|
438
Year 438 (Roman numerals, CDXXXVIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Theodosius II, Theodosius and Anicius Acilius Glabrio Faustus, Glabrio (or, less frequently, year 1191 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 438 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantium * Emperor Theodosius II forbids the divulging of secrets of naval carpentry, probably to avoid its spread to the rising Vandalic Kingdom, Vandal power in North Africa. * February 15 – The ''Codex Theodosianus'', a collection of edicts of Roman law, is published. * Aelia Eudocia, wife of Theodosius II, goes on a pilgrimage to Jerusalem, bringing back with her Relic, holy relics to prove her faith. Europe * The last gladiatorial fights are held in the Colosseum in Rome. * King Hermeric of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahram V
Bahram V (also spelled Wahram V or Warahran V; ), also known as Bahram Gur (New Persian: , "Bahram the onager [hunter]"), was the Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings (''shahanshah'') from 420 to 438. The son of the incumbent Sasanian shah Yazdegerd I (), Bahram was at an early age sent to the Lakhmids, Lahkmid court in al-Hira, where he was raised under the tutelage of the Lakhmid kings. After the assassination of his father, Bahram hurried to the Sasanian capital of Ctesiphon with a Lakhmid army, and won the favour of the nobles and priests, according to a long-existing popular legend, after withstanding a trial against two lions. Bahram V's reign was generally peaceful, with two brief wars—first against his western neighbours, the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire, and then against his eastern neighbours, the Kidarites, who were disturbing the Sasanian eastern provinces. It was also during his reign that the Arsacid dynasty of Armenia, Arsacid line of Sasanian Armeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aelia Eudocia
Aelia Eudocia Augusta (; ; 460 AD), also called Saint Eudocia, was an Eastern Roman empress by marriage to Emperor Theodosius II (). Daughter of an Athenian philosopher, she was also a poet, whose works include ''Homerocentones'', or Homeric retellings of Biblical stories. After an estrangement with Theodosius, she permanently settled in Jerusalem, where she supported the local population. Early life Aelia Eudocia was born with the name Athenaïs in Athens. The 6th century chronicler John Malalas describes her as Greek. Her exact year of birth is not known, but it is often given as 400 or 401 on the assumption that she was born around the same time of Emperor Theodosius II (401 AD). She was said to be of pagan background, and according to her contemporary Socrates Scholasticus, she was baptized shortly before her marriage to Theodosius. Her father, an Athenian sophist named Leontius, taught rhetoric at the Academy of Athens, where people from all over the Mediterranean came t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
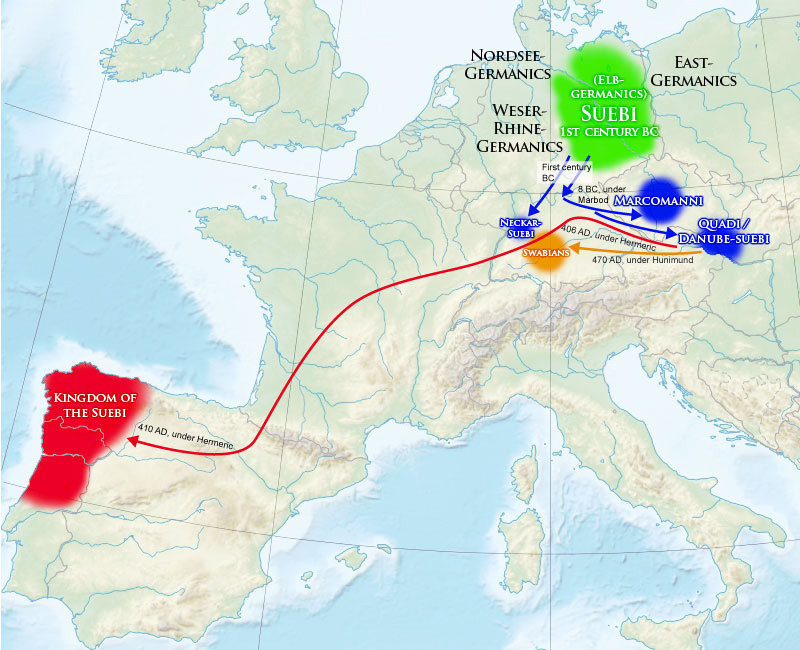
Suebic Kingdom Of Galicia
The Kingdom of the Suebi (), also called the Kingdom of Galicia () or Suebi Kingdom of Galicia (), was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from the Roman Empire. Based in the former Roman provinces of Gallaecia and northern Lusitania, the de facto kingdom was established by the Suebi about 409, and during the 6th century it became a formally declared kingdom identifying with Gallaecia. It maintained its independence until 585, when it was annexed by the Visigoths, and was turned into the sixth province of the Visigothic Kingdom in Hispania. History Origins Little is known about the Suebi who crossed the Rhine on the night of 31 December 406 AD and entered the Roman Empire. It is speculated that these Suevi are the same group as the Quadi, who are mentioned in early writings as living north of the middle Danube, in what is now lower Austria and western Slovakia,Thompson, ''Romans and Barbarians'', 152 and who played an important part in the Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazdegerd II
Yazdegerd II (also spelled Yazdgerd and Yazdgird; ), was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 438 to 457. He was the successor and son of Bahram V (). His reign was marked by wars against the Eastern Roman Empire in the west and the Kidarites in the east, as well as by his efforts and attempts to strengthen royal centralisation in the bureaucracy by imposing Zoroastrianism on the non-Zoroastrians within the country, namely the Christians. This backfired in Armenia, culminating in a large-scale rebellion led by the military leader Vardan Mamikonian, who was ultimately defeated and killed at the Battle of Avarayr in 451. Nevertheless, religious freedom was subsequently allowed in the country. Yazdegerd II was the first Sasanian ruler to assume the title of '' kay'' ("king"), which evidently associates him and the dynasty to the mythical Kayanian dynasty commemorated in the Avesta. His death led to a dynastic struggle between his two sons Hormizd III and Peroz I for the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rechila
Rechila (died 448) was the Suevic king of Galicia from 438 until his death. There are few primary sources for his life, but Hydatius was a contemporary Christian (non-Arian) chronicler in Galicia. When his father, Hermeric, turned ill in 438, he retired from active political life (dying in 441) and handed the reins of government and the royal title over to his son. He endeavoured to expand the Suevic kingdom to fill the vacuum left by the retiring Vandals and Alans. In 438 he defeated Andevotus, the '' comes Hispaniarum'', on the river Genil (Singillio). The Roman position in Iberia became so tenuous that three ''magistri utriusque militiae'' (masters of both services) were sent to the peninsula between 441 and 446. Invading southern Iberia, Rechila took the provincial capitals of Mérida in 439 and Seville in 441. These conquests were extremely significant, but nothing of the sequence of events leading to them is known. The provinces of Lusitania, Baetica, and Carthaginien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mons Colubrarius
The Battle of Mons Colubrarius was a battle in the Gothic War from 436 to 439. It was one of the many armed conflicts between the Gothic people and the Western Roman Empire during the first half of the fifth century. The main protagonists in the war were the Visigothic king Theodoric I and the commander-in-chief of the Western army General Aetius. The battle probably was fought near the French village Olonzac around 438 Year 438 (Roman numerals, CDXXXVIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Theodosius II, Theodosius and Anicius Acilius Glabrio Faustus, Glabrio (or, less frequ .... The Gothic War of 436-439 In the Gothic war that erupted in 436, the Goths initially had a predominance, but were forced to lay down their arms as a result of the successful offensive of the Romans under the leadership of Litorius in 437. The opponents made peace that, however, was short-lived, because the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Theodosianus
The ''Codex Theodosianus'' ("Theodosian Code") is a compilation of the laws of the Roman Empire under the Christian emperors since 312. A commission was established by Emperor Theodosius II and his co-emperor Valentinian III on 26 March 429 and the compilation was published by a constitution of 15 February 438. It went into force in the eastern and western parts of the empire on 1 January 439. The original text of the codex is also found in the ''Breviary of Alaric'' (also called ''Lex Romana Visigothorum''), promulgated on 2 February 506 by Visigoth King Alaric II. Development On 26 March 429, Emperor Theodosius II announced to the Senate of Constantinople his intention to form a committee to codify all of the laws (''leges'', singular ''lex'') from the reign of Constantine up to Theodosius II and Valentinian III.Peter Stein, pp. 37–38 The laws in the code span from 312 to 438, so by 438 the "volume of imperial law had become unmanageable". Twenty-two scholars, working in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late antiquity.Norman A. Stillman ''The Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetius (magister Militum)
Flavius Aetius (also spelled Aëtius; ; 390 – 21 September 454) was a Roman general and statesman of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most influential man in the Empire for two decades (433454). He managed policy in regard to the attacks of barbarian federates settled throughout the West. Notably, he mustered a large Roman and allied (''foederati'') army in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains, ending an invasion of Gaul by Attila in 451, though the Hun and his subjugated allies still managed to invade Italy the following year, an incursion best remembered for the Sack of Aquileia and the intercession of Pope Leo I. In 454, he was assassinated by the emperor Valentinian III. Aetius has often been called the "Last of the Romans". Edward Gibbon refers to him as "the man universally celebrated as the terror of Barbarians and the support of the Republic" for his victory at the Catalaunian Plains. J.B. Bury notes, "That he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermeric
Hermeric (died 441) was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438. Biography Before 419 Nothing is known for sure about Hermeric before 419, the year in which he is first mentioned; namely, he became king of the Suebi (or Suevi) in the city of Braga (Bracara Augusta) according to bishop Hydatius (who wrote his chronicle around the year 470). Although bishop Isidore of Seville, writing his '' Historia de regibus Gothorum, Vandalorum et Suevorum'' two centuries after the fact, claims that Hermeric was already king of the Suebi from 406, Isidore based himself on primarily on Jerome, Hydatius, Prosper of Aquitaine and Orosius, none of whom mentions Hermeric prior to 419. Hermeric was a pagan and an enemy of the Roman Empire throughout his life. He is given a reign of thirty-two years in most manuscripts of Isidore of Seville's '' Historia Suevorum'', but one manuscript does list his reign as fourteen years.Thompson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anicius Acilius Glabrio Faustus
Anicius Acilius Glabrio Faustus ( 425–443) was an aristocrat of the later Roman Empire. He was Urban prefect three times before 437, consul in 438, and briefly Praetorian prefect of Italy in 442. Faustus was selected to promulgate the ''Theodosian Code'' in the Western Empire. Faustus was the son of Acilius Glabrio Sibidius, who is known from a dedication to him from Faustus. Sibidius was a member of the lineage of the Acilii Glabriones, who descended from the consul of 191 BC, Manius Acilius Glabrio. Cameron states his mother was one of the house of the gens Anicia, although unable to identify the woman. His descendants include Rufius Achilius Maecius Placidus (cos. 481), Anicius Acilius Aginantius Faustus (cos. 483), and Rufius Achilius Sividius Rufius Achilius Sividius ( 483–488) was a Roman senator under Odoacer's rule. His brothers included Rufius Achilius Maecius Placidus, and Anicius Acilius Aginantius Faustus. Biography He is defined as "quaestor" (perhaps '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( ; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450), called "the Calligraphy, Calligrapher", was Roman emperor from 402 to 450. He was proclaimed ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' as an infant and ruled as the Eastern Empire's sole emperor after the death of his father Arcadius in 408. His reign was marked by the promulgation of the Theodosian law code and the construction of the Theodosian Walls of Constantinople. He also presided over the outbreak of two great Christological controversies, Nestorianism and Eutychianism. Early life Theodosius was born on 10 April 401 as the only son of Emperor Arcadius and his wife Aelia Eudoxia.''PLRE'' 2, p. iarchive:prosopography-later-roman-empire/PLRE-II/page/1100/mode/2up, 1100 On 10 January 402, at the age of 9 months, he was proclaimed co-''augustus'' by his father, thus becoming the youngest to bear the imperial title Michael III, up to that point. On 1 May 408, his father died and the seven-year-old boy became the sole emperor of the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |