|
82-BM-41
The 82-PM-41 (), M-41 or the 82-mm mortar Model 1941 () was a Soviet 82-millimeter calibre mortar developed during the Second World War as an infantry battalion mortar, and which began production in 1941. Design It differed from the Model 1937 by the presence of a removable wheel base, by the arched construction base plate (as in 107-mm and 120-mm mortars), and also a different two-legged construction. Wheels were slipped over the semi-axis of the bipod feet and removed during firing. Design improvements were made to reduce weight and production cost, and improve manoeuvrability. The ballistic data of the Model 1941 mortar were analogous to the Model 1937. The 82-mm mortar Model 1941 was more convenient to transport than the Model 1937, but was less steady during firing and had a worse centre of gravity. To correct shortcomings of the 82-mm mortar Model 1941 it was modernised during initial production; the construction of the bipod, wheel and fastening of the sight was chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of up to one thousand soldiers. A battalion is commanded by a lieutenant colonel and subdivided into several companies, each typically commanded by a major or a captain. The typical battalion is built from three operational companies, one weapons company and one headquarters company. In some countries, battalions are exclusively infantry, while in others battalions are unit-level organizations. The word ''battalion'' has its origins in the Late Latin word ''battalion'', which is derived from ''battalia'', meaning "battle" or "combat." The term was used to describe a large group of soldiers ready for battle. Over time, its meaning evolved in military terminology. The word "battalion" came into the English language in the 16th century from the French , meaning "battle squadron" (similar to the Italian meaning the same thing) and the Spanish , derived from the Vulgar Latin noun ("battle") and ultimately from the Classical L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War Weapons Of The Soviet Union
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. This corresponds to on the Celsius scale, on the Fahrenheit scale, and on the Rankine scale. Since temperature relates to the thermal energy held by an object or a sample of matter, which is the kinetic energy of the random motion of the particle constituents of matter, an object will have less thermal energy when it is colder and more when it is hotter. If it were possible to cool a system to absolute zero, all motion of the particles in a sample of matter would cease and they would be at complete rest in the classical sense. The object could be described as having zero thermal energy. Microscopically in the description of quantum mechanics, however, matter still has zero-point energy even at absolute zero, because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II Infantry Mortars Of The Soviet Union
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Institute For Strategic Studies
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) is an international research institute or think tank focusing on defence and security issues. Since 1997, its headquarters have been at Arundel House in London. It has offices on four continents, producing data and research on questions of defence, security and global affairs, publishing publications and online analysis, and convening major security summits. ''The Guardian'' newspaper has described the IISS as ‘one of the world’s leading security think tanks.’ The current Director-General and Chief Executive is Bastian Giegerich while Sir John Chipman is the Executive Chairman. The 2017 Global Go To Think Tank Index ranked IISS as the tenth-best think tank worldwide and the second-best Defence and National Security think tank globally, while Transparify ranked it third-largest UK think tank by expenditure, but gave it its lowest rating, describing it as deceptive, on funding transparency. Research The institu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kursk
The Battle of Kursk, also called the Battle of the Kursk Salient, was a major World War II Eastern Front battle between the forces of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union near Kursk in southwestern Russia during the summer of 1943, resulting in a Soviet victory. The Battle of Kursk is the single largest battle in the history of warfare. It ranks only behind the Battle of Stalingrad several months earlier as the most often-cited turning point in the European theatre of the war. It was one of the costliest battles of the Second World War, the single deadliest armoured battle in history, and the opening day of the battle, 5 July, was the single costliest day in the history of aerial warfare in terms of aircraft shot down. The battle was further marked by fierce house-to-house fighting and hand-to-hand combat. The battle began with the launch of the German offensive Operation Citadel (), on 5 July, which had the objective of pinching off the Kursk salient with attacks on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad ; see . rus, links=on, Сталинградская битва, r=Stalingradskaya bitva, p=stəlʲɪnˈɡratskəjə ˈbʲitvə. (17 July 19422 February 1943) was a major battle on the Eastern Front of World War II, beginning when Nazi Germany and its Axis allies attacked and became locked in a protracted struggle with the Soviet Union for control over the Soviet city of Stalingrad (now known as Volgograd) in southern Russia. The battle was characterized by fierce close-quarters combat and direct assaults on civilians in aerial raids; the battle epitomized urban warfare, being the single largest and costliest urban battle in military history. It was the bloodiest and fiercest battle of the entirety of World War II—and arguably in all of human history—as both sides suffered tremendous casualties amidst ferocious fighting in and around the city. The battle is commonly regarded as the turning point in the European theatre of World War II, as Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
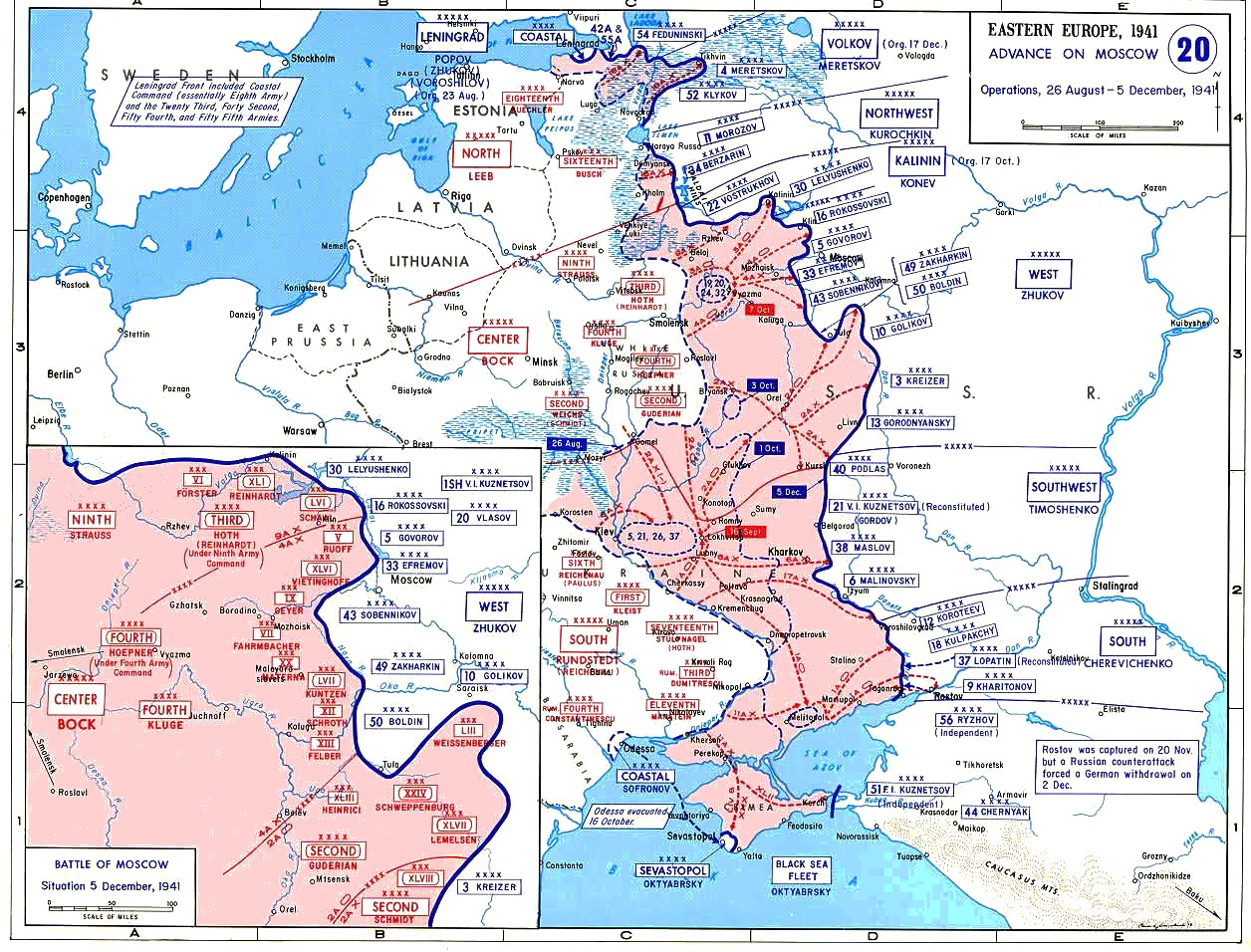
Battle For Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front during World War II, between October 1941 and January 1942. The Soviet defensive effort frustrated Hitler's attack on Moscow, the capital and largest city of the Soviet Union. Moscow was one of the primary military and political objectives for Axis forces in their invasion of the Soviet Union. The German Strategic Offensive, named Operation Typhoon, called for two pincer offensives, one to the north of Moscow against the Kalinin Front by the 3rd and 4th Panzer Armies, simultaneously severing the Moscow–Leningrad railway, and another to the south of Moscow Oblast against the Western Front south of Tula, by the 2nd Panzer Army, while the 4th Army advanced directly towards Moscow from the west. Initially, the Soviet forces conducted a strategic defence of Moscow Oblast by constructing three defensive belts, deploying newly raised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipod
A bipod is a V-shaped portable attachment that helps support and steady a device, usually a weapon such as a long gun or a mortar. The term comes from the Latin prefix and Greek root , meaning "two" and "foot" respectively. Bipods are designed to support the weight of the weapon's front portion and barrel, and provide significant stability against unwanted side-to-side movements (i.e. canting) while allowing free movements pivoting around the transverse axis ( pitching). Most modern bipods have foldable and/or telescoping legs, and allow some limited movements around the vertical axis (panning) and even the longitudinal axis ( tilting). A bipod by itself, with only two supporting legs, is not completely stable and needs to be reinforced by at least one more point of support to be steady, especially against the horizontal shearing force from recoils. This third point of support is typically the buttstock that is firmly pushed/braced against the shooter's body, but can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
107mm M1938 Mortar
The Soviet 107mm M1938 mortar was a scaled-down version of the 120mm M1938 mortar intended for use by mountain troops and light enough to be towed by animals on a cart. History In World War II, the 107mm mortar saw service with Soviet mountain infantry as a divisional artillery weapon. Weapons captured by the Germans were given the designation ''10.7 cm Gebirgsgranatwerfer 328(r)''. Its last significant use in battle was in the Vietnam War. The ability to break down the weapon made it particularly suited to the rugged terrain of Vietnam. The mortar fired a light HE round (OF-841) and a heavy HE round (OF-841A). The lighter HE round actually carried a larger bursting charge than the heavier HE round. Both rounds used GVMZ-series point detonation fuzes. Recently, the weapon has been seen in use by rebel forces during the 2011 Libyan civil war. Users * * * * * * * * * and many others See also Weapons of comparable role, performance and era * Ordnance ML 4.2 inch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
82-PM-37
The M-37 or 82-BM-37 (батальонный миномёт, battalion mortar) is a Soviet 82 millimeter calibre mortar designed by B.I. Shavyrin and accepted into service in 1937. The design of the M-37 is based on the earlier French Brandt mle 27/31 mortar with Russian modifications. The main difference between the 82-PM-37 and the earlier 82-PM-36 was the adoption of a round base plate, revised traverse/elevation controls, simplified sights and spring-loaded shock absorbers on the bi-pod to reduce the amount of relaying needed between shots. It was designed to be able to fire western 81 mm captured ammunition whilst not permitting the enemy the same advantage The German designation for captured M-37 mortars was ''8.2 cm GrW 274/2(r)''. The M-37M is an improved version with a lighter base plate and a device to prevent double loading. It was produced in China by Norinco as the Type 53, in Egypt by the Helwan Machine Tools Company as the Model 69 and in Bulgaria by Ars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortar (weapon)
A mortar today is usually a simple, lightweight, man-portable, Muzzleloader, muzzle-loaded cannon, consisting of a Smoothbore, smooth-bore (although some models use a Rifling, rifled barrel) metal tube fixed to a base plate (to spread out the recoil) with a lightweight bipod mount and a Sight (device), sight. Mortars are typically used as indirect fire weapons for close fire support with a variety of ammunition. Historically mortars were heavy Siege, siege artillery. Mortars launch explosive shell (projectile), shells (technically called Bomb, bombs) in high arching Projectile motion, ballistic trajectories. History Mortars have been used for hundreds of years. The earliest reported use of mortars was in Korea in a 1413 naval battle when Korean gunsmiths developed the ''wan'gu'' (gourd-shaped mortar) (완구, 碗口). The earliest version of the ''wan'gu'' dates back to 1407. Ch'oe Hae-san (1380–1443), the son of Ch'oe Mu-sŏn (1325–1395), is generally credited with inventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |