|
881 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 881 ( DCCCLXXXI) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Europe * February 12 – King Charles the Fat, the third son of the late Louis the German, is crowned as Holy Roman Emperor by Pope John VIII at Rome. * August 3 – Battle of Saucourt-en-Vimeu: The West Frankish kings Louis III, and his brother Carloman II, rout Viking raiders (near Abbeville). Britain * Battle of the Conwy: King Anarawd of Gwynedd (Wales) initiates a revenge attack on the Mercian armies, and defeats them on the River Conwy. * Anarawd, and his brothers Cadell and Merfyn, begin extensive military campaigns to quell resistance in Powys and Seisyllwg (approximate date). Arabian Empire * Zanj Rebellion: Abbasid general Al-Muwaffaq lays siege to the Zanj capital of Mukhtara, using his base on the opposite side of the River Tigris. Asia * Bakong, the first temple mountain of sandstone, is constructed by rulers of the Khmer Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles The Fat
Charles the Fat (839 – 13 January 888) was the emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 881 to 887. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, Charles was the youngest son of Louis the German and Hemma, and a great-grandson of Charlemagne. He was the last Carolingian emperor of legitimate birth and the last to rule a united kingdom of the Franks. Over his lifetime, Charles became ruler of the various kingdoms of Charlemagne's former empire. Granted lordship over Alamannia in 876, following the division of East Francia, he succeeded to the Italian throne upon the abdication of his older brother Carloman of Bavaria who had been incapacitated by a stroke. Crowned emperor in 881 by Pope John VIII, his succession to the territories of his brother Louis the Younger ( Saxony and Bavaria) the following year reunited the kingdom of East Francia. Upon the death of his cousin Carloman II in 884, he inherited all of West Francia, thus reuniting the entire Carolingian Empire. Usually con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
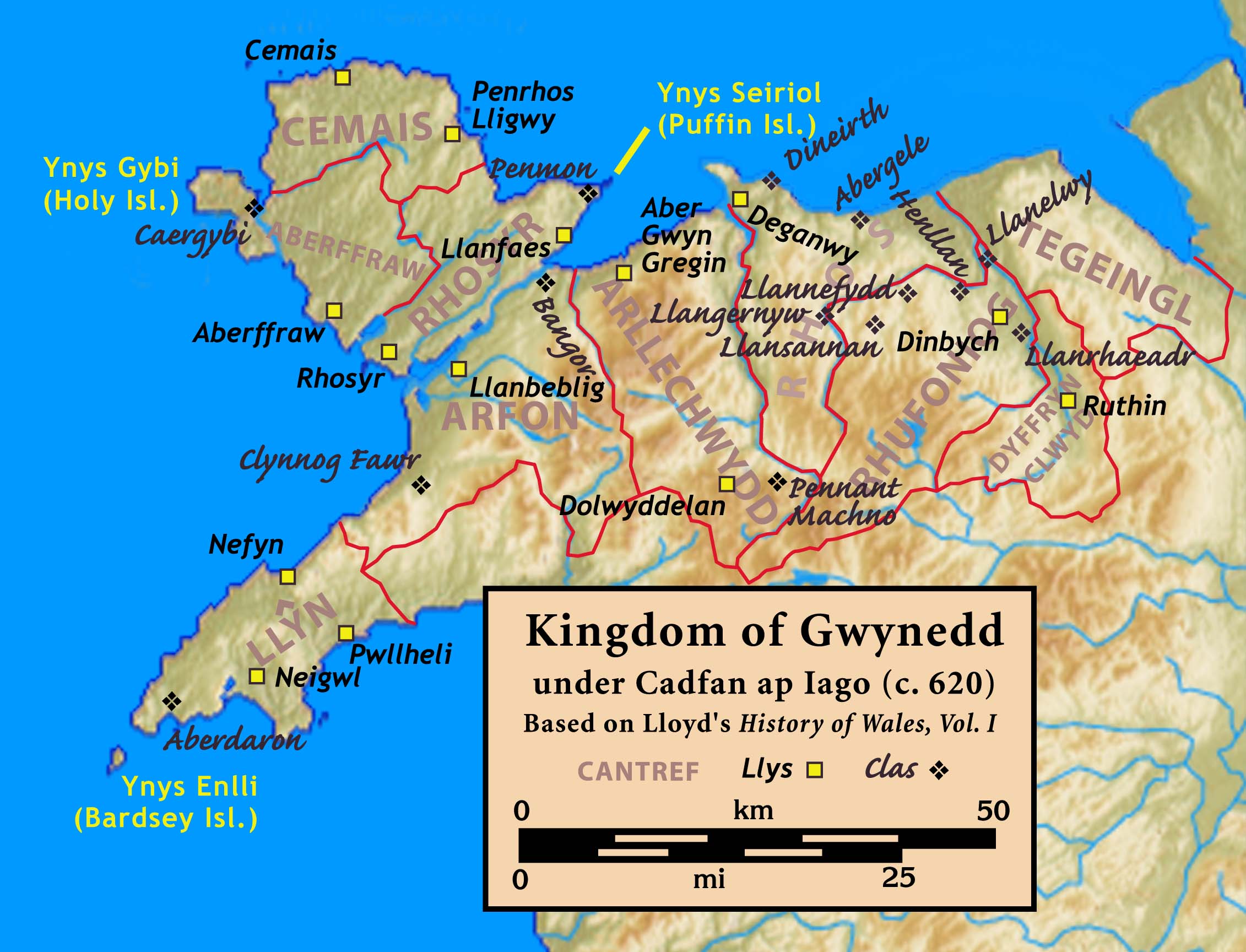
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire Succession of states, successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the list of rulers of Gwynedd, rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain, Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llywelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakong
Bakong ( ) is the first Khmer temple mountain of sandstone constructed by rulers of the Khmer Empire at Angkor near modern Siem Reap in Cambodia. In the final decades of the 9th century AD, it served as the official state temple of King Indravarman I in the ancient city of Hariharalaya, located in an area that today is called Roluos. The structure of Bakong took shape of stepped pyramid, popularly identified as temple mountain of early Khmer temple architecture. The striking similarity of the Bakong and Borobudur temple in Java, going into architectural details such as the gateways and stairs to the upper terraces, suggests strongly that Borobudur was served as the prototype of Bakong. Contact is inferred to have occurred between the Khmer kingdom and the Sailendra dynasty in Java, who would have transmitted to Cambodia not only ideas, but also technical and architectural details of Borobudur, including arched gateways in corbelling method. History In 802 AD, the first ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabian Deserts, before merging with the Euphrates and reaching to the Persian Gulf. The Tigris passes through historical cities like Mosul, Tikrit, Samarra, and Baghdad. It is also home to archaeological sites and ancient religious communities, including the Mandaeans, who use it for Masbuta, baptism. In ancient times, the Tigris nurtured the Assyria, Assyrian Empire, with remnants like the relief of Tiglath-Pileser I, King Tiglath-Pileser. Today, the Tigris faces modern threats from geopolitical instability, dam projects, poor water management, and climate change, leading to concerns about its sustainability. Efforts to protect and preserve the river's legacy are ongoing, with local archaeologists and activists working to safeguard its future ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanj
Zanj (, adj. , ''Zanjī''; from ) is a term used by medieval Muslim geographers to refer to both a certain portion of Southeast Africa (primarily the Swahili Coast) and to its Bantu inhabitants. It has also been used to refer to Africans collectively by Arab sources. This word is also the origin of the place-names Zanzibar ("coast of the Zanji") and the Sea of Zanj. The latinization Zingium serves as an archaic name for the coastal area in modern Kenya and Tanzania in southern East Africa. The architecture of these commercial urban settlements is now a subject of study for urban planning. For centuries the coastal settlements were a source of ivory, gold, and slaves, from sections of the conquered hinterland, to the Indian Ocean world. Etymology ''Zanj'' or ''Zang'' in Persian means the "country of the blacks". Other transliterations include ''Zenj'', ''Zinj'', and ''Zang''. Anthony Christie argued that the word ''zanj'' or ''zang'' may not be Arabic in origin: a Chines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block provision of supplies and reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (also known as sapping), or the use of deception or treachery to bypass defenses. Failing a military outcome, sieges can often be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Muwaffaq
Abu Ahmad Ṭalḥa ibn Al-Mutawakkil, Jaʿfar ibn al-Mu'tasim, Muḥammad ibn Harun al-Rashid, Hārūn al-Muwaffaq bi'Llah (; 29 November 843 – 2 June 891), better known by his as Al-Muwaffaq Billah (), was an Abbasid dynasty, Abbasid prince and military leader, who acted as the ''de facto'' regent of the Abbasid Caliphate for most of the reign of his brother, Caliph al-Mu'tamid. His stabilization of the internal political scene after the decade-long "Anarchy at Samarra", his successful defence of Iraq against the Saffarids and the suppression of the Zanj Rebellion restored a measure of the Caliphate's former power and began a period of recovery, which culminated in the reign of al-Muwaffaq's own son, the Caliph al-Mu'tadid. Early life Talha, commonly known by the Kunya (Arabic), teknonym Abu Ahmad, was born on 29 November 843, as the son of the Caliph al-Mutawakkil, Ja'far al-Mutawakkil () and a Byzantine Greek, Greek slave concubine, Ashar, known as Umm Ishaq. In 861, he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanj Rebellion
The Zanj Rebellion ( ) was a major revolt against the Abbasid Caliphate, which took place from 869 until 883. Begun near the city of Basra in present-day southern Iraq and led by one Ali ibn Muhammad, the insurrection involved both enslaved and freed Africans (collectively termed "Zanj" in this case) exported in the Indian Ocean slave trade and transported to slavery in the Abbasid Caliphate in the Middle East, principally to drain the region's salt marshes. It grew to involve slaves and freemen, including both Eastern Africans and Arabs, from several regions of the Caliphate, and claimed tens of thousands of lives before it was fully defeated. Several List of Muslim historians, Muslim historians, such as al-Tabari and al-Masudi, al-Mas'udi, consider the Zanj revolt to be one of the "most vicious and brutal uprisings" of the many disturbances that plagued the Abbasid central government. Modern scholars have characterized the conflict as being "one of the bloodiest and most destru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seisyllwg
Seisyllwg () was a petty kingdom of medieval Wales.Davies, p. 85 It is unclear when it emerged as a distinct unit, but according to later sources it consisted of the former Kingdom of Ceredigion plus the region known as Ystrad Tywi. Thus it covered the modern county of Ceredigion, part of Carmarthenshire, and the Gower Peninsula. It is evidently named after Seisyll, king of Ceredigion in the 7th or early 8th century, but it is unknown if he was directly responsible for its establishment. In the 10th century Seisyllwg became the centre of power for Hywel Dda, who came to rule most of Wales. In 920 Hywel merged Seisyllwg with the Kingdom of Dyfed to form the new kingdom of Deheubarth. Origins It is unclear when Seisyllwg emerged as a distinct unit. It is assumed to have been named for Seisyll ap Clydog, King of Ceredigion in the 7th or early 8th century, and as such he is traditionally regarded as its founder.Lloyd, p. 257 and note. Seisyll appears in the Harleian genealogies fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Powys
The Kingdom of Powys (; ) was a Welsh successor state, petty kingdom and principality that emerged during the Middle Ages following the end of Roman rule in Britain. It very roughly covered the northern two-thirds of the modern county of Powys and part of today's English West Midlands (see map). More precisely, and based on the Romano-British tribal lands of the Ordovices in the west and the Cornovii in the east, its boundaries originally extended from the Cambrian Mountains in the west to include the modern West Midlands region of England in the east. The fertile river valleys of the Severn and Tern are found there, and this region is referred to in later Welsh literature as "the Paradise of Powys" (an epithet retained in Welsh for the modern UK county). Name The name Powys is thought to derive from Latin ''pagus'' 'the countryside' and ''pagenses'' 'dwellers in the countryside', also the origins of French "pays" and English "peasant". During the Roman Empire, this regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merfyn Ap Rhodri
Merfyn ap Rhodri (died ) was a late 9th century prince of Gwynedd of the royal House of Aberffraw. He is sometimes credited with ruling the Kingdom of Powys after the death of his father Rhodri Mawr (Rhodri the Great) in 878. He was a paternal uncle of Hywel Dda and a grandson of Merfyn Frych (d. 844) and Nest ferch Cadell ap Brochwel.Pierce, T. J., (1959)RHODRI MAWR ('the Great') (died 877), king of Gwynedd, Powys, and Deheubarth ''Dictionary of Welsh Biography''. Retrieved 28 Apr 2025, from https://biography.wales/article/s-RHOD-MAW-0877 Merfyn was a younger son of Rhodri Mawr, son of Merfyn Frych and Angharad ferch Meurig, daughter of Meurig ap Dyfnwallon of the Kingdom of Ceredigion, who was the King of Seisyllwg in south western Wales. His mother Angharad was a descendant of Cunedda, founder of the Kingdom of Gwynedd, through his son, Ceredig ap Cunedda of Ceredigion through her paternal line. Mervyn's father Rhodri held power over much of Wales. He had at least two ful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadell Ap Rhodri
Cadell ap Rhodri (854–909) was King of Seisyllwg, a minor kingdom in southwestern Wales, from about 872 until his death. The son of Rhodri Mawr, King of Gwynedd, Cadell was in turn the father of Hywel Dda, who eventually came to rule most of Wales and caused Welsh laws to be codified. Cadell is considered the founder of the Welsh royal House of Dinefwr. Life Cadell was the second son of King Rhodri the Great of Gwynedd Gwynedd () is a county in the north-west of Wales. It borders Anglesey across the Menai Strait to the north, Conwy, Denbighshire, and Powys to the east, Ceredigion over the Dyfi estuary to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. The ci ... and Angharad ferch Meurig, a princess from Seisyllwg. He was named after his great great grandfather Cadell ap Brochwel of Powys, whose daughter Nest was the mother of his paternal grandfather Merfyn Frych. His older brother was Anarawd (Rhodri's successor as king in Gwynedd), and Merfyn, assumed to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |