|
549
__NOTOC__ Year 549 ( DXLIX) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 549 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Siege of Rome: The Ostrogoths under Totila besiege Rome for the third time, after Belisarius has returned to Constantinople. He offers a peace agreement, but this is rejected by Emperor Justinian I. * Totila conquers the city of Perugia (Central Italy) and stations a Gothic garrison. He takes bishop Herculanus prisoner, and orders him to be completely flayed. The Ostrogoth soldier asked to perform this gruesome execution shows pity, and decapitates Herculanus before the skin on every part of his body is removed. * In the Circus Maximus, first and largest circus in Rome, the last chariot races are held. Europe * January - Battle of Ciiil Conaire, Ireland: Ailill Inbanda a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theudigisel
Theudigisel (or Theudegisel) (in Latin language, Latin ''Theudigisclus'' and in Spanish language, Spanish, Galician language, Galician and Portuguese language, Portuguese ''Teudiselo'', ''Teudigiselo'', or ''Teudisclo''), ( 500 – December 549) was king of the Visigoths in Hispania and Septimania (548–549). Some Visigothic king lists skip Theudigisel, as well as Agila I, going directly from Theudis to Athanagild. Biography Theudigisel was a leading Ostrogoth general during the reign of Theudis (531–548), and was attested as the last member of the Amal dynasty, House of Theodoric, being the son of Theodahad (535–536) & grandnephew of Theodoric the Great. He had repelled the Franks from Spain after their invasion of 541, cutting them off in the pass of Valcarlos, but accepted a bribe to allow them to return to home. Years later, when Theudis was murdered by a disgruntled servant, Theudigisel had managed to make himself King of Visigoths shortly after his Predecessors death. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totila
Totila, original name Baduila (died 1 July 552), was the penultimate King of the Ostrogoths, reigning from 541 to 552 AD. A skilled military and political leader, Totila reversed the tide of the Gothic War (535–554), Gothic War, recovering by 543 almost all the territories in Italy that the Eastern Roman Empire had captured from his Ostrogothic Kingdom, Kingdom in 540. A relative of Theudis, sword-bearer of Theodoric the Great and king of the Visigoths, Totila was elected king by Ostrogoths, Ostrogothic nobles in the autumn of 541 after King Witigis had been carried off prisoner to Constantinople. Totila proved himself both as a military and political leader, winning the support of the lower classes by liberating slaves and distributing land to the peasants. After a successful Siege of Verona (541), defence at Verona, Totila pursued and defeated a numerically superior army at the Battle of Faventia (542), Battle of Faventia in 542 AD. Totila followed these victories by Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herculanus Of Perugia
Herculanus of Perugia (; died 549 AD) was a bishop of Perugia. He was canonized as a saint by the Catholic Church and is recognised as patron saint of Perugia. His main feast day is November 7; his second feast is celebrated on March 1. According to Pope Gregory the Great in his ''Dialogues'', Herculanus suffered martyrdom when Totila, king of the Ostrogoths, captured Perugia in 549. Before the city was captured, Herculanus is said to have tried to save the city by feeding the last sack of grain to the last lamb. This was meant to give the Ostrogoth forces the impression that the Perugians had food to spare, and were able to feed a weak lamb with their precious grain. With food to spare, they were thus able to withstand the siege. However, Totila was not fooled by this trick and captured the city just the same. Totila is said to have given orders for Herculanus to be completely flayed. However, the Ostrogoth soldier who had to perform this task took pity on the bishop and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot Racing
Chariot racing (, ''harmatodromía''; ) was one of the most popular Ancient Greece, ancient Greek, Roman Empire, Roman, and Byzantine Empire, Byzantine sports. In Greece, chariot racing played an essential role in aristocratic funeral games from a very early time. With the institution of formal races and permanent racetracks, chariot racing was adopted by many Greek states and their religious festivals. Horses and chariots were very costly. Their ownership was a preserve of the wealthiest aristocrats, whose reputations and status benefitted from offering such extravagant, exciting displays. Their successes could be further broadcast and celebrated through commissioned odes and other poetry. In standard Greek racing practise, each chariot held a single driver and was pulled by four horses, or sometimes two. Drivers and horses risked serious injury or death through collisions and crashes; this added to the excitement and interest for spectators. Most charioteers were slaves or cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agila I
Agila, sometimes Agila I or Achila I (died March 554), was Visigothic king of Hispania and Septimania (549 – March 554). Peter Heather notes that Agila's reign was during a period of civil war following the death of Amalaric, the last member of the old Visigothic dynasty, when ambitious Gothic nobles competed openly for the throne. Agila came to power after the assassination of Theudigisel, who had ruled for less than two years. However, opposition to his rule soon emerged. First was the revolt of the city of Corduba, which Isidore of Seville suggests was due to local Roman Catholics objecting to his Arianism: in his account, Isidore mentions that Agila defiled the church of a local saint, Acisclus, by drenching the sepulcher "with the blood of the enemy and of their pack-animals", and attributes the death of Agila's son in the conflict — along with the majority of his army, and the royal treasury — to "the agency of the saints". Peter Heather lists several groups who revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayback Machine
The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the World Wide Web founded by Internet Archive, an American nonprofit organization based in San Francisco, California. Launched for public access in 2001, the service allows users to go "back in time" to see how websites looked in the past. Founders Brewster Kahle and Bruce Gilliat developed the Wayback Machine to provide "universal access to all knowledge" by preserving archived copies of defunct web pages. The Wayback Machine's earliest archives go back at least to 1995, and by the end of 2009, more than 38.2 billion webpages had been saved. As of November 2024, the Wayback Machine has archived more than 916 billion web pages and well over 100 petabytes of data. History The Internet Archive has been archiving cached web pages since at least 1995. One of the earliest known pages was archived on May 8, 1995. Internet Archive founders Brewster Kahle and Bruce Gilliat launched the Wayback Machine in San Francisco, California ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565. His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was expressed by the partial recovery of the territories of the defunct Western Roman Empire. His general, Belisarius, swiftly conquered the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Subsequently, Belisarius, Narses, and other generals Gothic War (535–554), conquered the Ostrogothic Kingdom, restoring Dalmatia, Sicily, Italian peninsula, Italy, and Rome to the empire after more than half a century of rule by the Ostrogoths. The Liberius (praetorian prefect), praetorian prefect Liberius reclaimed the south of the Iberian Peninsula, establishing the province of Spania. These campaigns re-established Roman control over the western Mediterranean, increasing the Empire's annual revenue by over a million ''solidi''. During his reign, Justinian also subdued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
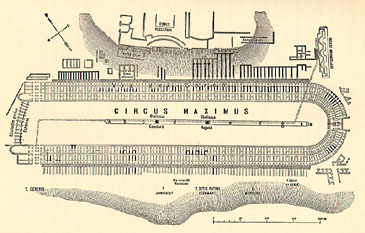
Circus Maximus
The Circus Maximus (Latin for "largest circus"; Italian language, Italian: ''Circo Massimo'') is an ancient Roman chariot racing, chariot-racing stadium and mass entertainment venue in Rome, Italy. In the valley between the Aventine Hill, Aventine and Palatine Hill, Palatine hills, it was the first and largest stadium in ancient Rome and its later Roman Empire, Empire. It measured in length and in width and could accommodate over 150,000 spectators. In its fully developed form, it became the model for Circus (building), circuses throughout the Roman Empire. The site is now a public park. Events and uses The Circus was Rome's largest venue for ''ludi'', public games connected to Religion in ancient Rome, Roman religious Roman festival, festivals. ''Ludi'' were sponsored by leading Romans or the Roman state for the benefit of the SPQR, Roman people (''populus Romanus'') and List of Roman deities, gods. Most were held annually or at annual intervals on the Roman calendar. Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian military group united under the command of Alaric I. Their exact origins are believed to have been diverse but they probably included many descendants of the Thervingi who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and Alaric's Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under Alaric, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sack of Rome (410), sacked Rome in August 410. The Visigoths were subsequently settled in southern Gaul as ''foederati'' to the Romans, a relationship that was established in 418. This developed as an independent kingdom with its Capital city, capital at Toulou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Rome (549-550)
Siege of Rome may refer to: * Siege of Rome (508 BC), by Lars Porsena, the Etruscan king of Clusium * Siege of Rome (408), see Sack of Rome (410) * Siege of Rome (409), see Sack of Rome (410) * Siege of Rome (472), by the Western Roman general Ricimer * Siege of Rome (537–538), by the Ostrogoths under Vitiges * Siege of Rome (546), by the Ostrogoths under Totila * Siege of Rome (549–550), by the Ostrogoths again under Totila * Siege of Rome (756), by the Lombards under Aistulf * Siege of Rome (1082–1084), by Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor * Siege of Rome (1849), by the French See also * Arab raid against Rome (846) * Capture of Rome (1870), by the Kingdom of Italy * Liberation of Rome (1944), by the Allies during World War II * Fall of Rome (other) * Sack of Rome (other) * Battle of Rome (other) * Battle for Rome (other) {{disambiguation Rome Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used when designating years in the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian and Julian calendar, Julian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means "in the year of the Lord" but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", taken from the full original phrase "", which translates to "in the year of our Lord Jesus Christ". The form "BC" is specific to English language, English, and equivalent abbreviations are used in other languages: the Latin (language), Latin form, rarely used in English, is (ACN) or (AC). This calendar era takes as its epoch (date reference), epoch the traditionally reckoned year of the annunciation, conception or Nativity of Jesus, birth of Jesus. Years ''AD'' are counted forward since that epoch and years ''BC'' are counted backward from the epoch. There is no year zero in this scheme; thus the year AD 1 immediately follows the year 1 BC. This dating system was devised in 525 by Dionysius Exiguus but was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2,746,984 residents in , Rome is the list of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, third most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. The Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, with a population of 4,223,885 residents, is the most populous metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city in Italy. Rome metropolitan area, Its metropolitan area is the third-most populous within Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber Valley. Vatican City (the smallest country in the world and headquarters of the worldwide Catholic Church under the governance of the Holy See) is an independent country inside the city boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |