|
79th Guards Rifle Division
The 79th Guards Rifle Division () was an infantry division of the Red Army during World War II. It was created on 1 March 1943 from the remnants of the 284th Rifle Division (Soviet Union), 284th Rifle Division, in recognition of that division's stalwart defense against the German 6th Army (Wehrmacht), Sixth Army in the Battle of Stalingrad, in particular the Mamayev Kurgan hill and parts of the city's center. The 79th Guards continued a record of distinguished service through the rest of the Great Patriotic War, and continued to serve postwar, in several roles, until being finally disbanded in 1992. It became the 20th Guards Mechanized Division in 1945, 27th Guards Tank Division in 1957, and the 79th Guards Tank Division in 1965. It served with the 8th Guards Army from 1943 until it was disbanded. World War II Formation The 79th Guards was one of several Guards rifle divisions created on 1 March 1943 in the aftermath of the fighting for Stalingrad. It was formed from the rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern Front (Soviet Union)
The Southwestern Front was a front of the Red Army during the Second World War, formed thrice. It was first created on June 22, 1941 from the Kiev Special Military District. The western boundary of the front in June 1941 was 865 km long, from the Pripyat River and the town of Wlodawa to the Prut River and the town of Lipkany at the border with Romania. It connected to the north with the Western Front, which extended to the Lithuanian border, and to the south with the Southern Front, which extended to the city of Odessa on the Black Sea. Operational history The Southwestern Front was on the main axis of attack by the German Army Group South during Operation Barbarossa. At the outbreak of war with Germany, the Front was commanded by Mikhail Kirponos and contained the Soviet 5th, 6th, 26th, and 12th Armies along the frontier. 16th and 19th Armies were in reserve behind the forward forces. These forces took part in the tank battles in western Ukraine Ukra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
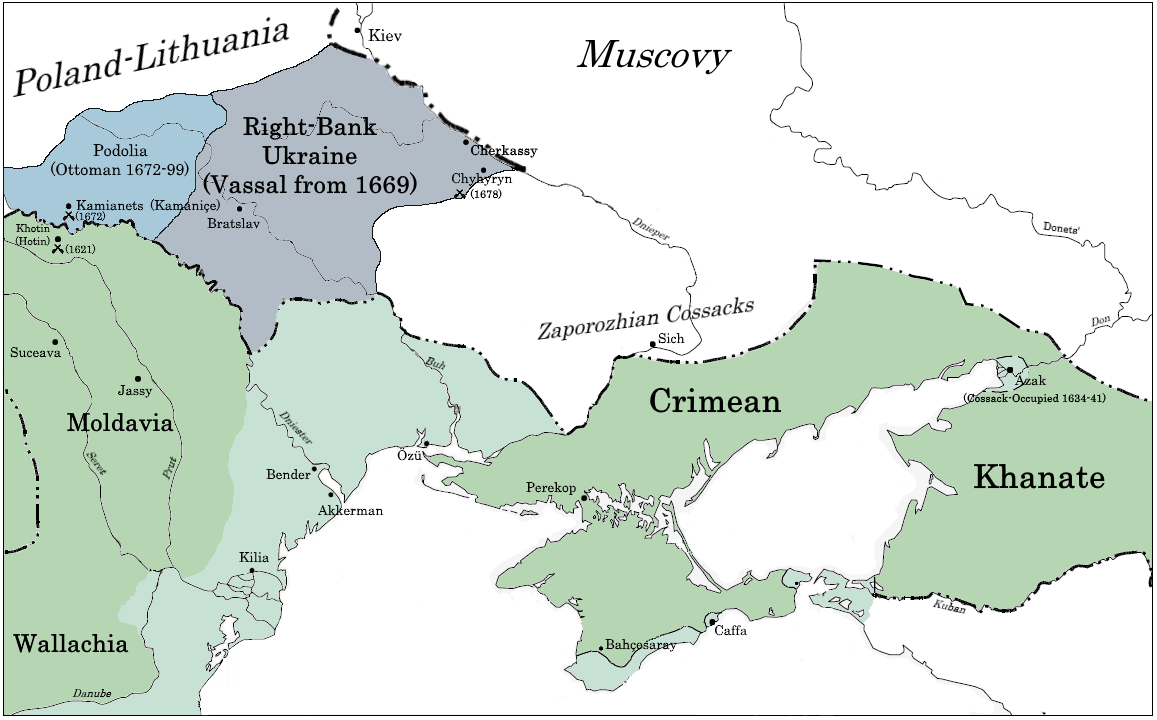
Right-bank Ukraine
The Right-bank Ukraine is a historical and territorial name for a part of modern Ukraine on the right (west) bank of the Dnieper River, corresponding to the modern-day oblasts of Vinnytsia, Zhytomyr, Kirovohrad, as well as the western parts of Kyiv and Cherkasy. It was separated from the left bank during the Ruin. Right-bank Ukraine is bordered by the historical regions of Volhynia and Podolia to the west, Moldavia to the southwest, Yedisan and Zaporizhzhia to the south, left-bank Ukraine to the east, and Polesia to the north. Main cities of the region include Cherkasy, Kropyvnytskyi, Bila Tserkva, Zhytomyr and Oleksandriia. History Since the Middle Ages, the region formed part of the Khazar Khanate, Kievan Rus', Mongol Empire, Golden Horde, Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland. Right-bank Ukraine was the target of slave raids by Tatars from the Black Sea steppes. The history of right- and left-bank Ukraine is closely associated with the Khmelnyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikopol, Ukraine
Nikopol (, ) is a city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality (hromada) in Nikopol Raion in the south of Ukraine, on the right bank of the Dnieper, Dnieper River, about 63 km south-east of Kryvyi Rih and 48 km south-west of Zaporizhzhia. Population: Nikopol is the fourth-most populous city in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. Located on a cape by the Kakhovka reservoir, it is a powerful industrial city with several pipe-producing factories, such as the Interpipe corporation, and steel rolling mills, such as the Nikopol Ferroalloy Plant, factory of ferroalloys, constituting Nikopol metropolitan area. Formerly, the settlement served as one of the Sich, capital cities of the Zaporizhian Sich and was known as one of the main crossings over the Dnieper. General information Renamed by the Russian Empire into Slaviansk and Greek Plan, later Nikopol (after ), the city has a rich preceding history. Between 1638 and 1652, it was the settlement of Mykytyn Rih (, literally ''Mykyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with a drainage basin of , it is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth- longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing what is now Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat River, a tributary of the Dnieper, just upstream from its confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaporizhia Offensive
Zaporizhzhia, formerly known as Aleksandrovsk or Oleksandrivsk until 1921, is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. It is the Capital city, administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zaporizhzhia has a population of Zaporizhzhia is known for the historic island of Khortytsia, multiple power stations and for being an important industrial centre. Steel, aluminium, aircraft engines, automobiles, transformers for substations, and other heavy industrial goods are produced in the region. Names and etymology The name ''Zaporizhzhia'' refers to the position of the city: "beyond the rapids"—downstream or south of the Dnieper Rapids. These were previously an impediment to navigation and the site of important portages. In 1932, the rapids were flooded to become part of the reservoir of the Dnieper Hydroelectric Station.Pospelov, pp. 25–26 Before 1921, the city was called Aleksandrovsk (or Oleksandrivsk), named after the original fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Dnieper
The Battle of the Dnieper was a military campaign that took place in 1943 on the Eastern Front of World War II. Being one of the largest operations of the war, it involved almost four million troops at one point and stretched over a front. Over four months, the eastern bank of the Dnieper was recovered from German forces by five of the Red Army's fronts, which conducted several assault river crossings to establish several lodgements on the western bank. Kiev was later liberated in the Second Battle of Kiev. 2,438 Red Army soldiers were awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union for their involvement. Strategic situation Following the Battle of Kursk, the Wehrmachts ''Heer'' and supporting ''Luftwaffe'' forces in the southern Soviet Union were on the defensive in southern Ukraine. By mid-August, Adolf Hitler understood that the forthcoming Soviet offensive could not be contained on the open steppe and ordered construction of a series of fortifications along the line of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barvenkovo
Barvinkove (, ) is a city in Izium Raion, Kharkiv Oblast, Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Barvinkove urban hromada, one of the communities of Ukraine. Population: History Barvinkove was first mentioned in 1653. At the beginning of its existence, Barvinkove was a wintering place (zymivnyk), receiving the status of a sloboda in the 18th century. The Cossacks built a wooden fortress on Chumatska Hill, from which they could see all the approaches to the town. In 1680 and 1690, the city suffered a plague epidemic. In 1708, Tsar Peter the Great visited the city, trying to persuade the people of Barvinok not to fight against him, but despite this, the local Cossacks supported Mazepa and fought for independence. In the times of the Nova Sich, Barvinokova Stinka was the administrative center of the Barvinkove Palanka. The last colonel, Ivan Garadzha, poured lard over the skin of more than one Sloboda lord, which Kharkiv Governor Shcherbynin complained about to Potemkin. Thus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donbas Strategic Offensive (July 1943)
The First Donbas strategic offensive, also known as the Mius-Donets Offensive, was a military campaign fought in the Donets Basin from 17 July to 2 August 1943, between the German and Soviet armed forces on the Eastern Front of World War II. The Germans contained the Soviet offensive in its northern portion after initial gains and pushed the southern portion back to its starting point. Background In July 1943, while the Battle of Kursk was raging to the north, two German armies of Army Group South in the Donets Basin confronted two Soviet army groups on a 660-kilometer front. After the Wehrmacht launched Operation Citadel, the task of the Soviet troops in sectors of the front secondary to the Kursk Bulge became offensive operations in order to force the Wehrmacht to use their available reserves. The troops of the Southern Front and Southwestern Front began to regroup. Troops that had previously been distributed along the front for defensive purposes were now assembled into stri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donbas
The Donbas (, ; ) or Donbass ( ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern Ukraine. The majority of the Donbas is occupied by Russia as a result of the Russo-Ukrainian War. The word ''Donbas'' is a portmanteau formed from "Donets Basin", an abbreviation of "Donets Coal Basin" (; ). The name of the coal basin is a reference to the Donets Ridge; the latter is associated with the Donets river. There are numerous definitions of the region's extent. The '' Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine'' defines the "small Donbas" as the northern part of Donetsk and the southern part of Luhansk regions of Ukraine, and the attached part of Rostov region of Russia. The historical coal mining region excluded parts of Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts, and included areas in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast and Southern Russia. A Euroregion of the same name is composed of Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts in Ukraine and Rostov Oblast in Russia. The Donbas formed the historical border betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izyum
Izium or Izyum (, ; ) is a city on the Donets River in Kharkiv Oblast, eastern Ukraine that serves as the administrative center of Izium Raion and Izium urban hromada. It is about southeast of the city of Kharkiv, the oblast's administrative center. Izium has a population of making it the second-most populous city in Kharkiv Oblast behind Kharkiv proper. It has held economic significance for centuries due to its position as a transportation link between Kharkiv and the Donbas region to the southeast. The area around Izium has been periodically inhabited since ancient times, but the modern city has its origins in a 17th-century fortress defending against Tatar raids. Izium was the site of several battles during World War II, but still grew rapidly during the 20th century due to its importance as a transport hub. During the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Russian forces occupied the city in April 2022 after a battle that destroyed much of the city. However, the city was recaptur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |