|
3MV-4
The 3MV planetary probe (short for 3rd generation Mars-Venus) is a designation for a common design used by early Soviet unmanned probes to Mars and Venus. It was an incremental improvement of earlier 2MV probes and was used for Zond 1, Zond 2 and Zond 3 missions to Mars as well as several Venera probes. It was standard practice of the Soviet space program to use standardized components as much as possible. All probes shared the same general characteristics and differed usually in equipment necessary for specific missions. Each probe also incorporated improvements based on experience with earlier missions. Original Design (1963-1965) The probe consisted of three primary parts. Orbital Compartment The core of the stack was a pressurized compartment called the Orbital Compartment. This part housed the spacecraft's control electronics, radio transmitters and receivers, batteries, astro-orientation equipment, and so on. The compartment was pressurized to around 100 kPa and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos 96
Kosmos 96 (russian: Космос 96 meaning ''Cosmos 96''), or 3MV-4 No.6, was a Soviet spacecraft intended to explore Venus. A 3MV-4 spacecraft launched as part of the Venera programme, Kosmos 96 was to have made a flyby of Venus, however, due to a launch failure, it did not depart low Earth orbit. Its re-entry into Earth's atmosphere is often speculated as the cause of the Kecksburg UFO incident. Mission This was the third and last spacecraft prepared for a Venus encounter. The 3MV-4 No.6 spacecraft was originally built for a mission to Mars, with launch scheduled for late 1964. After it was not launched by the end of its launch window, the spacecraft was repurposed, along with two other spacecraft which were launched as Venera 2 and Venera 3, to explore Venus. Instruments The eight scientific instruments were: * Three-component magnetometer * An imaging system * A solar X-radiation detector * Cosmic ray gas-discharge counters * Piezoelectric detectors * Ion traps * A photo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera 2
Venera 2 (russian: Венера-2 meaning ''Venus 2''), also known as 3MV-4 No.4 was a Soviet spacecraft intended to explore Venus. A 3MV-4 spacecraft launched as part of the Venera programme, it failed to return data after flying past Venus. Venera 2 was launched by a Molniya carrier rocket, flying from Site 31/6 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. The launch occurred at 05:02 UTC on 12 November 1965, with the first three stages placing the spacecraft and Blok-L upper stage into a low Earth parking orbit before the Blok-L fired to propel Venera 2 into heliocentric orbit bound for Venus, with perihelion of 0.716 AU, aphelion of 1.197 AU, eccentricity of 0.252, inclination of 4.29 degrees and orbital period of 341 days. The Venera 2 spacecraft was equipped with cameras, as well as a magnetometer, solar and cosmic x-ray detectors, piezoelectric detectors, ion traps, a Geiger counter and receivers to measure cosmic radio emissions. The spacecraft made its closest approach to Venus at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos 21
Kosmos 21 (russian: Космос 21 meaning ''Cosmos 21'') was a Soviet spacecraft. This mission has been tentatively identified by NASA as a technology test of the Venera series space probes. It may have been an attempted Venus impact, presumably similar to the later Kosmos 27 mission, or it may have been intended from the beginning to remain in geocentric orbit. In any case, the spacecraft never left Earth orbit after insertion by the Molniya launcher. The orbit decayed on 14 November 1963, three days after launch. Launch Kosmos 21 was launched at 06:23:34 GMT on 11 November 1963, atop a Molniya 8K78 s/n G103-18 carrier rocket flying from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. Spacecraft designation Beginning in 1963, the name Kosmos was given to Soviet spacecraft which remained in Earth orbit, regardless of whether that was their intended final destination. The designation of this mission as an intended planetary probe is based on evidence from Soviet and non-Soviet sourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 2
Zond 2 was a Soviet space probe, a member of the Zond program, and was the sixth Soviet spacecraft to attempt a flyby of Mars. (See Exploration of Mars) It was launched on November 30, 1964 at 13:12 UTC onboard Molniya 8K78 launch vehicle from Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan, USSR. The spacecraft was intended to survey Mars but lost communication before arrival. History Zond-2 carried a phototelevision camera of the same type later used to photograph the Moon on Zond 3. The camera system also included two ultraviolet spectrometers. As on Mars 1, an infrared spectrometer was installed to search for signs of methane on Mars. Zond 2 also carried six PPTs that served as actuators of the attitude control system. They were the first PPTs used on a spacecraft. The PPT propulsion system was tested during 70 minutes. Zond 2, a ''Mars 3MV-4A'' craft, was launched on November 30, 1964. During some maneuvering in early May 1965, communications were lost. Running on half power due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 3
Zond 3 was a 1965 space probe which performed a flyby of the Moon far side, taking a number of quality photographs for its time. It was a member of the Soviet Zond program while also being part of the Mars 3MV project. It was unrelated to Zond spacecraft designed for manned circumlunar missions (Soyuz 7K-L1). It is believed that Zond 3 was initially designed as a companion spacecraft to Zond 2 to be launched to Mars during the 1964 launch window. The opportunity to launch was missed, and the spacecraft was launched on a Mars-crossing trajectory as a spacecraft test, even though Mars was no longer attainable. Spacecraft design The spacecraft was of the 3MV-4 type, similar to Zond 2. In addition to a 106.4 mm focal length imaging system for visible light photography and ultraviolet spectrometry at 285-355 μm, it carried ultraviolet (190-275 μm) and infrared (3-4 μm) spectrophotometers, radiation sensors ( gas-discharge and scintillation counters), charged particle detec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera
The Venera (, , which means "Venus" in Russian) program was the name given to a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Ten probes successfully landed on the surface of the planet, including the two Vega program and Venera-Halley probes, while thirteen probes successfully entered the Venusian atmosphere. Due to the extreme surface conditions on Venus, the probes could only survive for a short period on the surface, with times ranging from 23 minutes to two hours. The ''Venera'' program established a number of precedents in space exploration, among them being the first human-made devices to enter the atmosphere of another planet ( Venera 3 on 1 March 1966), the first to make a soft landing on another planet ( Venera 7 on 15 December 1970), the first to return images from another planet's surface ( Venera 9 on 8 June 1975), the first to record sounds on another planet ( Venera 13 on 30 October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos 27
Kosmos 27 (russian: Космос 27 meaning ''Cosmos 27''), also known as Zond 3MV-1 No.3 was a space mission intended as a Venus impact probe. The spacecraft was launched by a Molniya 8K78 carrier rocket from Baikonur. The Blok L stage and probe reached Earth orbit successfully, but the attitude control system failed to operate. Launch Kosmos 27 was launched at 03:24:43 GMT on 27 March 1964, atop a Molniya 8K78 s/n T15000-27 carrier rocket flying from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. Spacecraft Kosmos 27 was a "third-generation" deep space planetary probes of the 3MV series of the Soviet Union. The Soviet engineers planned four types of the 3MV, the 3MV-1 (for Venus impact), 3MV-2 (for Venus flyby), 3MV-3 (for Mars impact), and 3MV-4 (for Mars flyby). The primary difference over the second-generation was vastly improved (and in many cases doubled) orientation system elements as well as improved onboard propulsion systems. While these four versions were meant to study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
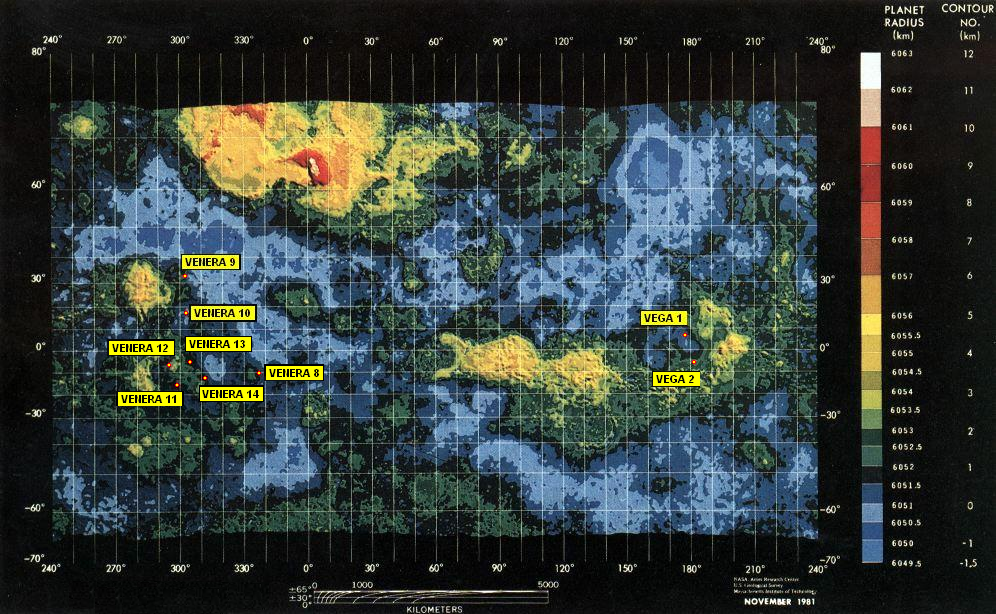
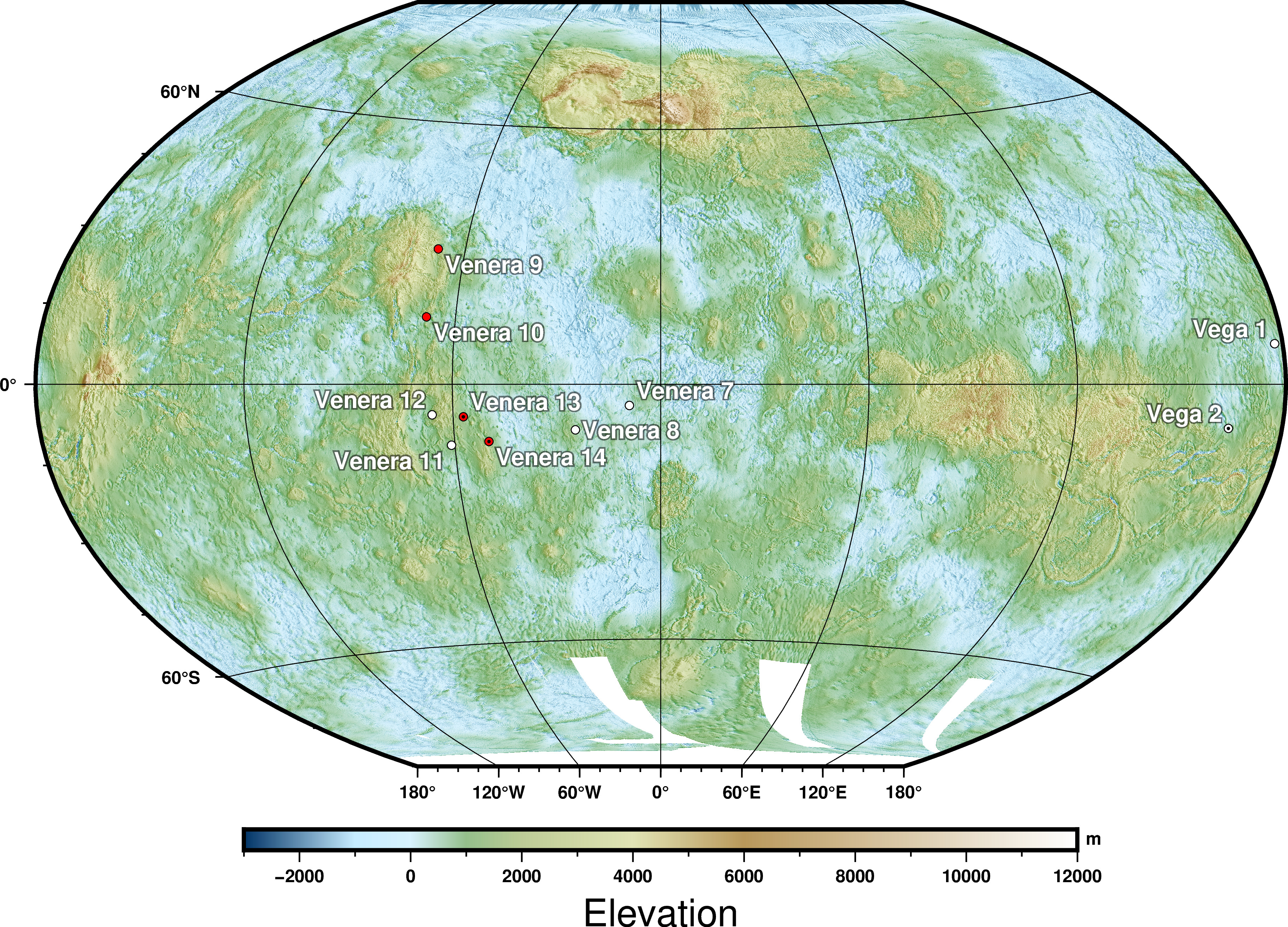
Venera 9
Venera 9 (russian: Венера-9, lit=Venus-9), manufacturer's designation: 4V-1 No. 660, was a Soviet uncrewed space mission to Venus. It consisted of an orbiter and a lander. It was launched on June 8, 1975, at 02:38:00 UTC and had a mass of . The orbiter was the first spacecraft to orbit Venus, while the lander was the first to return images from the surface of another planet. Orbiter The orbiter entered Venus orbit on October 20, 1975. Its mission was to act as a communications relay for the lander and to explore cloud layers and atmospheric parameters with several instruments and experiments. It performed 17 survey missions from October 26, 1975, to December 25, 1975. The orbiter consisted of a cylinder with two solar panel wings and a high gain parabolic antenna attached to the curved surface. A bell-shaped unit holding propulsion systems was attached to the bottom of the cylinder, and mounted on top was a sphere which held the lander. Orbiter design The instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera 6
Venera 6 (''russian: link=no, Венера-6'' meaning ''Venus 6''), or 2V (V-69) No.331, was a Soviet spacecraft, launched towards Venus to obtain atmospheric data. It had an on-orbit dry mass of . The spacecraft was very similar to Venera 4 although it was of a stronger design. When the atmosphere of Venus was approached, a capsule with a mass of was jettisoned from the main spacecraft. This capsule contained scientific instruments. During descent towards the surface of Venus, a parachute opened to slow the rate of descent. For 51 minutes on May 17, 1969, while the capsule was suspended from the parachute, data from the Venusian atmosphere were returned. It landed at . The spacecraft also carried a medallion bearing the State Coat of Arms of the Soviet Union and a bas-relief of Lenin to the night side of Venus. Given the results from Venera 4, the Venera 5 and Venera 6 landers contained new chemical analysis experiments tuned to provide more precise measurements of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera 7
Venera 7 (russian: Венера-7, lit=Venus 7) was a Soviet spacecraft, part of the Venera series of probes to Venus. When it landed on the Venusian surface on 15 December 1970, it became the first spacecraft to soft land on another planet and the first to transmit data from there back to Earth. Design The lander was designed to be able to survive pressure of up to and temperatures of . This was significantly greater than what was expected to be encountered but significant uncertainties as to the surface temperatures and pressure of Venus resulted in the designers’ opting for a large margin of error. The degree of hardening added mass to the probe which limited the amount of mass available for scientific instruments both on the probe itself and the interplanetary bus. The interplanetary bus carried a solar wind charged particle detector and a cosmic ray detector. On the lander there were temperature and pressure sensors as well as an accelerometer to measure atmospheric d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 482
Kosmos 482 (russian: Космос 482 meaning ''Cosmos 482''), launched March 31, 1972, at 04:02:33 UTC, was an attempted Venus probe which failed to escape low Earth orbit. It is expected to crash back to Earth between 2023 and 2025. Its landing module, which weighs , is highly likely to reach the surface of Earth in one piece as it was designed to withstand 300 G's of acceleration and 100 atmospheres of pressure. Beginning in 1962, the name Kosmos was given to Soviet spacecraft which remained in Earth orbit, regardless of whether that was their intended final destination. The designation of this mission as an intended planetary probe is based on evidence from Soviet and non-Soviet sources and historical documents. Typically Soviet planetary missions were initially put into an Earth parking orbit as a launch platform with a rocket engine and attached probe. The probes were then launched toward their targets with an engine burn with a duration of roughly four minutes. If the engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OKB-1
PAO S. P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia (russian: Ракетно-космическая корпорация «Энергия» им. С. П. Королёва, Raketno-kosmicheskaya korporatsiya "Energiya" im. S. P. Korolyova), also known as RSC Energia (, RKK "Energiya"), is a Russian manufacturer of spacecraft A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to spaceflight, fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth ... and space station components. The company is the prime developer and contractor of the Russian crewed spaceflight program; it also owns a majority of Sea Launch. Its name is derived from Sergei Korolev, the first chief of its design bureau, and the Russian word for energy. Overview Energia is the largest company of the Russian space industry and one of its key players. It is responsible for all opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |