|
420 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 420 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. The denomination 420 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Greece * The young and popular Alcibiades is elected "Strategos" (one of a board of ten generals) and begins to dominate Athenian life and politics. A Quadruple Alliance of Athens, Argos, Mantineia and Elis, which has been organised by Alcibiades (in opposition to Nicias) confronts a Spartan-Boeotian alliance. * Around 420 BC, Spartans were excluded from participating in the Olympic Games due to their ongoing conflicts with other Greek city-states, violating a peace treaty. This exclusion was part of a broader effort to maintain the peaceful atmosphere of the games. By topic Drama * Euripides' play '' The Suppliant Women'' is performed. * Euripides' play ''Phaethon'' is performed. Births Deaths * Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. Although the term is primarily used for Rome's pre-Julian calendars, it is often used inclusively of the Julian calendar established by Julius Caesar in 46 BC. According to most Roman accounts, #Romulus, their original calendar was established by their Roman legend, legendary list of kings of Rome, first king Romulus. It consisted of ten months, beginning in spring with March and leaving winter as an unassigned span of days before the next year. These months each had 30 or 31 days and ran for 38 nundinal cycles, each forming a kind of eight-day weeknine days inclusive counting, counted inclusively in the Roman mannerand ending with religious rituals and a Roman commerce, public market. This fixed calendar bore traces of its origin as an observational calendar, observational lunar calendar, lunar one. In particular, the most important days of each monthits kalends, nones (calendar), nones, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinisation of names, Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia (; modern Greek, modern: ; ancient Greek, ancient: ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Central Greece (administrative region), Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its largest city is Thebes, Greece, Thebes. Boeotia was also a region of ancient Greece, from before the 6th century BC. Geography Boeotia lies to the north of the eastern part of the Gulf of Corinth. It also has a short coastline on the Gulf of Euboea. It bordered on Megaris (now West Attica) in the south, Attica in the southeast, Euboea in the northeast, Opuntian Locris (now part of Phthiotis) in the north and Phocis in the west. The main mountain ranges of Boeotia are Mount Parnassus in the west, Mount Helicon in the southwest, Cithaeron in the south and Parnitha in the east. Its longest river, the Cephissus (Boeotia), Cephissus, flows in the central part, where most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
490 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 490 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Camerinus and Flavus (or, less frequently, year 264 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 490 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Greece * Darius I sends an expedition, under Artaphernes and Datis the Mede, across the Aegean to attack the Athenians and the Eretrians. Hippias, the aged ex-tyrant of Athens, is on one of the Persian ships in the hope of being restored to power in Athens. * When the Ionian Greeks in Asia Minor rebelled against Persia in 499 BC, Eretria joined Athens in sending aid to the rebels. As a result, Darius makes a point of punishing Eretria during his invasion of Greece. The city is sacked and burned and its inhabitants are enslaved. He intends the same fate for Athens. * September 12 &ndas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its methods and assumptions. Historically, many of the individual sciences, such as physics and psychology, formed part of philosophy. However, they are considered separate academic disciplines in the modern sense of the term. Influential traditions in the history of philosophy include Western philosophy, Western, Islamic philosophy, Arabic–Persian, Indian philosophy, Indian, and Chinese philosophy. Western philosophy originated in Ancient Greece and covers a wide area of philosophical subfields. A central topic in Arabic–Persian philosophy is the relation between reason and revelation. Indian philosophy combines the Spirituality, spiritual problem of how to reach Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlighten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Socratic Philosophy
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of these early philosophers spanned the workings of the natural world as well as human society, ethics, and religion. They sought explanations based on natural law rather than the actions of gods. Their work and writing has been almost entirely lost. Knowledge of their views comes from ''testimonia'', i.e. later authors' discussions of the work of pre-Socratics. Philosophy found fertile ground in the ancient Greek world because of the close ties with neighboring civilizations and the rise of autonomous civil entities, '' poleis''. Pre-Socratic philosophy began in the 6th century BC with the three Milesians: Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes. They all attributed the '' arche'' (a word that could take the meaning of "origin", "substance" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protagoras
Protagoras ( ; ; )Guthrie, p. 262–263. was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher and rhetorical theorist. He is numbered as one of the sophists by Plato. In his dialogue '' Protagoras'', Plato credits him with inventing the role of the professional sophist. Protagoras is also believed to have created a major controversy during ancient times through his statement that "Of all things the measure is Man, of the things that are, that they are, and of the things that are not, that they are not" which was usually rendered simply as "Man is the measure of all things," interpreted (possibly wrongly, since he disagreed) by Plato to mean that there is no objective truth; Protagoras seems to have meant that each person's own personal history, experiences and expectations, developed over their lifetime, determine their judgments, opinions, and statements regarding "truth" (which is the title of the book in which Protagoras made this statement). When a person makes a judgment about a certain thin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaethon (play)
''Phaethon'' () is the title of a lost tragedy written by Athenian playwright Euripides, first produced circa 420 BC, and covered the myth of Phaethon, the young mortal boy who asked his father the sun god Helios to drive his solar chariot for a single day. The play has been lost, though several fragments of it survive. Another treatment of the myth had been delivered earlier by Aeschylus in his lost play '' Heliades'' ("daughters of the Sun"), whose content and plot are even more fragmentary and obscure. The influence of Euripides' play on Ovid's version of the myth can be easily recognized.Diggle, p7–8/ref> From this now lost play only twelve fragments remain, covering around 400 lines or so. Plot Euripides' version of the myth was set in a mortal landscape, with Phaethon nominally the son of the Oceanid nymph Clymene by her lawful husband and putative father of her children Merops, king of the far-eastern land of Aethiopia, but in truth her product of an illicit affair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Suppliants (Euripides)
''The Suppliants'' (, ''Hiketides''; Latin ''Supplices''), also called ''The Suppliant Women'', first performed in 423 BC, is an ancient Greek play by Euripides. Background After Oedipus leaves Thebes, his sons fight for control of it. Polynices lays siege to Thebes against his brother Eteocles. Polynices has married the daughter of Adrastus, King of Argos. And so Polynices has on his side the Argive army, leaders of which are the Seven against Thebes. The invaders lose the battle, and Polynices and Eteocles both die. Creon of Thebes, Creon takes power in Thebes and decrees the invaders are not to be buried. The mothers of the dead seek someone to help reverse this, so their sons can be buried. The population of Plataea came to Athens as suppliants after the destruction of their city in 427 BC, a few years before the performance of this play. They were allowed to stay in Athens and, exceptionally, they were granted Athenian citizenship. This event may have influenced the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
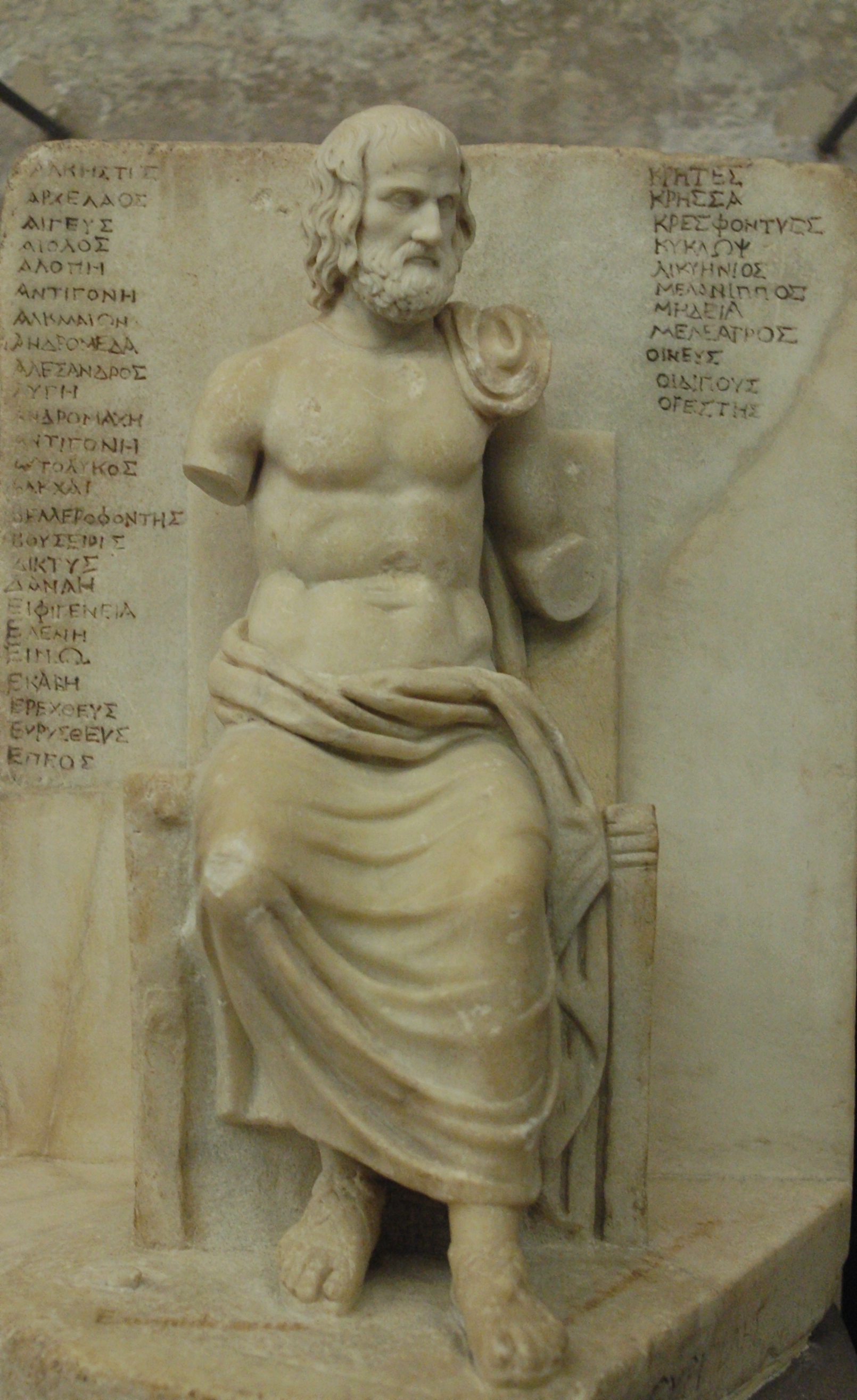
Euripides
Euripides () was a Greek tragedy, tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to him, but the ''Suda'' says it was ninety-two at most. Of these, eighteen or nineteen have survived more or less complete (''Rhesus (play), Rhesus'' is suspect). There are many fragments (some substantial) of most of his other plays. More of his plays have survived intact than those of Aeschylus and Sophocles together, partly because his popularity grew as theirs declinedMoses Hadas, ''Ten Plays by Euripides'', Bantam Classic (2006), Introduction, p. ixhe became, in the Hellenistic Age, a cornerstone of ancient literary education, along with Homer, Demosthenes, and Menander.L.P.E.Parker, ''Euripides: Alcestis'', Oxford University Press (2007), Introduction p. lx Euripides is identified with theatrical innovations that have profoundly influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used when designating years in the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian and Julian calendar, Julian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means "in the year of the Lord" but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", taken from the full original phrase "", which translates to "in the year of our Lord Jesus Christ". The form "BC" is specific to English language, English, and equivalent abbreviations are used in other languages: the Latin (language), Latin form, rarely used in English, is (ACN) or (AC). This calendar era takes as its epoch (date reference), epoch the traditionally reckoned year of the annunciation, conception or Nativity of Jesus, birth of Jesus. Years ''AD'' are counted forward since that epoch and years ''BC'' are counted backward from the epoch. There is no year zero in this scheme; thus the year AD 1 immediately follows the year 1 BC. This dating system was devised in 525 by Dionysius Exiguus but was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |