|
42nd Division (Imperial Japanese Army)
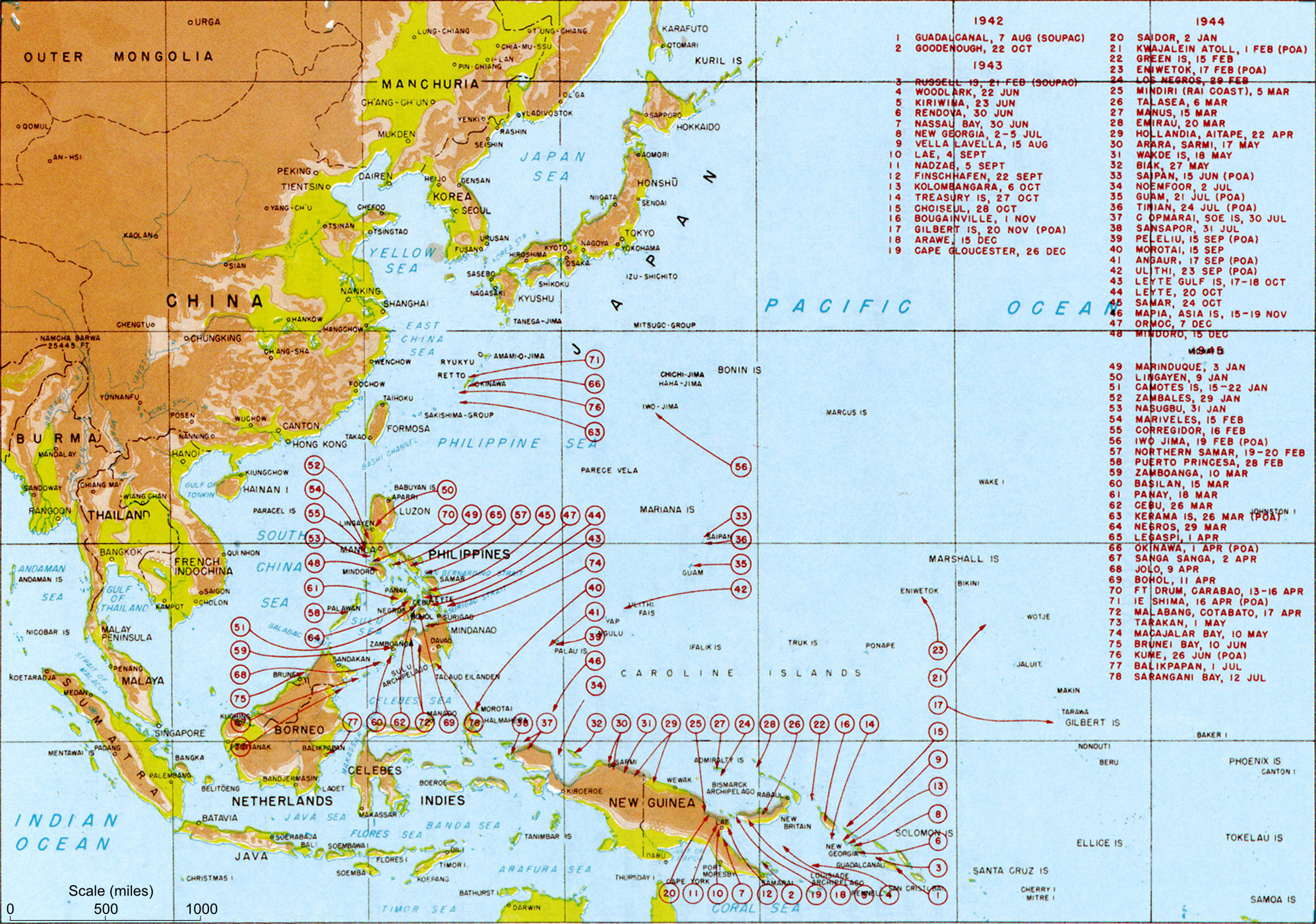
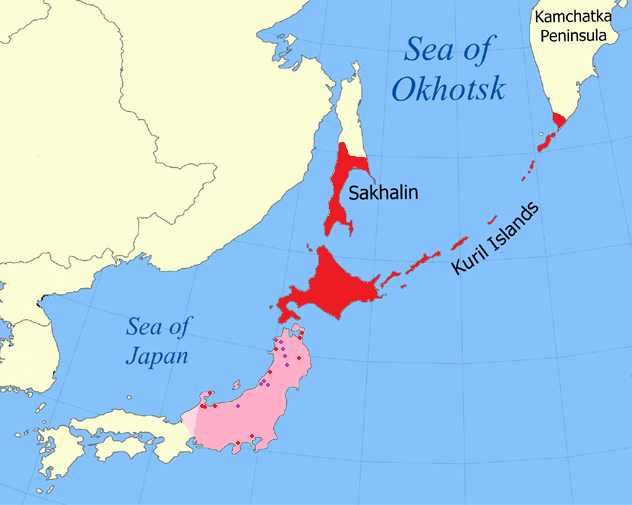
The was an infantry division of the Imperial Japanese Army. Its call sign was the The Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) ''42nd Division'' was raised as a triangular division (type B, standard) on 1 June 1943 in Sendai, simultaneously with 43rd, 46th and 47th divisions. It was assigned 16 March 1944 to 27th army. An Itarkioi and Ketoebone detachments from ''42nd division'' have engaged in garrison duties at Simushir island (in Kuril Islands). The 12th field artillery regiment was detached from the ''42nd division'' in May 1944. As the 27th army was abolished 1 February 1945, the ''42nd division'' was transferred to Hokkaido and submitted directly to 5th area army. In July 1945, several thousands of personnel were detached to form other military units. While digging in at Wakkanai, Hokkaido to oppose a possible Soviet invasion from Sakhalin across the La Perouse Strait LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States. La, LA, or L.A. m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simushir
Simushir (russian: Симушир, ja, 新知島, translit=Shimushiru-tō, ain, シムシㇼ, translit=Simusir), meaning ''Large Island'' in Ainu, is an uninhabited volcanic island near the center of the Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It was formerly known as Marikan. History At the time of European contact, Simushir was inhabited by the Ainu. The island appears on an official map showing the territories of Matsumae Domain, a feudal domain of Edo period Japan dated 1644, and these holdings were officially confirmed by the Tokugawa shogunate in 1715. Russian explorer Gerasim Izmailov was marooned on Simushir in the early 1770s. He spent a full year subsisting on "scallops, grass, and roots". Sovereignty initially passed to Russia under the terms of the Treaty of Shimoda, but was returned to the Empire of Japan per the Treaty of Saint Petersburg along with the rest of the Kuril islands. The island was formerly administered as part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Disestablished In 1945
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese World War II Divisions
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies ( Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japane ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organization Of Kita And Minami Fortresses
The Kita and Minami Fortresses (Japanese ''kita'', "north" and ''minami'', "south") were defensive structures of the Imperial Japanese Army and Imperial Japanese Navy in the Kuril Archipelago. The most northerly points were on the Kokutan and Kurabu Zaki capes, and its coastal front on the Shumushu Strait near Lopatka Cape in the Soviet Union's Kamchatka peninsula. This military organization was under the Twenty-Seventh Army (Chishima Area Base Unit or Kuril Area Army), led by Shozo Terakura. The Twenty-seventh Army was under the leadership of the Fifth Area Army, under the command of Kiichiro Higuchi whose headquarters was in Sapporo, Hokkaidō. The Twenty-Seventh Army was composed of the 42nd and 91st Divisions. Kurile fortresses These defensive structures in the Kurile Islands were somewhat similar to the Karafuto fortifications. The key Japanese position was on Shumushu Island, whose defense consisted of permanent emplacements protected by field and AA artil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Mixed Brigades (Imperial Japanese Army)
Between 1937 and 1945 the Japanese Imperial Army formed 126 Independent Mixed Brigades (numbered 1–136 with some gaps), typically composed of various units detached from other formations. Some were composed of separate, independent assets (usually Independent Infantry Battalions). These brigades were task organized under unified command and were normally used in support roles, as security, force protection, POW and internment camp guards and labor in occupied territories. An Independent Mixed Brigade had between 5,000 and 11,000 troops. History The first two of these Independent Mixed Brigades formed by the Kwangtung Army in the 1930s were the IJA 1st Independent Mixed Brigade and the IJA 11th Independent Mixed Brigade. Each of these brigades was organized in a unique manner; the 1st was disbanded in 1937 while the 11th was formed into the IJA 26th Division in 1938. Later a series of Independent Mixed Brigades were formed for the purpose of garrisoning the large territories ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had become incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of the Japanese armed forces in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Perouse Strait
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States. La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * La (musical note), or A, the sixth note * "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figure 8'' (album) * ''L.A.'' (EP), by Teddy Thompson * ''L.A. (Light Album)'', a Beach Boys album * "L.A." (Neil Young song), 1973 * The La's, an English rock band * L.A. Reid, a prominent music producer * Yung L.A., a rapper * Lady A, an American country music trio * "L.A." (Amy Macdonald song), 2007 * "La", a song by Australian-Israeli singer-songwriter Old Man River Other media * l(a, a poem by E. E. Cummings * La (Tarzan), fictional queen of the lost city of Opar (Tarzan) * ''Lá'', later known as Lá Nua, an Irish language newspaper * La7, an Italian television channel * LucasArts, an American video game developer and publisher * Liber Annuus, academic journal Business, organizations, and government agencies * L.A. Screenings, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proposed Soviet Invasion Of Hokkaido
During the Soviet-Japanese War in August 1945, the Soviet Union made plans to invade Hokkaido, the northernmost of Japan's four main Home Islands. Opposition from the United States and doubts within the Soviet high command caused the plans to be canceled before the invasion could begin. Background In the last days of World War II, the Soviet Union declared war on Japan, as Stalin secretly agreed at Tehran and Yalta. The Soviet declaration of war was a major factor for the surrender of Japan on August 15. Richard B. Frank, ''Downfall: The End of the Imperial Japanese Empire'', New York: Random House, Penguin, 2001 .Extracts on-lineRobert James Maddox, ''Hiroshima in History: The Myths of Revisionism'', Columbia, Missouri, USA: University of Missouri Press, 2007 . Although all other Allies, including the United States, ceased all hostilities upon the surrender, Stalin ordered his troops to continue fighting to capture more Japanese territory and put the Soviets in a stronge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |