|
313th Rifle Division (Soviet Union)
The 313th Rifle Division was a standard Red Army rifle division formed on July 15, 1941 in the Udmurt ASSR before being sent to the vicinity of Leningrad, first in the 7th Separate Army east of Lake Ladoga, and later in 32nd Army of Karelian Front, where it spent most of the war facing the Finnish Army in East Karelia. In consequence the division saw relatively uneventful service on this mostly quiet front until the summer of 1944, when it took part in the offensive that drove Finland out of the war. When this was accomplished, the division was redeployed to take the fight into Poland and then into the German heartland in the winter and spring of 1945. It ended the war north of Berlin after compiling a very distinguished record of service. Formation The 313th began forming on July 15, 1941 in the Udmurt ASSR in the Urals Military District. Its basic order of battle was as follows: * 1068th Rifle Regiment * 1070th Rifle Regiment * 1072nd Rifle Regiment * 856th Artillery Regiment Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army Flag
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to Orange (colour), orange and opposite Violet (color), violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–750 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary color (made from magenta and yellow) in the CMYK color model, and is the complementary color of cyan. Reds range from the brilliant yellow-tinged Scarlet (color), scarlet and Vermilion, vermillion to bluish-red crimson, and vary in shade from the pale red pink to the dark red burgundy (color), burgundy. Red pigment made from ochre was one of the first colors used in prehistoric art. The Ancient Egyptians and Mayan civilization, Mayans colored their faces red in ceremonies; Roman Empire, Roman generals had their bodies colored red to celebrate victories. It was also an important color in China, where it was used to color early pottery and later the gates and walls of palaces. In the Renaissance, the brillian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koszalin
Koszalin (; ; , ) is a city in northwestern Poland, in Western Pomerania. It is located south of the Baltic Sea coast, and intersected by the river Dzierżęcinka. Koszalin is also a county-status city and capital of Koszalin County of West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Founded in the Middle Ages, Koszalin was a seaport until the 17th century, and one of the main cities of Central Pomerania (along with Kołobrzeg and Słupsk). From 1950 to 1998 it was the administrative capital of Central Pomerania, as the Koszalin Voivodeship, and remains its largest city. Located on the main Expressway S6 (Poland), highway and railroad between the Tricity, Poland, Tricity and Szczecin, Koszalin is an important regional industrial, cultural and educational center. It is home to the Koszalin University of Technology, Polish Air Force Training Center and the Polish Border Guard Academy. Its Gothic architecture, Gothic Cathedral serves as the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Koszalin–Kołobrzeg. Kos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd Guards Tank Corps
Third or 3rd may refer to: Numbers * 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3 * , a fraction of one third * 1⁄60 of a ''second'', i.e., the third in a series of fractional parts in a sexagesimal number system Places * 3rd Street (other) * Third Avenue (other) * Highway 3 Music Music theory *Interval number of three in a musical interval **Major third, a third spanning four semitones **Minor third, a third encompassing three half steps, or semitones **Neutral third, wider than a minor third but narrower than a major third **Augmented third, an interval of five semitones **Diminished third, produced by narrowing a minor third by a chromatic semitone *Third (chord), chord member a third above the root *Degree (music), three away from tonic **Mediant, third degree of the diatonic scale **Submediant, sixth degree of the diatonic scale – three steps below the tonic ** Chromatic mediant, chromatic relationship by thirds *Ladder of thirds, similar to the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Belorussian Front
The 2nd Belorussian Front (, ''Vtoroi Belorusskiy front'', also romanized "Byelorussian SSR, Byelorussian"), was a Front (military formation), major formation of the Soviet Army during World War II, being equivalent to a Western army group. It was created in February 1944 as the Soviets were pushing the Germans back towards Byelorussia. General Colonel Pavel Kurochkin was its first commander. On hiatus in April 1944, its headquarters were reformed from the army headquarters of the disbanding 10th Army (Soviet Union), 10th Army. They took part in the Battle of Berlin, capture of Berlin, the capital of Nazi Germany. History The 2nd Belorussian Front was formed on the western axis on 24 February 1944 in accordance with a Stavka of the Supreme High Command, Stavka directive of 17 February, and included the 47th Army, 47th, 61st Army (Soviet Union), 61st, 70th Army (Soviet Union), 70th Armies, supported by the 6th Air Army and the Dnieper Flotilla. ''General-polkovnik'' Pavel Kur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
132nd Rifle Corps
Thirteen or 13 may refer to: * 13 (number) * Any of the years 13 BC, AD 13, 1913, or 2013 Music Albums * 13 (Black Sabbath album), ''13'' (Black Sabbath album), 2013 * 13 (Blur album), ''13'' (Blur album), 1999 * 13 (Borgeous album), ''13'' (Borgeous album), 2016 * 13 (Brian Setzer album), ''13'' (Brian Setzer album), 2006 * 13 (Die Ärzte album), ''13'' (Die Ärzte album), 1998 * 13 (The Doors album), ''13'' (The Doors album), 1970 * 13 (Havoc album), ''13'' (Havoc album), 2013 * 13 (HLAH album), ''13'' (HLAH album), 1993 * 13 (Indochine album), ''13'' (Indochine album), 2017 * 13 (Marta Savić album), ''13'' (Marta Savić album), 2011 * 13 (Norman Westberg album), ''13'' (Norman Westberg album), 2015 * 13 (Ozark Mountain Daredevils album), ''13'' (Ozark Mountain Daredevils album), 1997 * 13 (Six Feet Under album), ''13'' (Six Feet Under album), 2005 * 13 (Suicidal Tendencies album), ''13'' (Suicidal Tendencies album), 2013 * 13 (Solace album), ''13'' (Solace album), 2003 * 13 ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th Army (Soviet Union)
The 19th Army was a field army of the Soviet Union's Red Army, formed in 1941 and active during the Second World War. The army was formed three times, although only two of its formations saw combat. Its third formation was disbanded in June 1945 and its troops used to reinforce the Northern Group of Forces. First formation The army was first formed in June 1941 in the North Caucasus Military District under the command of General Lieutenant Ivan Konev. Division Commissar I.P. Sheklanov became Member of the Army's Military Soviet. Initially the army consisted of * 25th Rifle Corps (127th Rifle Division, 134th Rifle Division, and 162nd Rifle Division) * 34th Rifle Corps ( 129th Rifle Division, 158th Rifle Division, and 171st Rifle Division) * 38th Rifle Division * 442nd Corps Artillery Regiment * 471st Corps Artillery Regiment * and other units. Sources disagree as to whether a Mechanized Corps, either the 25th or the 26th, was directly subordinate to the Army as well. Three w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg. It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake Baikal, and the List of lakes by area, 14th largest freshwater lake by area in the world. It is comparable in size to Lake Ontario. ''Ladoga Lacus'', a methane lake on Saturn's moon Titan (moon), Titan, is named after the lake. Etymology In one of Nestor the Chronicler, Nestor's chronicles from the 12th century a lake called "the Great Nevo" is mentioned, a clear link to the Neva River and possibly further to Finnish language, Finnish ''nevo'' 'sea' or ''neva'' 'bog, quagmire'.:ru:Поспелов, Евгений Михайлович, Evgeny Pospelov: ''Geographical names of the world. Toponymic dictionary.'' Second edition. Astrel, Moscow 2001, pp. 106f. Ancient Norse sagas and Hanseatic treaties both mention a city made of lakes named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
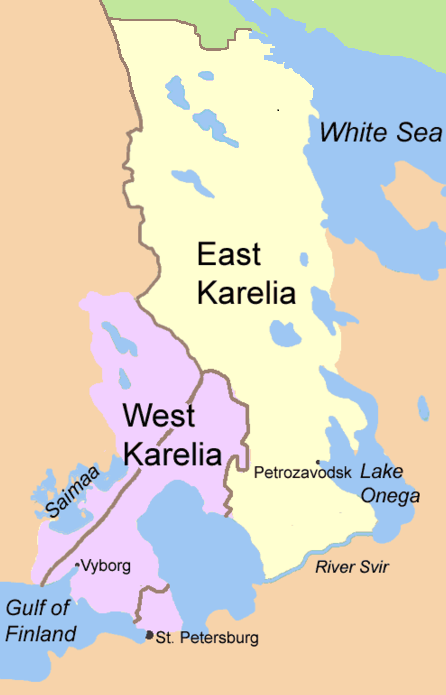
East Karelia
East Karelia (, ), also rendered as Eastern Karelia or Russian Karelia, is a name for the part of Karelia that is beyond the eastern border of Finland and since the Treaty of Stolbovo in 1617 has remained Eastern Orthodox and a part of Russia. It is separate from the western part of Karelia, called '' Finnish Karelia'' or historically ''Swedish Karelia'' (before 1808). Most of East Karelia has become part of the Republic of Karelia within the Russian Federation. It consists mainly of the old historical regions of Viena Karjala ( English: White Karelia) and Aunus Karjala ( English: Olonets Karelia). Culture and ideology 19th-century ethnic-nationalist Fennomans saw East Karelia as the ancient home of Finnic culture, "un-contaminated" by either Scandinavians or Slavs. In the sparsely populated East Karelian backwoods, mainly in White Karelia, Elias Lönnrot (1802–1884) collected the folk tales that ultimately would become Finland's national epic, the Kalevala (published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim
Baron Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim (, 4 June 1867 – 27 January 1951) was a Finnish military commander, aristocrat, and statesman. He served as the military leader of the White Guard (Finland), Whites in the Finnish Civil War (1918), as List of regents#Finland, Regent of Finland (1918–1919), as Chief of Defence (Finland), commander-in-chief of the Finnish Defence Forces during Finland in World War II, World War II (1939–1945), and as the sixth president of Finland (1944–1946). He became Finland's only Field marshal (Finland), field marshal in 1933 and was appointed honorary Marshal of Finland in 1942. Born into a Swedish-speaking population of Finland, Swedish-speaking family in the Grand Duchy of Finland, Mannerheim made a career in the Imperial Russian Army, serving in the Russo-Japanese War and the Eastern Front (World War I), Eastern Front of World War I and rising by 1917 to the rank of lieutenant general. He had a prominent place in the Coronation of Nicholas II and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyborg
Vyborg (; , ; , ; , ) is a town and the administrative center of Vyborgsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Karelian Isthmus near the head of Vyborg Bay, northwest of St. Petersburg, east of the Finnish capital Helsinki, and south of Russia's border with Finland, where the Saimaa Canal enters the Gulf of Finland. The most recent census population of Vyborg is Vyborg was founded as a medieval fortress in Finland under Swedish rule during the Third Swedish Crusade. After numerous wars between the Russians and Swedes, the Treaty of Nöteborg in 1323 defined the border of eastern Finland, and would separate the two cultures. Vyborg remained under Swedish rule until it was captured by the Russians during the Great Northern War. Under Russian rule, Vyborg was the seat of Vyborg Governorate until it was incorporated into the newly established Grand Duchy of Finland, an autonomous part of the Russian Empire. Finland declared its independence from R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (; ; ) is the approximately stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the westernmost point of Lake Ladoga, Pekonlahti. If the Karelian Isthmus is defined as the entire territory of present-day Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast to the north of the Neva and also a tiny part of the Republic of Karelia, the area of the isthmus is about . The smaller part of the isthmus to the southeast of the old Russia-Finland border is considered historically as Northern Ingria, rather than part of the Karelian Isthmus itself. The rest of the isthmus was historically a part of Finnish Karelia. This was conquered by the Russian Empire during the Great Northern War in 1712 and included within the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland (1809–1917) of the Russian Empire. When Finland became independent in 1917, the isthmus (excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |