|
50s
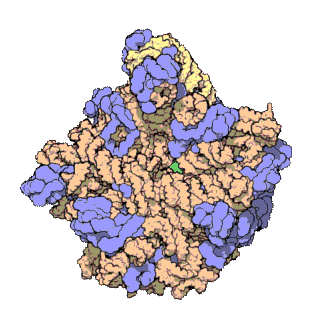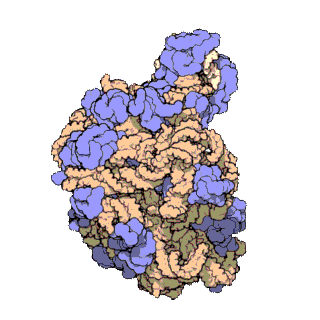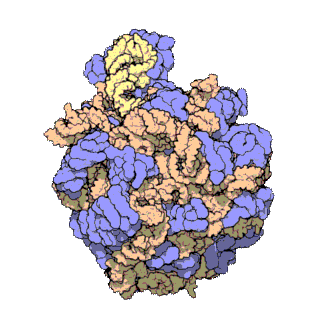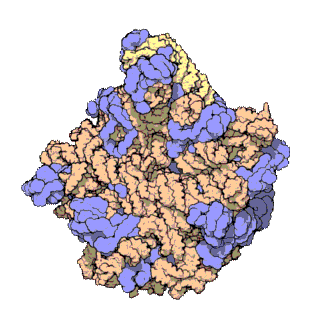
50 S is the larger subunit of the 70S ribosome of prokaryotes, i.e. bacteria and archaea. It is the site of inhibition for antibiotics such as macrolides, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, and the pleuromutilins. It includes the 5S ribosomal RNA and 23S ribosomal RNA. Despite having the same sedimentation rate, bacterial and archaeal ribosomes can be quite different. Structure 50S, roughly equivalent to the 60S ribosomal subunit in eukaryotic cells, is the larger subunit of the 70S ribosome of prokaryotes. The 50S subunit is primarily composed of proteins but also contains single-stranded RNA known as ribosomal RNA (rRNA). rRNA forms secondary and tertiary structures to maintain the structure and carry out the catalytic functions of the ribosome. X-ray crystallography has yielded electron density maps allowing the structure of the 50S in '' Haloarcula marismortui'' (archaeon) to be determined to 2.4 Å resolutionand of the 50S in the '' Deinococcus radiodurans'' (bact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the riboso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
70S Ribosome
Ribosomes () are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain via an anticodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
23S Ribosomal RNA
The 23S rRNA is a 2,904 nucleotide long (in ''E. coli'') component of the large subunit (50S) of the bacterial/archean ribosome and makes up the peptidyl transferase center (PTC). The 23S rRNA is divided into six secondary structural domains titled I-VI, with the corresponding 5S rRNA being considered domain VII. The ribosomal peptidyl transferase activity resides in domain V of this rRNA, which is also the most common binding site for antibiotics that inhibit translation, making it a target for ribosomal engineering. A well-known member of this antibiotic class, chloramphenicol, acts by inhibiting peptide bond formation, with recent 3D-structural studies showing two different binding sites depending on the species of ribosome. Numerous mutations in domains of the 23S rRNA with Peptidyl transferase activity have resulted in antibiotic resistance. 23S rRNA genes typically have higher sequence variations, including insertions and/or deletions, compared to other rRNAs. The eukary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form SSU rRNA, small and LSU rRNA, large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and Translation (biology), translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins, though this ratio differs between Prokaryote, prokaryotes and Eukaryote, eukaryotes. Structure Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can vary across organisms, Base pair, base-pairing within these sequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague (disease), plague, cholera, and typhoid fever. Its use by mouth or by injection is only recommended when safer antibiotics cannot be used. Monitoring both blood levels of the medication and blood cell levels every two days is recommended during treatment. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, nausea, and diarrhea. The bone marrow suppression may result in death. To reduce the risk of side effects treatment duration should be as short as possible. People with liver or kidney problems may need lower doses. In young infants, a condition known as gray baby syndrome may occur which results in a swollen stomach and Hypotension, low blood pressure. Its use near the end of pregnancy and during breastfeeding is typically not re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svedberg
In chemistry, a Svedberg unit or svedberg (symbol S, sometimes Sv) is a non- SI metric unit for sedimentation coefficients. The Svedberg unit offers a measure of a particle's size indirectly based on its sedimentation rate under acceleration (i.e. how fast a particle of given size and shape settles out of suspension). The svedberg is a measure of time, defined as exactly 10−13 seconds (100 fs). For biological macromolecules like ribosomes, the sedimentation rate is typically measured as the rate of travel in a centrifuge tube subjected to high g-force. The svedberg (S) is distinct from the SI unit sievert or the non-SI unit sverdrup, which also use the symbol Sv, and to the SI unit Siemens which uses the symbol S too. Naming The unit is named after the Swedish chemist Theodor Svedberg (1884–1971), winner of the 1926 Nobel Prize in chemistry for his work on disperse systems, colloids and his invention of the ultracentrifuge. Factors The Svedberg coef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form SSU rRNA, small and LSU rRNA, large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and Translation (biology), translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins, though this ratio differs between Prokaryote, prokaryotes and Eukaryote, eukaryotes. Structure Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can vary across organisms, Base pair, base-pairing within these sequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5S Ribosomal RNA
The 5S ribosomal RNA (5S rRNA) is an approximately 120 nucleotide-long ribosomal RNA molecule with a mass of 40 kDa. It is a structural and functional component of the large subunit of the ribosome in all domains of life (bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes), with the exception of mitochondrial ribosomes of fungi and animals. The designation 5S refers to the molecule's sedimentation coefficient in an ultracentrifuge, which is measured in Svedberg units (S). Biosynthesis In prokaryotes, the 5S rRNA gene is typically located in the rRNA operons downstream of the small and the large subunit rRNA, and co-transcribed into a polycistronic precursor. A particularity of eukaryotic nuclear genomes is the occurrence of multiple 5S rRNA gene copies (5S rDNA) clustered in tandem repeats, with copy number varying from species to species. Eukaryotic 5S rRNA is synthesized by RNA polymerase III, whereas other eukaryotic rRNAs are cleaved from a 45S precursor transcribed by RNA polymerase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clindamycin
Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media (middle ear infections), and endocarditis. It can also be used to treat acne, and some cases of methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). In combination with quinine, it can be used to treat malaria. It is available by mouth, by injection into a vein, and as a cream or a gel to be applied to the skin or in the vagina. Common side effects include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, skin rashes, and pain at the site of injection. It increases the risk of hospital-acquired ''Clostridioides difficile'' colitis about fourfold and thus is only recommended for use when other antibiotics are not appropriate. It appears to be generally safe in pregnancy. It is of the lincosamide class and works by blocking bacteria from making protein. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolides
Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocycle, macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but has since been used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential Life extension, longevity therapeutic. Macrolides are a diverse group with many members of very different properties: * Macrolides with 14-, 15-, or 16-membered rings and two attached sugar molecules are antibiotics that bind to bacterial ribosomes, the key representative being erythromycin. The term "macrolide antibiotics" tend to refer to just this class. * Some macrolides with very large (20+ membered) rings are immunosuppresants, the prototypical one being rapamycin. * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
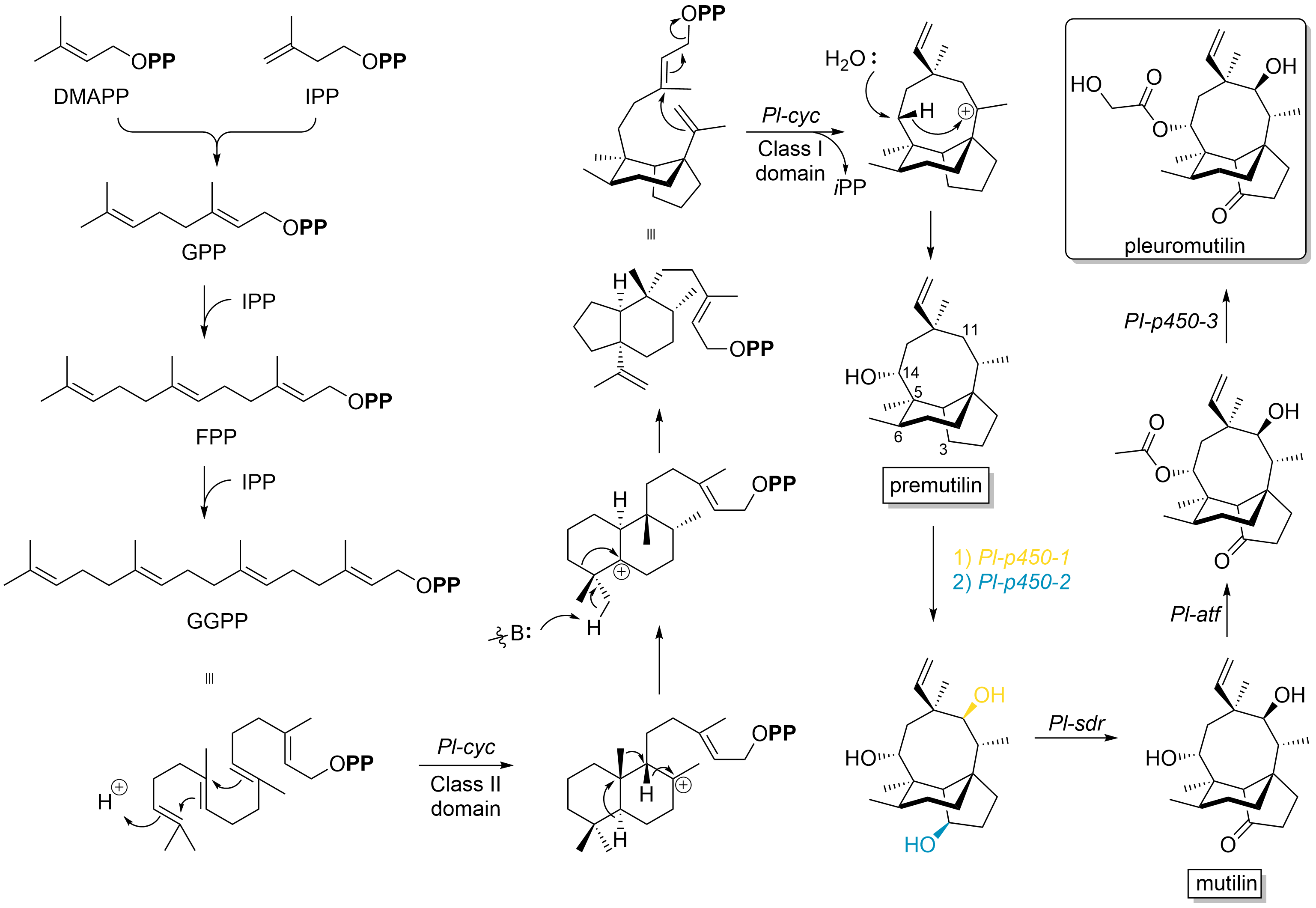
Pleuromutilin
Pleuromutilin and its derivatives are antibacterial drugs that inhibit protein synthesis in bacteria by binding to the peptidyl transferase component of the 50S subunit of ribosomes. This class of antibiotics includes the licensed drugs lefamulin (for systemic use in humans), retapamulin (approved for topical use in humans), valnemulin and tiamulin (approved for use in animals) and the investigational drug azamulin. History Pleuromutilin was discovered as an antibiotic in 1951. It is derived from the fungi '' Omphalina mutila'' (formerly ''Pleurotus mutilus'') and '' Clitopilus passeckerianus'' (formerly ''Pleurotus passeckerianus''), and has also been found in '' Drosophila subatrata'', '' Clitopilus scyphoides'', and some other '' Clitopilus'' species. Total synthesis The total synthesis of pleuromutilin has been reported. Biosynthesis Pleuromutilin belongs to the class of secondary metabolites known as terpenes, which are produced in fungi through the mevalonate pathw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptidyl Transferase
The peptidyl transferase center (, PTC) is an Aminoacyltransferases, aminoacyltransferase ribozyme (RNA enzyme) located in the large subunit of the ribosome. It forms peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids during the Translation (genetics), translation process of protein biosynthesis. It is also responsible for peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis, allowing the release of the synthesized peptide chain at the end of translation. Peptidyl transferase activity is not mediated by any ribosomal proteins, but entirely by ribosomal RNA (rRNA). The catalytic activity of the PTC is a significant piece of evidence supporting the RNA World hypothesis. The PTC is a highly conserved region with a very slow rate of mutation. It is considered to be among the most ancient elements of the ribosome, probably predating the last universal common ancestor. The position of the PTC is analogous in all ribosomes (domain V in 23S numbering), being a part of the large subunit ribosomal RNA with the name only va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |