Real-estate bubble, real estate bubble, it was the impetus for the subprime mortgage crisis. Housing prices peaked in early 2006, started to decline in 2006 and 2007, and reached new lows in 2011. On December 30, 2008, the Case–Shiller index, Case–Shiller home price index reported the largest price drop in its history. The credit crisis resulting from the bursting of the housing bubble is an important cause of the Great Recession in the United States. Increased foreclosure rates in 2006–2007 among U.S. homeowners led to a Subprime mortgage crisis, crisis in August 2008 for the Subprime mortgage, subprime, Alt-A, collateralized debt obligation (CDO), mortgage loan, mortgage, Fixed income, credit, hedge fund, and foreign bank markets. In October 2007, Henry Paulson, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |