|
9-Borabicyclo(3.3.1)nonane
9-Borabicyclo .3.1onane or 9-BBN is an organoborane compound. This colourless solid is used in organic chemistry as a hydroboration reagent. The compound exists as a hydride-bridged dimer, which easily cleaves in the presence of reducible substrates. 9-BBN is also known by its nickname 'banana borane'. This is because rather than drawing out the full structure, chemists often simply draw a banana shape with the bridging boron. Preparation 9-BBN is prepared by the reaction of 1,5-cyclooctadiene and borane usually in ethereal solvents, for example: The compound is commercially available as a solution in tetrahydrofuran and as a solid. 9-BBN is especially useful in Suzuki reactions. Its highly regioselective addition on alkenes allows the preparation of terminal alcohols by subsequent oxidative cleavage with H2O2 in aqueous KOH. The steric demand of 9-BBN greatly suppresses the formation of the 2-substituted isomer compared to the use of borane. See also * Organoboron chemistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoborane
Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry studies organoboron compounds, also called organoboranes. These chemical compounds combine boron and carbon; typically, they are organic derivatives of borane (BH3), as in the trialkyl boranes. Organoboranes and -borates enable many chemical transformations in organic chemistry — most importantly, hydroboration and carboboration. Most reactions transfer a nucleophilic boron substituent to an electrophilic center either inter- or intramolecularly. In particular, α,β-unsaturated borates and borates with an α leaving group are highly susceptible to intramolecular 1,2-migration of a group from boron to the electrophilic α position. Oxidation or protonolysis of the resulting organoboranes generates many organic products, including alcohols, carbonyl compounds, alkenes, and halides. Properties of the B-C bond The C-B bond has low polarity (electronegativity 2.55 for carbon and 2.04 for boron). Alkyl boron compounds are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,5-cyclooctadiene
1,5-Cyclooctadiene (also known as cycloocta-1,5-diene) is a cyclic compound, cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , specifically . There are three configurational isomers with this structure, that differ by the arrangement of the four C–C single bonds adjacent to the double bonds. Each pair of single bonds can be on the same side () or on opposite sides () of the double bond's plane; the three possibilities are denoted , , and ; or (), (), and (). (Because of overall symmetry, is the same configuration as .) Generally abbreviated COD, the isomer of this diene is a useful precursor to other organic compounds and serves as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. It is a colorless liquid with a strong odor. 1,5-Cyclooctadiene can be prepared by dimerization of butadiene in the presence of a nickel catalyst, a coproduct being 4-Vinylcyclohexene, vinylcyclohexene. Approximately 10,000 tons were produced in 2005. Organic reactions COD reacts with borane to give 9-Borabicy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoboron Chemistry
Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry studies organoboron compounds, also called organoboranes. These chemical compounds combine boron and carbon; typically, they are organic derivatives of borane (BH3), as in the trialkyl boranes. Organoboranes and -borates enable many chemical transformations in organic chemistry — most importantly, hydroboration and carboboration. Most reactions transfer a nucleophilic boron substituent to an electrophilic center either inter- or intramolecularly. In particular, α,β-unsaturated borates and borates with an α leaving group are highly susceptible to intramolecular 1,2-migration of a group from boron to the electrophilic α position. Oxidation or protonolysis of the resulting organoboranes generates many organic products, including alcohols, carbonyl compounds, alkenes, and halides. Properties of the B-C bond The C-B bond has low polarity (electronegativity 2.55 for carbon and 2.04 for boron). Alkyl boron compounds are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a substance ''consumed'' in the course of a chemical reaction. ''Solvents'', though involved in the reaction mechanism, are usually not called reactants. Similarly, ''catalysts'' are not consumed by the reaction, so they are not reactants. In biochemistry, especially in connection with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the reactants are commonly called substrates. Definitions Organic chemistry In organic chemistry, the term "reagent" denotes a chemical ingredient (a compound or mixture, typically of inorganic or small organic molecules) introduced to cause the desired transformation of an organic substance. Examples include the Collins reagent, Fenton's reagent, and Grignard reagents. Analytical chemistry In analytical chemistry, a reag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borane
Borane is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . Because it tends to dimerize or form adducts, borane is very rarely observed. It normally dimerizes to diborane in the absence of other chemicals. It can be observed directly as a continuously produced, transitory, product in a flow system or from the reaction of laser ablated atomic boron with hydrogen. Structure and properties BH3 is a trigonal planar molecule with D3h symmetry. The experimentally determined B–H bond length is 119 pm. In the absence of other bases, it dimerizes to form diborane. Thus, it is an intermediate in the preparation of diborane according to the reaction: :BX3 +BH4− → HBX3− + (BH3) (X=F, Cl, Br, I) :2 BH3 → B2H6 The standard enthalpy of dimerization of BH3 is estimated to be −170 kJ mol−1. The boron atom in BH3 has 6 valence electrons. Consequently, it is a strong Lewis acid and reacts with any Lewis base ('L' in equation below) to form an adduct: :BH3 + L � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
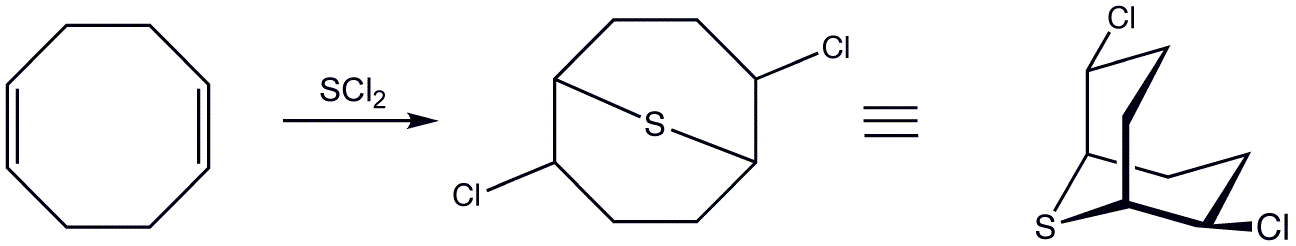
Synthesis Of 9-BBN Dimer
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to: Science Chemistry and biochemistry *Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors **Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organic compounds ***Total synthesis, the complete organic synthesis of complex organic compounds, usually without the aid of biological processes ***Convergent synthesis or linear synthesis, a strategy to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical syntheses **Dehydration synthesis, a chemical synthesis resulting in the loss of a water molecule *Biosynthesis, the creation of an organic compound in a living organism, usually aided by enzymes **Photosynthesis, a biochemical reaction using a carbon molecule to produce an organic molecule, using sunlight as a catalyst **Chemosynthesis, the synthesis of biological compounds into organic waste, using methane or an oxidized molecule as a catalyst **Amino acid synthesis, the synthesis of an amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, butanone. Production About 200,000 tonnes of tetrahydrofuran are produced annually. The most widely used industrial process involves the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1,4-Butanediol, 1,4-butanediol. Ashland Inc., Ashland/ISP is one of the biggest producers of this chemical route. The method is similar to the production of diethyl ether from ethanol. The butanediol is derived from Condensation reaction, condensation of acetylene with formaldehyde followed by hydrogenation. DuPont developed a process for producing THF by oxidizing Butane#Isomers, ''n''-butane to crude maleic anhydride, follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzuki Reaction
The Suzuki reaction or Suzuki coupling is an organic reaction that uses a palladium complex catalyst to cross-couple a boronic acid to an organohalide. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of noble metal catalysis in organic synthesis. This reaction is sometimes telescoped with the related Miyaura borylation; the combination is the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. It is widely used to synthesize poly olefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon–carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base. The organoboron species is usually synthesized by hydroboration or carboboration, allowing for rapid generation of molecular complexity. Several reviews have been publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regioselective
In organic chemistry, regioselectivity is the preference of chemical bonding or breaking in one direction over all other possible directions. It can often apply to which of many possible positions a reagent will affect, such as which proton a strong base will abstract from an organic molecule, or where on a substituted benzene ring a further substituent will be added. A specific example is a halohydrin formation reaction with 2-propenylbenzene: : Because of the preference for the formation of one product over another, the reaction is selective. This reaction is regioselective because it selectively generates one constitutional isomer rather than the other. Various examples of regioselectivity have been formulated as rules for certain classes of compounds under certain conditions, many of which are named. Among the first introduced to chemistry students are Markovnikov's rule for the addition of protic acids to alkenes, and the Fürst-Plattner rule for the addition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkenes
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Preferred IUPAC name, recommends using the name "alkene" only for Open-chain compound, acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for Cyclic compound, cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ''n'' being a >1 natural number (which is two hydrogens less than the corresponding alkane). When ''n'' is four or more, isomers are possible, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |