|
425 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 425 ( CDXXV) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Theodosius and Valentinianus (or, less frequently, year 1178 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 425 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Roman civil war: Summer – Joannes, Roman usurper, is defeated at the fortified city of Ravenna and brought to Aquileia. After a humiliating parade on a donkey and the insults of the populace, he is executed. * October 23 – Valentinian III, six-year-old son of Galla Placidia, is installed as emperor (''Augustus'') of the Western Roman Empire. Real power is in the hands of his mother who becomes a regent. * Flavius Aetius leads a force of Huns (60,000 men) into Northern Italy. He reaches a compromise with Placidia, in return f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, each with a fixed integer value. The modern style uses only these seven: The use of Roman numerals continued long after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, decline of the Roman Empire. From the 14th century on, Roman numerals began to be replaced by Arabic numerals; however, this process was gradual, and the use of Roman numerals persisted in various places, including on clock face, clock faces. For instance, on the clock of Big Ben (designed in 1852), the hours from 1 to 12 are written as: The notations and can be read as "one less than five" (4) and "one less than ten" (9), although there is a tradition favouring the representation of "4" as "" on Roman numeral clocks. Other common uses include year numbers on monuments and buildin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus (honorific)
''Augustus'' (plural ''Augusti''; , ; "majestic", "great" or "venerable") was the main title of the Roman emperors during Antiquity. It was given as both name and title to Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus (often referred to simply as Augustus) in 27 BC, marking his accession as Rome's first emperor. On his death, it became an official title of his successor, and was so used by all emperors thereafter. The feminine form '' Augusta'' was used for Roman empresses and other female members of the imperial family. The masculine and feminine forms originated in the time of the Roman Republic, in connection with things considered divine or sacred in traditional Roman religion. Their use as titles for major and minor Roman deities of the Empire associated the imperial system and family with traditional Roman virtues and the divine will and may be considered a feature of the Roman imperial cult. In Rome's Greek-speaking provinces, "Augustus" was translated as '' Sebastos'' (Σεβασ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
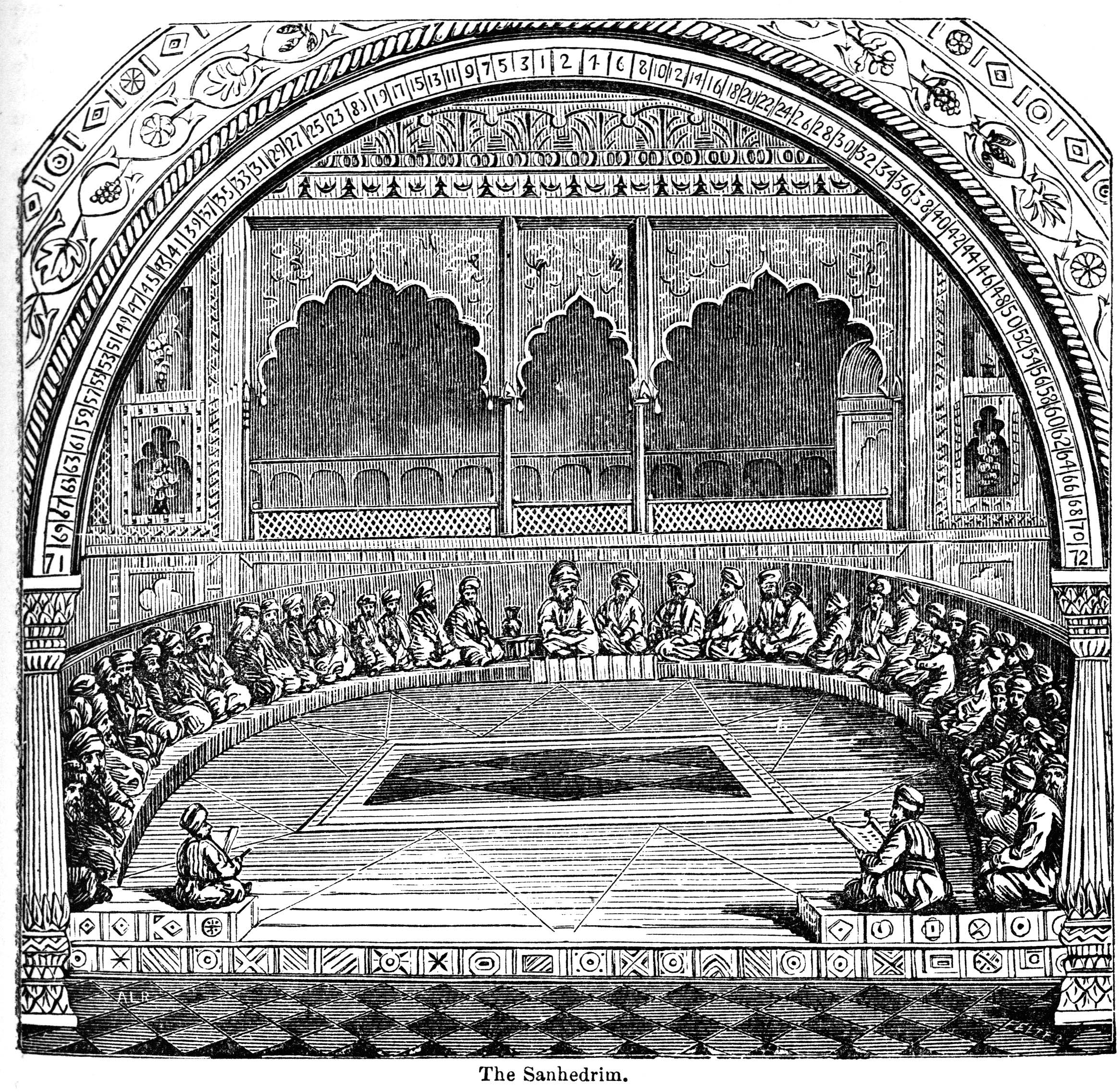
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Middle Aramaic , a loanword from , 'assembly,' 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was a Jewish legislative and judicial assembly of either 23 or 70 elders, existing at both a local and central level in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite courts called sanhedrins: Greater and Lesser. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city. There was only one Great Sanhedrin of 70 judges, which, among other roles, acted as a supreme court, taking appeals from cases that lesser courts decided. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier usually refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the Nasi, who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the Av Beit Din or the chief of the court, who was second to the Nasi and 69 general members. In the Second Temple period, the Great Sanhedrin met in the Temple in Jerusalem, in a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamaliel VI
Gamaliel VI (c. 370–425) was the last '' nasi'' of the ancient Sanhedrin. Gamaliel came into office around the year 400. On October 20, 415, an edict issued by the Emperors Honorius and Theodosius II stripped Gamaliel of his rank of honorary prefect. This decree also banned him from building new synagogues, adjudicating disputes between Jews and Christians, converting non-Jews to Judaism, and owning Christian slaves. Gamaliel probably died in 425, as the Codex Theodosianus The ''Codex Theodosianus'' ("Theodosian Code") is a compilation of the laws of the Roman Empire under the Christian emperors since 312. A commission was established by Emperor Theodosius II and his co-emperor Valentinian III on 26 March 429 an ... mentions an edict from the year 426, which transformed the patriarch's tax into an imperial tax after the death of the patriarch. Theodosius did not allow the appointment of a successor and in 429 terminated the Jewish patriarchate. Gamliel appears to have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plague (disease)
Plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium '' Yersinia pestis''. Symptoms include fever, weakness and headache. Usually this begins one to seven days after exposure. There are three forms of plague, each affecting a different part of the body and causing associated symptoms. Pneumonic plague infects the lungs, causing shortness of breath, coughing and chest pain; bubonic plague affects the lymph nodes, making them swell; and septicemic plague infects the blood and can cause tissues to turn black and die. The bubonic and septicemic forms are generally spread by flea bites or handling an infected animal, whereas pneumonic plague is generally spread between people through the air via infectious droplets. Diagnosis is typically by finding the bacterium in fluid from a lymph node, blood or sputum. Those at high risk may be vaccinated. Those exposed to a case of pneumonic plague may be treated with preventive medication. If infected, treatment is with antibiotics a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empires between its consecration in 330 until 1930, when it was renamed to Istanbul. Initially as New Rome, Constantinople was founded in 324 during the reign of Constantine the Great on the site of the existing settlement of Byzantium, and shortly thereafter in 330 became the capital of the Roman Empire. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century, Constantinople remained the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Although the city had been known as Istanbul since 1453, it was officially renamed as Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, who took control of the region on behalf of the Roman Republic, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Gallia Belgica, Belgica, and Gallia Aquitania, Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. This material culture was found throughout Gaul and as far east as modern-day southern Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary. Warbands led by the Gaul Brennus (leader of the Senones), Brennos Battle of the Allia, sacked Rome in 387 BC, becoming the only time Rome was conquered by a foreign enemy in 800 years. However, Gallia Cisalpina was conquered by the Romans in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magister Militum
(Latin for "master of soldiers"; : ) was a top-level military command used in the late Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, the emperor remaining the supreme commander) of the empire. The office continued to exist end evolve during the early Byzantine Empire. In Greek language, Greek sources, the term is translated either as ''strategos#Byzantine use, strategos'' or as ''stratelates'' (although these terms were also used non-technically to refer to commanders of different ranks). Establishment and development of the command The office of ''magister militum'' was created in the early 4th century, most likely when the Western Roman emperor Constantine the Great defeated all other contemporary Roman emperors, which gave him control over their respective armies. Because the Praetorian Guards and their leaders, the praetorian prefect, Praetorian Prefects, had suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Italy
Northern Italy (, , ) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. The Italian National Institute of Statistics defines the region as encompassing the four Northwest Italy, northwestern Regions of Italy, regions of Piedmont, Aosta Valley, Liguria and Lombardy in addition to the four Northeast Italy, northeastern Regions of Italy, regions of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, Trentino-Alto Adige, Veneto, Friuli-Venezia Giulia and Emilia-Romagna. With a total area of , and a population of 27.4 million as of 2022, the region covers roughly 40% of the Italian Republic and contains 46% of its population. Two of Italy's largest metropolitan areas, Milan and Turin, are located in the region. Northern Italy's GDP was estimated at Euro, €1 trillion in 2021, accounting for 56.5% of the Italian economy. Northern Italy has a rich and distinct culture. Thirty-seven of the fifty-nine List of World Heritage Sites in Italy, World Heritage Sites in Italy are found in the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, causing the westwards movement of Goths and Alans. By 430, they had established a vast, but short-lived, empire on the Danubian frontier of the Roman empire in Europe. Either under Hunnic hegemony, or fleeing from it, several central and eastern European peoples established kingdoms in the region, including not only Goths and Alans, but also Vandals, Gepids, Heruli, Suebians and Rugians. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |