|
4-Hydroxytryptamines
4-Hydroxytryptamine (4-HT, 4-HTA), also known as ''N'',''N''-didesmethylpsilocin, is a naturally occurring tryptamine alkaloid. It is closely related chemically to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the psychedelic psilocin, and is the active form of the tryptamine alkaloid norbaeocystin. The compound is a serotonin receptor agonist, including of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor, but in contrast to certain closely related compounds like psilocin, appears to be non-hallucinogenic. 4-HT may occur naturally in '' Psilocybe baeocystis'' and ''Psilocybe cyanescens''. It may serve as an alternative precursor in the biosynthesis of psilocybin (4-PO-DMT) in psilocybin mushrooms. Pharmacology 4-HT is a potent agonist of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor similarly to psilocin ( = 38nM and 21nM, respectively). It also shows affinity for the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor (Ki = 40nM), the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor (Ki = 95nM), and the serotonin 5-HT1B receptor (Ki = 1,050nM). The drug produces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocin
Psilocin, also known as 4-hydroxy-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (4-HO-DMT), is a substituted tryptamine alkaloid and a serotonergic psychedelic. It is present in most psychedelic mushrooms together with its phosphorylated counterpart psilocybin. Psilocybin, as well as synthetic esters such as 4-AcO-DMT (psilacetin; ''O''-acetylpsilocin) and 4-PrO-DMT (''O''-propionylpsilocin), are prodrugs of psilocin. Acting on the serotonin 5-HT2A receptors, psilocin's psychedelic effects are directly correlated with the drug's occupancy at these receptor sites. It also interacts with other serotonin receptors and targets. The subjective mind-altering effects of psilocin are highly variable in their qualitative nature but resemble those of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and ''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (DMT). Psilocin is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. Uses Psilocin is used recreationally, spirituality or shamanically, and medically. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin Receptor Agonist
A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT), a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors. Non-selective agonists Serotonergic psychedelics such as tryptamines (e.g., psilocybin, psilocin, , 5-MeO-DMT, bufotenin), lysergamides (e.g., , ergine ()), phenethylamines (e.g., mescaline, 2C-B, 25I-NBOMe), and amphetamines (e.g., , ) are non-selective agonists of serotonin receptors. Their hallucinogenic effects are specifically mediated by activation of the 5-HT2A receptor. Drugs that increase extracellular serotonin levels such as serotonin reuptake inhibitors (e.g., fluoxetine, venlafaxine), serotonin releasing agents (e.g., fenfluramine, ), and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (e.g., phenelzine, moclobemide) are indirect non-selective serotonin receptor agonists. They are used variously as antidepressant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precursor (biochemistry)
In chemistry, a precursor is a compound that participates in a chemical reaction that produces another compound. In biochemistry, the term "precursor" often refers more specifically to a chemical compound preceding another in a metabolic pathway, such as a protein precursor. Illicit drug precursors In 1988, the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances introduced detailed provisions and requirements relating the control of precursors used to produce drugs of abuse. In Europe the Regulation (EC) No. 273/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council on drug precursors was adopted on 11 February 2004. (European law on drug precursors) Illicit explosives precursors On January 15, 2013, the Regulation (EU) No. 98/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the marketing and use of explosives precursors was adopted. The Regulation harmonises rules across Europe on the making available, introduction, possession and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system, thus protecting the brain from harmful or unwanted substances in the blood. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the Capillary, capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive transport, passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and Molecular mass, large or Hydrophile, hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
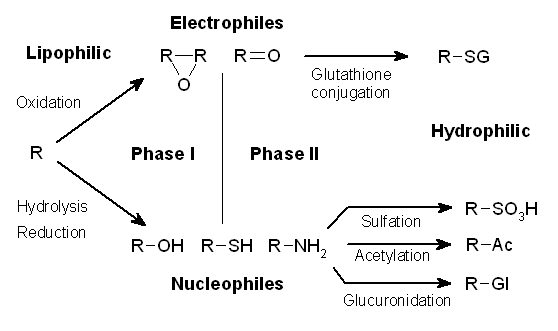
Metabolic Stability
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds (although in some cases the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves cause toxic effects). The study of drug metabolism is the object of pharmacokinetics. Metabolism is one of the stages (see ADME) of the drug's transit through the body that involves the breakdown of the drug so that it can be excreted by the body. The metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs is an important aspect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds (although in some cases the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves cause toxic effects). The study of drug metabolism is the object of pharmacokinetics. Metabolism is one of the stages (see ADME) of the drug's transit through the body that involves the breakdown of the drug so that it can be excreted by the body. The metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs is an important as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of Bilateria, bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the Limb (anatomy), limbs and Organ (anatomy), organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins. The peripheral nervous system can be divided into a somatic nervous system, somatic division and an autonomic nervous system, autonomic division. Each of these can further be differentiated into a sensory and a motor sector. In the somatic nervous system, the cranial nerves are part of the PNS with the exceptions of the olfactory nerve and epithelia and the optic nerve (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonergic Drug
{{disambig ...
A serotonergic substance, medication, or receptor protein is one that affects neurotransmission pathways that involve serotonin, as follows: * Serotonergic drugs ** Serotonin receptor agonists ** Serotonin receptor antagonists ** Serotonin reuptake inhibitors ** Serotonin releasing agents ** Serotonergic psychedelics * Serotonergic cells ** Serotonergic cell groups A serotonergic substance, medication, or receptor protein is one that affects neurotransmission pathways that involve serotonin, as follows: * Serotonergic drugs ** Serotonin receptor agonists ** Serotonin receptor antagonists ** Serotonin reupta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT1B Receptor
5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1B also known as the 5-HT1B receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HTR1B'' gene. The 5-HT1B receptor is a 5-HT receptor subtype. Tissue distribution and function 5-HT1B receptors are widely distributed throughout the central nervous system with the highest concentrations found in the frontal cortex, basal ganglia, striatum, and the hippocampus. The function of the 5-HT1B receptor differs depending upon its location. In the frontal cortex, it is believed to act as a terminal receptor inhibiting the release of dopamine. In the basal ganglia and the striatum, evidence suggests 5-HT signaling acts on an autoreceptor, inhibiting the release of serotonin and decreasing glutamatergic transmission by reducing miniature excitatory postsynaptic potential (mEPSP) frequency, respectively. In the hippocampus, a recent study has demonstrated that activation of postsynaptic 5-HT1B heteroreceptors produces a facilitation in excitatory synapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT1A Receptor
The serotonin 1A receptor (or 5-HT1A receptor) is a subtype of serotonin receptors, or 5-HT receptors, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarization and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene. Distribution The 5-HT1A receptor is the most widespread of all the 5-HT receptors. In the central nervous system, 5-HT1A receptors exist in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, Septum pellucidum, septum, amygdala, and Raphe nuclei, raphe nucleus in high densities, while low amounts also exist in the basal ganglia and thalamus. The 5-HT1A receptors in the raphe nucleus are largely somatodendritic autoreceptors, whereas those in other areas such as the hippocampus are postsynaptic receptors. Function Neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2C Receptor
The 5-HT2C receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). Like all 5-HT2 receptors, it is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gq/G11 and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. ''HTR2C'' denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor, that in humans is located on the X chromosome. As males have one copy of the gene and females have one of the two copies of the gene repressed, polymorphisms at this receptor can affect the two sexes to differing extent. Structure At the cell surface the receptor exists as a homodimer. The crystal structure has been known since 2018. Distribution 5-HT2C receptors are located mainly in the choroid plexus, and in rats is also found in many other brain regions in high concentrations, including parts of the hippocampus, anterior olfactory nucleus, substantia nigra, several brainstem nuclei, amygdala, subthalamic nucleus and lateral habenula. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity (pharmacology)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from Latin ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |