|
86th Congress
The 86th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1959, to January 3, 1961, during the last two years of the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1950 United States census until Alaska and Hawaii were admitted as states in 1959. Then, the membership of the House temporarily increased to 437 (seating one member from each of those newly admitted states and leaving the apportionment of the other 435 seats unchanged); it would remain at 437 until reapportionment resulting from the 1960 census. The Democrats maintained full control of Congress, with greatly increased majorities in both chambers. Major events * January 7, 1959: The United States recognizes the new Cuban government of Fidel Castro * February 12, 1959: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Capitol
The United States Capitol, often called the Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the Seat of government, seat of the United States Congress, the United States Congress, legislative branch of the Federal government of the United States, federal government. It is located on Capitol Hill at the eastern end of the National Mall in Washington, D.C. Although no longer at the geographic center of the Geography of Washington, D.C., national capital, the U.S. Capitol forms the origin point for the street-numbering system of the district as well as Quadrants of Washington, D.C., its four quadrants. Like the principal buildings of the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive and Federal judiciary of the United States, judicial branches, the Capitol is built in a neoclassical architecture, neoclassical style and has a white exterior. Central sections of the present building were completed in 1800. These were partly destroyed in the Burning of Washington, 1814 Burni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Sandburg
Carl August Sandburg (January 6, 1878 – July 22, 1967) was an American poet, biographer, journalist, and editor. He won three Pulitzer Prizes: two for his poetry and one for his biography of Abraham Lincoln. During his lifetime, Sandburg was widely regarded as "a major figure in contemporary literature", especially for volumes of his collected verse, including '' Chicago Poems'' (1916), ''Cornhuskers'' (1918), and ''Smoke and Steel'' (1920). He enjoyed "unrivaled appeal as a poet in his day, perhaps because the breadth of his experiences connected him with so many strands of American life". When he died in 1967, President Lyndon B. Johnson observed that "Carl Sandburg was more than the voice of America, more than the poet of its strength and genius. He was America." Life Carl Sandburg was born in a three-room cottage at 313 East Third Street in Galesburg, Illinois, to Clara Mathilda (née Anderson) and August Sandberg, Sandburg's father's last name was originally "Danielso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple-Use Sustained-Yield Act Of 1960
The Multiple-Use Sustained-Yield Act of 1960 (or MUSYA) (Public Law 86-517) is a federal law passed by the United States Congress on June 12, 1960. This law authorizes and directs the Secretary of Agriculture to develop and administer the renewable resources of timber, range, water, recreation and wildlife on the national forests for multiple use and sustained yield of the products and services. This is the first law to have the five major uses of national forests contained in one law equally, with no use greater than any other. By the 1950s, the national forests no longer held enough resources to meet the growing needs of an increasing population and expanding economy. The U.S. Forest Service had operated within broad authorities since Gifford Pinchot Gifford Pinchot (August 11, 1865October 4, 1946) was an American forester and politician. He served as the fourth chief of the U.S. Division of Forestry, as the first head of the United States Forest Service, and as the 28th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Act Of 1960
The Civil Rights Act of 1960 () is a United States federal law that established federal inspection of local voter registration polls and introduced penalties for anyone who obstructed someone's attempt to register to vote. It dealt primarily with discriminatory laws and practices in the segregated South, by which African-Americans and Tejanos had been effectively disenfranchised since the late 19th and start of the 20th century. This was the fifth Civil Rights Act to be enacted in United States history. Over an 85-year period, it was preceded only by the Civil Rights Act of 1957, whose shortcomings largely influenced its creation. This law served to more effectively enforce what was set forth in the 1957 act through eliminating certain loopholes in it, and to establish additional provisions. Aside from addressing voting rights, the Civil Rights Act of 1960 also imposed criminal penalties for obstruction of court orders to limit resistance to the Supreme Court's school desegrega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narcotics Manufacturing Act Of 1960
Narcotics Manufacturing Act of 1960 is a federal declaration affirming the United States commitment to international convention protocols constricting the non-medical and non-scientific manufacturing of narcotic drugs. The Act of Congress recognizes the Convention for Limiting the Manufacture and Regulating the Distribution of Narcotic Drugs and 1948 Protocol establishing deterrents for the chemical synthesis and dispensation of illicit drugs. The public law exemplifies a scientific class of narcotic drugs produced from the natural product of the coca leaf and opium poppy. Provisions of the Act The codified law was drafted as twenty-two sections providing administrative jurisdiction for basic scientific class of opiates and opioids. ''21 U.S.C. §§ 501-502'' :* Short Title :* Necessity for Legislation :* Definitions ''26 U.S.C. §§ 4702 & 4731'' :* Amendments to Internal Revenue Code of 1954 ''21 U.S.C. §§ 503-512'' :* Notifications, Findings, and Decisions under The 1948 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landrum–Griffin Act
The Labor Management Reporting and Disclosure Act of 1959 (also "LMRDA" or the Landrum–Griffin Act), is a US labor law that regulates labor unions' internal affairs and their officials' relationships with employers. Background After enactment of the Taft–Hartley Act in 1947, the number of union victories in National Labor Relations Board (NLRB)-conducted elections declined. During the 12-year administration of the Wagner Act, which was enacted in 1935, unions won victories in over 80 percent of elections. But in that first year after passage of the Taft–Hartley Act in 1947, unions won only around 70 percent of the representation elections conducted by the agency. During the mid-to-late 1950s, the labor movement was under intense Congressional scrutiny for corruption, racketeering, and other misconduct. Enacted in 1959 after revelations of corruption and undemocratic practices in the International Brotherhood of Teamsters, International Longshoremen's Association, United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
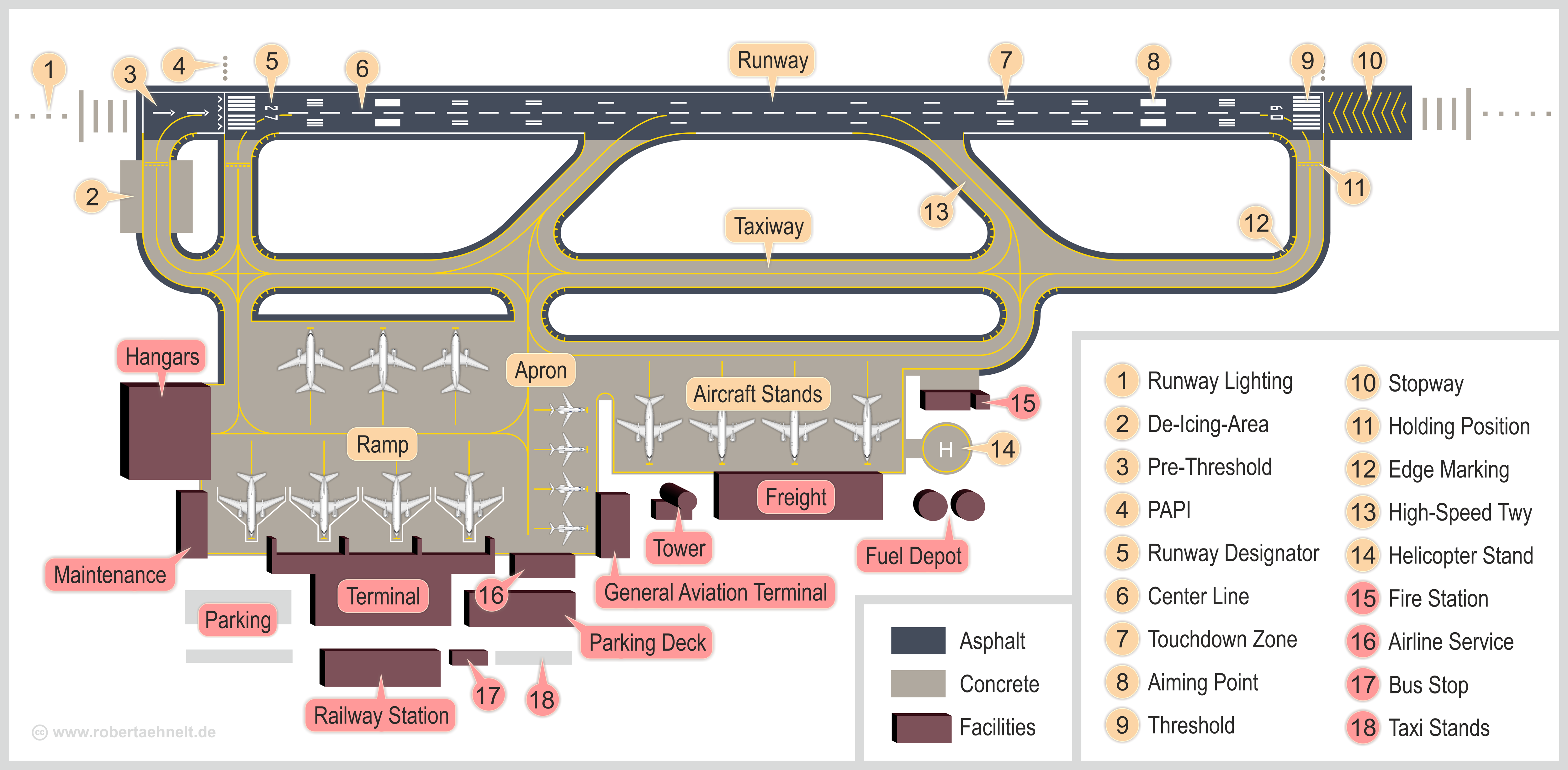
Airport Construction Act
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. They usually consist of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Airport operations are extremely complex, with a complicated system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1960 United States Presidential Election
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 1960. The Democratic ticket of Senator John F. Kennedy and his running mate, Senate Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson, narrowly defeated the Republican ticket of incumbent Vice President Richard Nixon and his running mate, U.N. Ambassador Henry Cabot Lodge Jr. This was the first election in which 50 states participated, marking the first participation of Alaska and Hawaii, and the last in which the District of Columbia did not. It was also the first election in which an incumbent president—in this case, Dwight D. Eisenhower—was ineligible to run for a third term because of the term limits established by the 22nd Amendment. Nixon faced little opposition in the Republican race to succeed popular incumbent Eisenhower. Kennedy, the junior senator from Massachusetts, established himself as the Democratic frontrunner with his strong performance in the 1960 Democratic primaries, including key victories in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spans . Thailand Template:Borders of Thailand, is bordered to the northwest by Myanmar, to the northeast and east by Laos, to the southeast by Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the southwest by the Andaman Sea; it also shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the southeast and Indonesia and India to the southwest. Bangkok is the state capital and List of municipalities in Thailand#Largest cities by urban population, largest city. Tai peoples, Thai peoples migrated from southwestern China to mainland Southeast Asia from the 6th to 11th centuries. Greater India, Indianised kingdoms such as the Mon kingdoms, Mon, Khmer Empire, and Monarchies of Malaysia, Malay states ruled the region, competing with Thai states s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Bhumibol Adulyadej
Bhumibol Adulyadej (5 December 192713 October 2016), titled Rama IX, was King of Thailand from 1946 until his death in 2016. His reign of 70 years and 126 days is the longest of any Thai monarch, the longest on record of any independent Asian sovereign, and the third-longest of any sovereign state. Born in the United States, Bhumibol spent his early life in Switzerland, in the aftermath of the 1932 Siamese revolution, which toppled Thailand's centuries-old absolute monarchy, ruled at the time by his uncle, King Prajadhipok (Rama VII). He ascended to the throne in June 1946, succeeding his brother, King Ananda Mahidol (Rama VIII), who had died under mysterious circumstances. In the course of his rule, Bhumibol presided over Thailand's transformation into a major US ally and a regional economic power. Between 1985 and 1994, Thailand was the world's fastest-growing economy, according to the World Bank, and in the 1990s was predicted by many international journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1960 U-2 Incident
On 1 May 1960, a United States Lockheed U-2, U-2 reconnaissance aircraft, spy plane was shot down by the Soviet Air Defence Forces while conducting photographic aerial reconnaissance inside Soviet Union, Soviet territory. Flown by American pilot Francis Gary Powers, the aircraft had taken off from PAF Base Peshawar, Peshawar, Pakistan, and crashed near Sverdlovsk, Russia, Sverdlovsk (present-day Yekaterinburg), after being hit by a surface-to-air missile. Powers parachuted to the ground and was captured. Initially, American authorities claimed the incident involved the loss of a civilian weather research aircraft operated by NASA, but were forced to admit the mission's true purpose a few days later after the Soviet government produced the captured pilot and parts of the U-2's surveillance equipment, including photographs of Soviet military bases. The incident occurred during the tenures of American president Dwight D. Eisenhower and Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev, around two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greensboro Sit-ins
The Greensboro sit-ins were a series of nonviolent protests in February to July 1960, primarily in the Woolworth store — now the International Civil Rights Center and Museum — in Greensboro, North Carolina, which led to the F. W. Woolworth Company department store chain removing its policy of racial segregation in the Southern United States. While not the first sit-in of the civil rights movement, the Greensboro sit-ins were an instrumental action, and also the best-known sit-ins of the civil rights movement. They are considered a catalyst to the subsequent sit-in movement, in which 70,000 people participated. This sit-in was a contributing factor in the formation of the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC). Previous sit-ins In August 1939, African-American attorney Samuel Wilbert Tucker organized the Alexandria Library sit-in in Virginia (now the Alexandria Black History Museum). In 1942, the Congress of Racial Equality sponsored sit-ins in Chicago, as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |