|
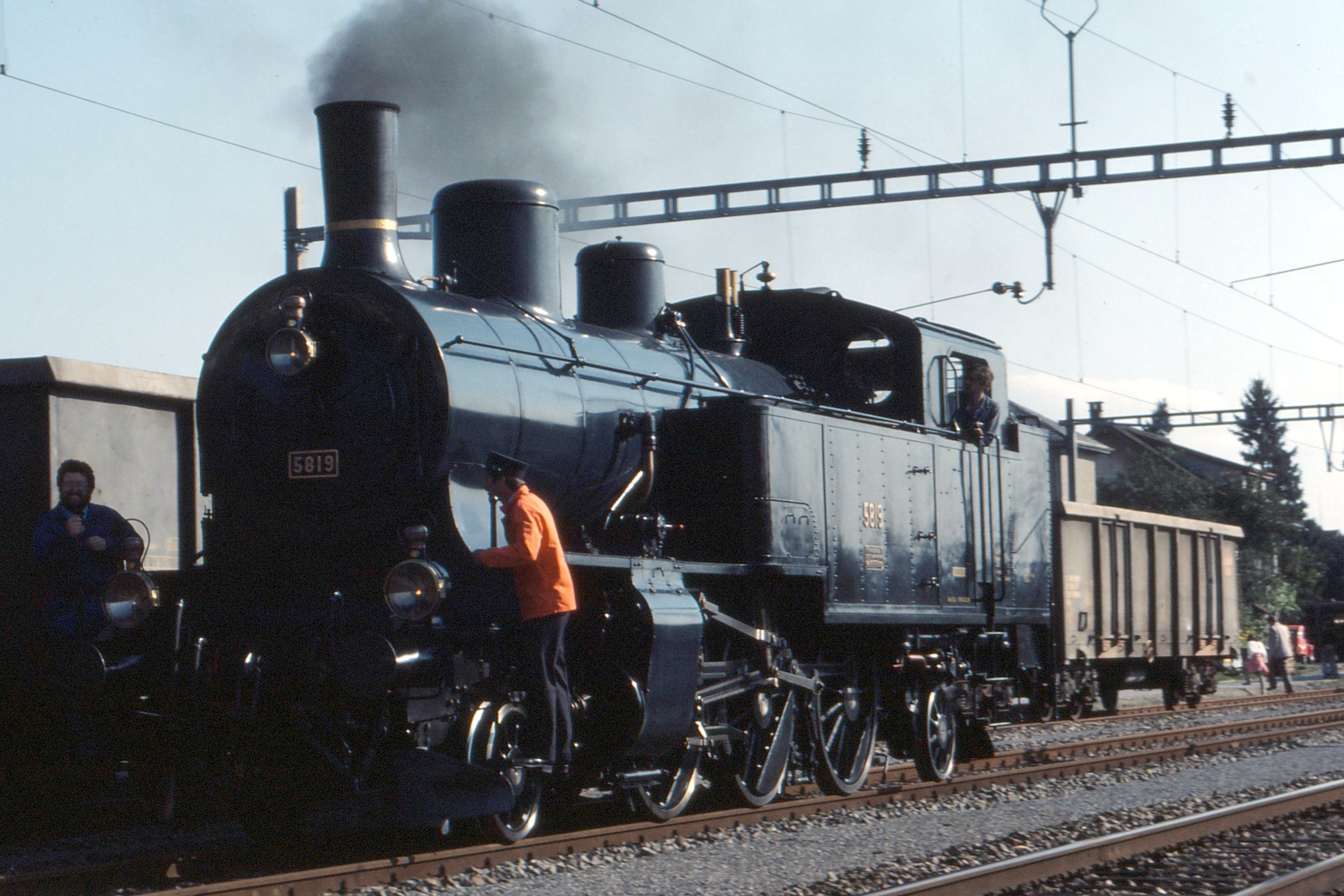
6-8-6 Locomotives
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, represents the arrangement of six unpowered leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels, and six unpowered trailing wheels. Other equivalent classifications are: * UIC classification: 3D3 (also known as German classification and Italian classification) * French classification: 343 * Turkish classification: 410 * Swiss classification: 4/10. The only known example of the 6-8-6 wheel arrangement is the experimental Pennsylvania Railroad Pennsylvania Railroad class S2, S2 steam turbine locomotive. Notes References * 6-8-6 locomotives, Whyte notation, 8,6-8-6 {{steam-loco-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Crescent, 1985, p. 226. describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is used in much of the world, notable exceptions being the United Kingdom and North America. The classification system is managed by the International Union of Railways (UIC). Structure The UIC uses the following structure: ; Upper-case letters : Indicate driving axles, starting at A for a single axle. B thus indicates two and C indicates three consecutive pairs of driving wheels. ; Lower-case "o" : Related to driving axles (minimum 2, "B"), indicates they are individually driven by separate traction motors. ; Numbers : Consecutive non-driving axles, starting with 1 for a single axle. ; Prime symbol " ′ " : The axles indicated by a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Turbine Locomotive
A steam turbine locomotive was a steam locomotive which transmitted steam power to the wheels via a steam turbine. Numerous attempts at this type of locomotive were made, mostly without success. In the 1930s this type of locomotive was seen as a way to both revitalize steam power and challenge the diesel locomotives then being introduced. Advantages * High efficiency at high speed. * Far fewer moving parts, hence potentially greater reliability. * Conventional piston steam locomotives give a varying, Sine wave, sinusoidal torque, making wheelslip much more likely when starting. * The side rods and valve gear of conventional steam locomotives create horizontal forces that cannot be fully balanced without substantially increasing the vertical forces on the track, known as hammer blow. Disadvantages * High efficiency is ordinarily obtained ''only'' at high speed and high power output (though some Swedish and UK locomotives were designed and built to operate with an efficiency equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania Railroad Class S2
The Pennsylvania Railroad's S2 class was a steam turbine locomotive designed and built in a collaborative effort by Baldwin Locomotive Works and Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company, as an attempt to prolong the dominance of the steam locomotive by adapting technology that had been widely accepted in the marine industry. One was built, #6200, delivered in September 1944. The S2 was the sole example of the 6-8-6 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, with a six-wheel leading truck keeping the locomotive stable at speed, eight powered and coupled driving wheels, and a six-wheel trailing truck supporting the large firebox. The S2 used a direct-drive steam turbine provided by the Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company, geared to the center pair of axles with the outer two axles connected by side rods; the fixed gear ratio was 18.5:1. Such design was to prevent energy loss and S2 achieved a mechanical efficiency of 97% which means only 3% of steam energy was lost wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its peak in 1882, the Pennsylvania Railroad was the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Over its existence, Pennsylvania Railroad acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe railroads. Its only formidable rival was the New York Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Classification
For more than a century, the Swiss locomotive, multiple unit, motor coach and railcar classification system, in either its original or updated forms, has been used to name and classify the rolling stock operated on the railways of Switzerland. It started out as a uniform system for the classification and naming of all rolling stock, powered and unpowered, but had been replaced and amended by the UIC classification of goods wagons. Overview and evolution The Swiss classification system was created by the Swiss federal railways department, and applied originally to the rolling stock of private railways, operating under government concessions. In 1902, when the Swiss Federal Railways was founded as a government railway, that new railway also became bound by the system. Unlike the Whyte notation and AAR wheel arrangement, AAR system, both of which are used to classify wheel arrangements, and the UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, the Swiss system, in both its or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Classification
In the Turkish classification system for railway locomotives, the number of powered axles are followed by the total number of axles. It is identical to the Swiss system except that the latter places a slash between the two numbers. Thus 0-6-0 becomes 33 4-6-2 becomes 36 2-6-4 becomes 36 2-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ... becomes 45 See also * UIC classification system Locomotive classification systems Locomotives of Turkey {{europe-rail-transport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Classification
Under the French classification system for locomotive wheel arrangements, the system is slightly different for steam and electric/diesel vehicles. Steam The French system counts axles, rather than wheels. As with Whyte notation, a conventional rigid locomotive will have three digits corresponding to its axle configuration: The first digit is the number of leading unpowered axles; the second digit the number of powered axles; The third digit the number of trailing unpowered axles. Examples 0-6-0 = 030 2-6-0 = 130 0-6-2 = 031 4-6-2 = 231 2-8-0 = 140 4-8-0 = 240 4-6-4 = 232 4-8-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and four trailing wheels on two axles. The type wa ... = 242 2-6-6-2 = 130+031 Electric and diesel With electric and diesel vehicles include DMUs a letter A-B-C-D replaces 1-2-3-4 for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UIC Classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Crescent, 1985, p. 226. describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is used in much of the world, notable exceptions being the United Kingdom and North America. The classification system is managed by the International Union of Railways (UIC). Structure The UIC uses the following structure: ; Upper-case letters : Indicate driving axles, starting at A for a single axle. B thus indicates two and C indicates three consecutive pairs of driving wheels. ; Lower-case "o" : Related to driving axles (minimum 2, "B"), indicates they are individually driven by separate traction motors. ; Numbers : Consecutive non-driving axles, starting with 1 for a single axle. ; Prime symbol " ′ " : The axles indicated by a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PRR S2
The Pennsylvania Railroad's S2 class was a steam turbine locomotive designed and built in a collaborative effort by Baldwin Locomotive Works and Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company, as an attempt to prolong the dominance of the steam locomotive by adapting technology that had been widely accepted in the marine industry. One was built, #6200, delivered in September 1944. The S2 was the sole example of the 6-8-6 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, with a six-wheel leading truck keeping the locomotive stable at speed, eight powered and coupled driving wheels, and a six-wheel trailing truck supporting the large firebox. The S2 used a direct-drive steam turbine provided by the Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company, geared to the center pair of axles with the outer two axles connected by side rods; the fixed gear ratio was 18.5:1. Such design was to prevent energy loss and S2 achieved a mechanical efficiency of 97% which means only 3% of steam energy was lost w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trailing Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, truck. On some large locomotives, a booster engine was mounted on the trailing truck to provide extra tractive effort when starting a heavy train and at low speeds on gradients. Trailing wheels were used in some early locomotives but fell out of favor for a time during the latter 19th century. As demand for more powerful locomotives increased, trailing wheels began to be used to support the crew cab and rear firebox area. Trailing wheels first appeared on American locomotives between 1890 and 1895, but their axle worked in rigid pedestals. It enabled boilers to be lowered, since the top of the main frames was dropped down behind the driving wheels and under the firebox. The firebox could also be longer and wider, increasing the heating su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled together with side rods (also known as coupling rods); normally one pair is directly driven by the main rod (or connecting rod) which is connected to the end of the piston rod; power is transmitted to the others through the side rods. On diesel and electric locomotives, the driving wheels may be directly driven by the traction motors. Coupling rods are not usually used, and it is quite common for each axle to have its own motor. Jackshaft drive and coupling rods were used in the past (e.g. in the Swiss Crocodile locomotive) but their use is now confined to shunter locomotives. On an articulated locomotive or a duplex locomotive, driving wheels are grouped into sets with wheels within each set linked together. Diameter Drivin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |