|
40th Infantry Division (Russian Empire)
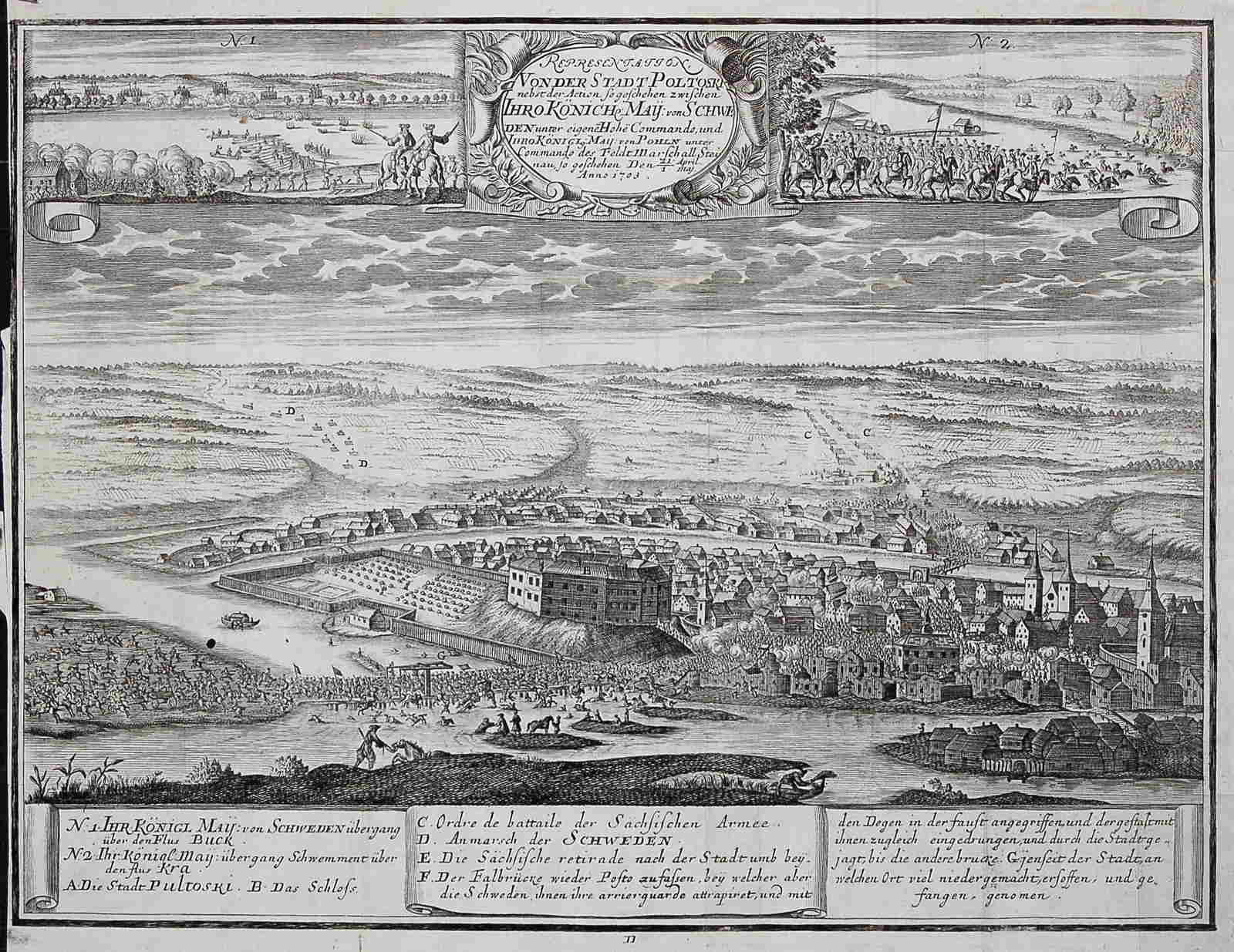
The 40th Infantry Division (, ''40-ya Pekhotnaya Diviziya'') was an infantry formation of the Russian Imperial Army. During the First World War on 13 July 1915 the 40th Infantry Division, alongside the 50th Infantry Division successfully defended the Pultusk bridgehead from German forces attempting to cross the river Narew at Pułtusk. Organization *1st Brigade **157th Imeretinsky Infantry Regiment (formed 11/6/1863) **158th Kutaisi Infantry Regiment (formed 11/6/1863) The 1st Brigade participated in the Battle of Kars. From 1892 the 1st Brigade was based at the Babruysk fortress, Belarus Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a .... *2nd Brigade **159th Infantry Regiment **160th Infantry Regiment *40th Artillery Brigade References {{Russian Empire Divisions Infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas II Of Russia
Nicholas II (Nikolai Alexandrovich Romanov; 186817 July 1918) or Nikolai II was the last reigning Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1 November 1894 until Abdication of Nicholas II, his abdication on 15 March 1917. He Wedding of Nicholas II and Alexandra Feodorovna, married Alexandra Feodorovna (Alix of Hesse), Alix of Hesse (later Alexandra Feodorovna) and had five children: the OTMA sisters – Grand Duchess Olga Nikolaevna of Russia, Olga, born in 1895, Grand Duchess Tatiana Nikolaevna of Russia, Tatiana, born in 1897, Grand Duchess Maria Nikolaevna of Russia, Maria, born in 1899, and Grand Duchess Anastasia Nikolaevna of Russia, Anastasia, born in 1901 — and the tsesarevich Alexei Nikolaevich, Tsarevich of Russia, Alexei Nikolaevich, who was born in 1904, three years after the birth of their last daughter, Anastasia. During his reign, Nicholas gave support to the economic and political reforms promoted by his prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babruysk Station
Babruysk Railway Station is a railway station in Babruysk, Belarus. History The station was built by Karl Otto Georg von Meck as part of the third section of the Libau–Romny Railway constructed 1871–1874. The Minsk-Babruysk section was completed onin September 1873, with the first locomotive arriving that November. Over the next few decades the facilities of the railway service was improved, with a station building being completed in 1900. In 1932 a new connection to Starushki was added. Tsar Nicholas II visited Babruysk Station in December, 1904, where he reviewed the 1st Brigade of the 40th Infantry Division of the Imperial Russian Army The Imperial Russian Army () was the army of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of Regular army, regular troops and ..., stationed at the nearby Babruysk fortress. 10 billion rubles was spent in the 2004 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Coat Of Arms Of Russian Empire
Lesser, from Eliezer (, "Help/Court of my God"), is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Adolf Lesser (1851–1926), German physician * Aleksander Lesser (1814–1884), Polish painter and art critic * Anton Lesser (born 1952), British actor * Axel Lesser (born 1946), East German cross country skier * Edmund Lesser (1852–1918), German dermatologist * Erik Lesser (born 1988), German biathlete * Friedrich Christian Lesser (1692–1754), German theologian * Gabriele Lesser (born 1960), German historian and journalist * George Lesser, American musician * Gerald S. Lesser (1926–2010), American psychologist * Henry Lesser (born 1963), German footballer * J Lesser (born 1970), American musician * Len Lesser Leonard King Lesser (December 3, 1922 – February 16, 2011) was an American character actor and comedian best known for his recurring role as Uncle Leo on ''Seinfeld''. He was also known for his role as Garvin on '' Everybody Loves Raymond.'' ... (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Imperial Army
The Imperial Russian Army () was the army of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of Regular army, regular troops and two forces that served on separate regulations: the Cossacks, Cossack troops and the Islam in Russia, Muslim troops. A regular Russian army existed after the end of the Great Northern War in 1721.День Сухопутных войск России. Досье [''Day of the Ground Forces of Russia. Dossier''] (in Russian). TASS. 31 August 2015. During his reign, Peter the Great accelerated the modernization of Russia's armed forces, including with a decree in 1699 that created the basis for recruiting soldiers, military regulations for the organization of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
50th Infantry Division (Russian Empire)
The 50th Infantry Division (, ''50-ya Pekhotnaya Diviziya'') was an infantry formation of the Russian Imperial Army. Its headquarters was located at Saint Petersburg. Organization It was part of the 18th Army Corps (Russian Empire), 18th Army Corps. *1st Brigade ** 197th Lesnoi Infantry Regiment ** 198th Alexander Nevsky Infantry Regiment *2nd Brigade ** 199th Kronstadt Infantry Regiment ** 200th Kronshlotsky Infantry Regiment *50th Artillery Brigade References {{Russian Empire Divisions Infantry divisions of the Russian Empire Military units and formations disestablished in 1918 Saint Petersburg Governorate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial German Army
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the leadership of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, and was dissolved in 1919, after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I (1914–1918). In the Federal Republic of Germany, the term refers to the German Army, the land component of the . Formation and name The states that made up the German Empire contributed their armies; within the German Confederation, formed after the Napoleonic Wars, each state was responsible for maintaining certain units to be put at the disposal of the Confederation in case of conflict. When operating together, the units were known as the German Federal Army, Federal Army (). The Federal Army system functioned during List of wars: 1800–1899, various conflicts of the 19th century, such as the First Schleswig War from 1848 to 1852. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narew
The Narew (; ; or ) is a 499-kilometre (310 mi) river primarily in north-eastern Poland. It is a tributary of the river Vistula. The Narew is one of Europe's few braided rivers, the term relating to the twisted channels resembling braided hair. Around 57 kilometres (35 mi) of the river flows through western Belarus. Etymology The name of the river is from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*nr'' primarily associated with ''water'' (compare Neretva, Neris, Ner and Nur) or from a Lithuanian language verb ''nerti'' associated primarily with ''diving'' and ''flood''. Name of the lower portion The portion of the river between the junctions with the Western Bug and the Vistula is also known as the Bugonarew, Narwio-Bug, Narwo-Bug, Bugo-Narew, Narwiobug or Narwobug. At the confluence near Zegrze the Bug is 1.6× longer, drains a 1.4× larger basin, and has a slightly greater average discharge (158 m³/s at Wyszków vs 146 m³/s at Pułtusk for the Narew, both ~25 km abov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pułtusk
Pułtusk () is a town in Poland, by the river Narew. Located north of Warsaw in the Masovian Voivodeship, it has a population of 19,224 as of 2023. Known for its historic architecture and Europe's longest paved marketplace ( in length), it is a popular weekend destination for the residents of Warsaw. Pułtusk is one of the oldest towns in Poland, having received town rights from Duke Siemowit I of Masovia in 1257. Throughout the 15th and 17th centuries, the settlement was a significant economic centre of Masovia. The favourable geographical placement of the town on the Narew, along which goods were transported to the port of Gdańsk on the Baltic Sea, contributed to the town's importance. Pułtusk was also the site of notable events, such as the Napoleon's 1806 battle, and the world's largest meteorite shower to date in 1868, among others. History Middle Ages The town has existed since at least the 10th century. In the Middle Ages, the Castle in Pułtusk was one of the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kars
The Battle of Kars was a Russian victory over the Ottoman Empire during the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878). The battle for the city took place on November 17, 1877, and resulted in the Russians capturing the city along with a large portion of the Ottoman forces defending the city. Although the actual battle for the city lasted a single night, fighting for the city began in the summer of that year. The idea of taking the city was considered impossible by some in Russian high command and many soldiers, who thought it would lead to needlessly high Russian casualties without any hopes of success due to the strength of the Ottoman position. Loris Melikov and others among the Russian command, however, devised a plan of attack that saw Russian forces conquer the city after a night of long and hard fighting. The Ottoman defeat at Kars had widespread consequences regionally, and the city was formally annexed at the Treaty of Berlin. Battles in the build up to the attack The start to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |