|
6th Canadian Infantry Brigade
The 6th Canadian Infantry Brigade was an infantry brigade of the Canadian Army that fought during World War I and World War II. Raised in 1915, it formed part of the 2nd Canadian Division and fought on the Western Front during World War I before being disbanded. Later, it was re-raised in September 1939 and subsequently took part in Allied operations in north-west Europe in 1944 and 1945. History World War I Formed in early 1915, the 6th Brigade formed part of the 2nd Canadian Division that was raised as part of the Canadian Expeditionary Force. Departing Canada in May 1915, further training was conducted in the United Kingdom around Shorncliffe before the brigade was committed to the Western Front in September 1915. The brigade's first major actions commenced early the following year around St Eloi, after which the brigade participated in many significant actions for the next two-and-a-half years that it was deployed along the Western Front. World War II Dieppe, Operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Army
The Canadian Army () is the command (military formation), command responsible for the operational readiness of the conventional ground forces of the Canadian Armed Forces. It maintains regular forces units at bases across Canada, and is also responsible for the Army Reserve, the largest component of the Primary Reserve. The army is headed by the Commander of the Canadian Army and Chief of the Army Staff, who is subordinate to the Chief of the Defence Staff (Canada), Chief of the Defence Staff. The army is also supported by 3,000 civilian employees from the public service. The army was formed in 1855, as the Canadian Militia#Active militias, Active Militia, in response to the threat of the United States to the Province of Canada after the British garrison left for the Crimean War. This militia was later subdivided into the Permanent Active Militia and the Non-Permanent Active Militia. Finally, in 1940, an order in council changed the name of the Active Militia to the Canadian Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Canadian Division
The 2nd Canadian Division (2 Cdn Div; ) is a formation of the Canadian Army in the province of Quebec, Canada. The present command was created 2013 when Land Force Quebec Area was re-designated. The main unit housed in this division is the Royal 22nd Regiment based at CFB Valcartier near Quebec City, which is the largest regiment in the Canadian Army. The division draws its historical lineage from formations that existed during the First and Second World Wars. History During the First World War, the division fought on the Western Front before being disbanded in 1919. It was reformed on 1 September 1939, as part of the First Canadian Army, at the outbreak of the Second World War, adopting the designation "2nd Canadian Infantry Division". It was initially composed of volunteers within brigades established along regional lines, though a halt in recruitment in the early months of the war caused a delay in the formation of brigade and divisional headquarters. With questions c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klever Reichswald
The Klever Reichswald is a state forest in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, between the rivers Rhine and Meuse at the German–Dutch border. The forest is located in the municipal territories of Kleve, Goch, Kranenburg and Bedburg-Hau. It is the largest coherent wooded area of the lower Rhine and the largest coherent public state forest of North Rhine-Westphalia with an area of 51 km2 (5100 ha).City Cleve''The Reichswald'' Landscape and forest The Reichswald is on the ridge of the lower Rhine, which was created by glaciers. In the Ice Age a range of hills were created, which contrasts the flat Rhine plain. 31 of the hills reach heights above 50 meters. One of the highest hills is the Rupenberg with 95 meters, located at the eastern end of the Reichswald. The forest is a closed mixed deciduous forest dominated by copper beech. For some areas the oak is predominant; for some other parts conifer forest is dominant. In the west the Reichswald merges into woodland of the prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Spring
Operation Spring (July 25–27, 1944) was an offensive operation of the Second World War conducted by II Canadian Corps during the Normandy campaign in 1944. The plan was intended to create pressure on the German forces operating on the British and Canadian front simultaneous with Operation Cobra, an American offensive. Operation Spring was intended to capture Verrières Ridge and the villages on the south slope of the ridge. A successful German defence of the ridge contained the offensive on the first day, and inflicted many casualties on the Canadians. Background The districts of Caen north of the Orne were captured during Operation Charnwood (8–9 July 1944) and those south of the Orne had been captured on July 19, during Operation Goodwood, in Operation Atlantic by the II Canadian Corps (Lieutenant-General Guy Simonds) at a cost of 1,349 casualties. About south of Caen, Verrières Ridge blocked a direct advance by Allied forces on Falaise. Attempts to take the ridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Atlantic
Operation Atlantic (18–21 July 1944) was a Canadian offensive during the Battle of Normandy in the Second World War. The offensive, launched in conjunction with Operation Goodwood by the Second Army, was part of operations to seize the French city of Caen and vicinity from German forces. It was initially successful, with gains made on the flanks of the Orne River near Saint-André-sur-Orne but an attack by the 4th and 6th Canadian Infantry Brigades of the 2nd Canadian Infantry Division, against strongly defended German positions on Verrières Ridge to the south was a costly failure. Background Operation Overlord The capture of the historic Norman town of Caen, while "ambitious", was the most important D-Day objective assigned to British Lieutenant-General John Crocker's I Corps and its component British 3rd Infantry Division, which landed on Sword on 6 June 1944.Ellis, p. 171 Operation Overlord plans called for British Second Army to secure the city and form a line from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Charnwood
Operation Charnwood was an Anglo-Canadian offensive that took place from 8 to 9 July 1944, during the Battle for Caen, part of the larger Operation Overlord (code-name for the Battle of Normandy) in the Second World War. The operation was intended to capture the German-occupied city of Caen (), which was an important objective for the Allies during the opening stages of Overlord. It was also hoped that the attack would forestall the transfer of German armoured units from the Anglo-Canadian sector to the American sector to the west, where an offensive was being prepared. The British and Canadians advanced on a broad front and by the evening of the second day had taken Caen up to the Orne and Odon rivers. Preceded by a controversial bombing raid that destroyed much of the historic Old City of Caen, Operation Charnwood began at dawn on 8 July, with three infantry divisions attacking German positions north of Caen, behind a creeping barrage. Supported by three armoured brigade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
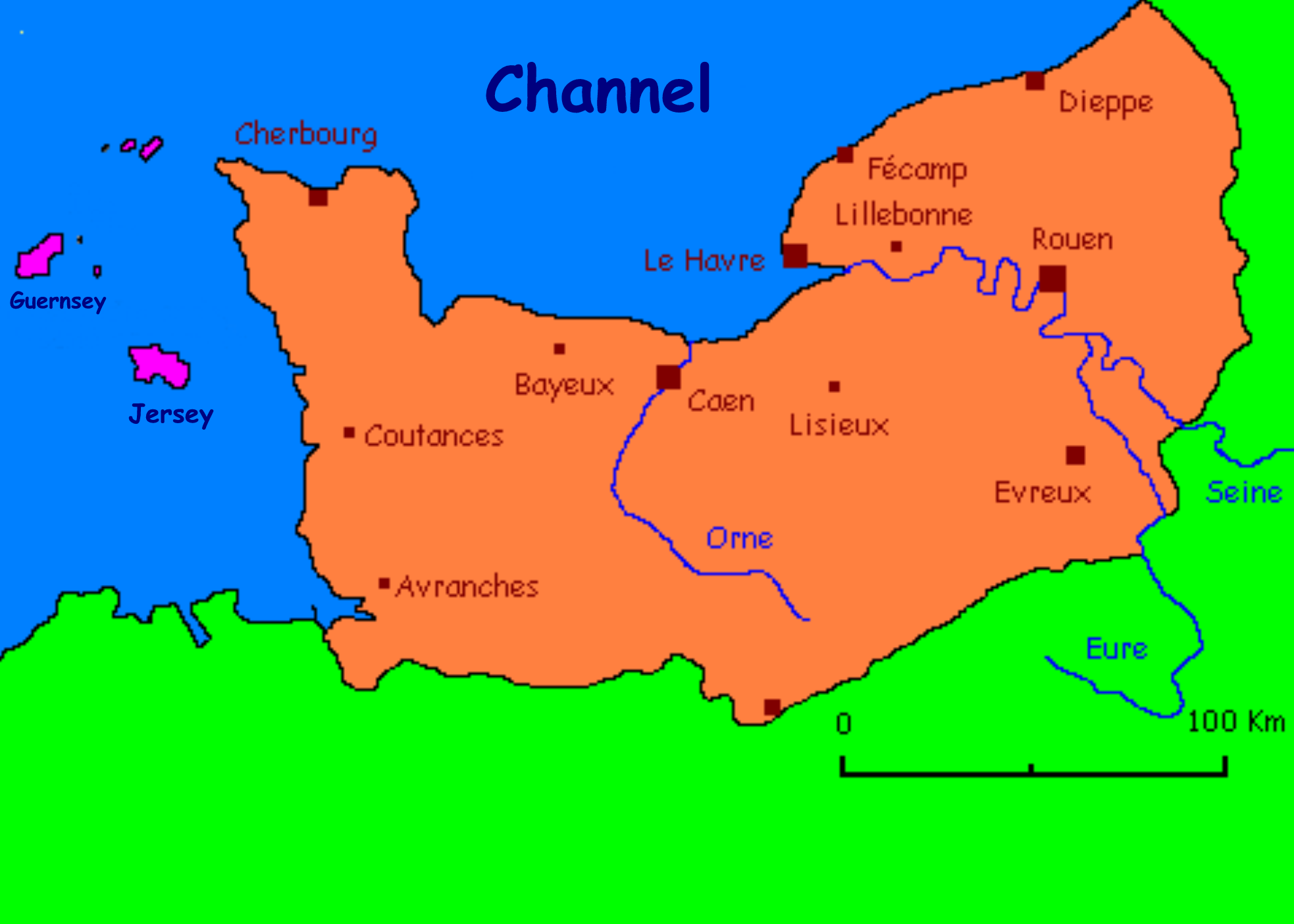
Caen
Caen (; ; ) is a Communes of France, commune inland from the northwestern coast of France. It is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Calvados (department), Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its Functional area (France), functional urban area has 470,000,Comparateur de territoire , INSEE, retrieved 20 June 2022. making Caen the second largest urban area in Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the 19th largest in France. It is also the third largest commune in all of Normandy after Le Havre and Rouen. It is located northwest of Paris, connected to the South of England by the Caen (Ouistreham) to Portsmouth ferry route through the English Channel. Situated a few miles from the coast, the landing beaches, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
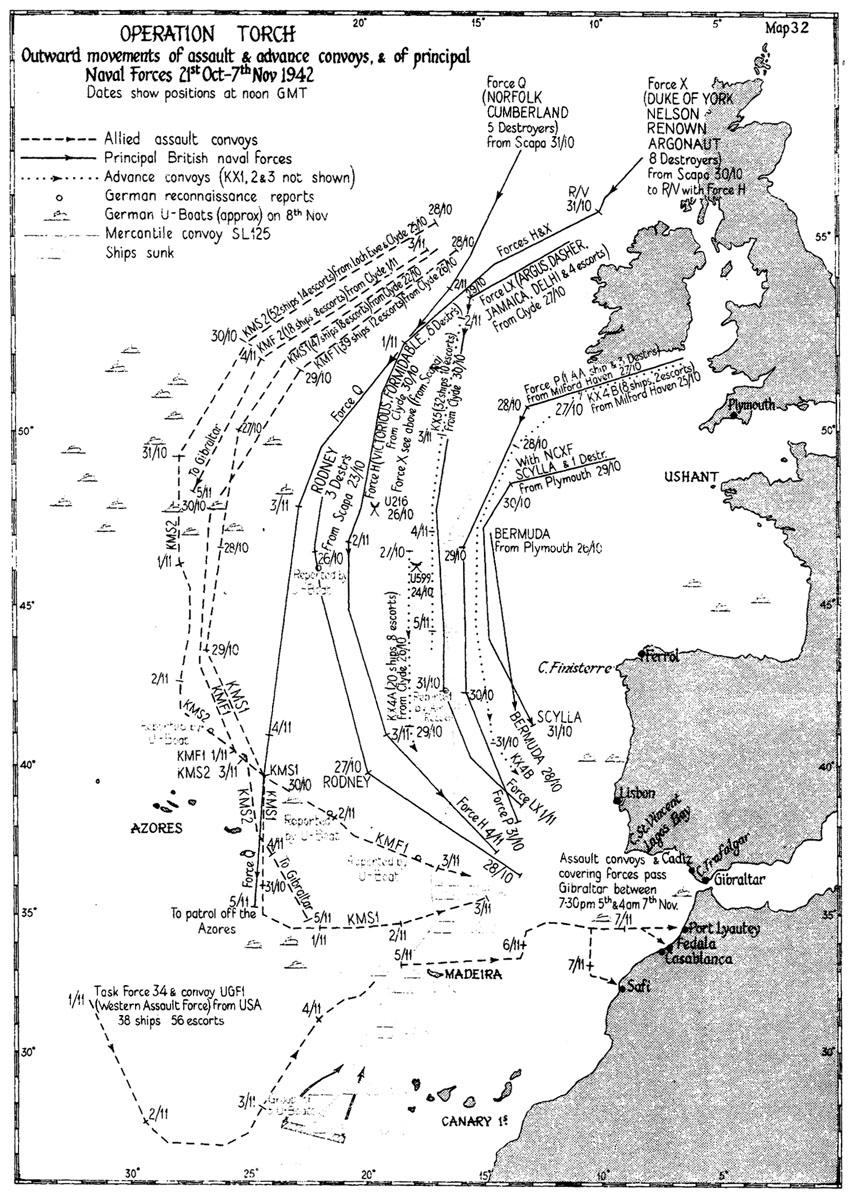
Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8–16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while allowing American armed forces the opportunity to begin their fight against Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy on a limited scale. The French colonies were aligned with Germany via Vichy France but the loyalties of the population were mixed. Reports indicated that they might support the Allies. The American General Dwight D. Eisenhower, supreme commander of the Allied forces in Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II, Mediterranean theater of the war, approved plans for a three-pronged attack on Casablanca (Western), Oran (Centre) and Algiers (Eastern), then a rapid move on Tunis to catch Axis forces in North Africa from the west in conjunction with the British advance from Egypt. The Western Task Force encountered unexpected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early Middle Ages, medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the English Navy of the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the early 18th century until the World War II, Second World War, it was the world's most powerful navy. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial German Navy, Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk (air base), Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the Luftwaffe's existence was publicly acknowledged and officially established on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a Luftwaffe detachment sent to aid Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalist for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Commandos
The Commandos, also known as the British Commandos, were formed during the World War II, Second World War in June 1940, following a request from Winston Churchill, for special forces that could carry out Raid (military), raids against German-occupied Europe. Initially drawn from within the British Army from soldiers who volunteered for the Special Service Brigade, the Commandos' ranks were eventually filled by members of all branches of the British Armed Forces and a number of foreign volunteers from German-occupied countries. By the end of the war 25,000 men had passed through the Commando course at Commando Basic Training Centre (United Kingdom), Achnacarry. This total includes not only the British volunteers, but volunteers from Sacred Band (World War II), Greece, 1st Marine Infantry Parachute Regiment, France, 5th Special Air Service, Belgium, No. 10 (Inter-Allied) Commando, Netherlands, Canada, Norway and Poland. The United States Army Rangers and Marine Raiders, US Marine Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieppe
Dieppe (; ; or Old Norse ) is a coastal commune in the Seine-Maritime department, Normandy, northern France. Dieppe is a seaport on the English Channel at the mouth of the river Arques. A regular ferry service runs to Newhaven in England. Famous for its scallops, Dieppe also has a popular pebbled beach, a 15th-century castle and the churches of Saint-Jacques and Saint-Remi. The mouth of the river Scie lies at Hautot-sur-Mer, directly to the west of Dieppe. The inhabitants of the town of Dieppe are called () and () in French. History First recorded as a small fishing settlement in 1030, Dieppe was an important prize fought over during the Hundred Years' War. It housed the most advanced French school of cartography in the 16th century. Two of France's best navigators, Michel le Vasseur and his brother Thomas le Vasseur, lived in Dieppe when they were recruited to join the expedition of René Goulaine de Laudonnière which departed Le Havre for Florida on April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |