|
312th Aeronautical Systems Group
The 312th Aeronautical Systems Group is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last active in June 2010 at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, where it was a component of Air Force Materiel Command. During World War II, as the 312th Bombardment Group, it operated primarily in the Southwest Pacific Theater as an A-20 Havoc light bomber unit assigned to Fifth Air Force. The group also flew the B-32 Dominator on several evaluation combat missions at the end of the war. It was awarded both the Distinguished Unit Citation and the Philippine Presidential Unit Citation for its combat service in New Guinea; the Western Pacific; Leyte, and Luzon. History : '' see: 312th Aeronautical Systems Wing for related lineage and history'' World War II The 312th Bombardment Group was activated on 15 March 1942 at Bowman Field (Fort Knox) Kentucky. It was redesignated 312th Bombardment Group (Dive) in July 1942 and trained in the United States for several months with Douglas A-24 Bans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Force Materiel Command
The Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC) is a Major Command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force (USAF). AFMC was created on July 1, 1992, through the amalgamation of the former Air Force Logistics Command (AFLC) and the former Air Force Systems Command (AFSC). AFMC is headquartered at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Dayton, Ohio. AFMC is one of nine Air Force List of Major Commands of the United States Air Force, Major Commands and has a workforce of approximately 80,000 military and civilian personnel. It is the Air Force's largest command in terms of funding and second in terms of personnel. AFMC's operating budget represents 31 percent of the total Air Force budget and AFMC employs more than 40 percent of the Air Force's total civilian workforce. The command conducts research, development, testing and evaluation, and provides the acquisition and life cycle management services and logistics support. The command develops, acquires and sustains the air power needed to defen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowman Field (Kentucky)
Bowman Field is a public airport southeast of downtown Louisville, in Jefferson County, Kentucky. The airport covers and has two runways. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) calls it a reliever airport for nearby Louisville Muhammad Ali International Airport. History Established in 1919, Bowman Field is Kentucky's first commercial airport and is the oldest continually operating commercial airfield in North America. It was founded by Abram H. Bowman, who was drawn to aviation by the interest generated during World War I. Bowman found an outlet for his enthusiasm after meeting and forming a brief partnership with Louisvillian Robert H. Gast, a pilot and World War I veteran of the Royal Flying Corps. Bowman leased a parcel of land east of Louisville from the U.S. Government in 1919 to operate the airfield, which opened in 1921. The first business ventures began with the aerial photography business in 1921, and the 465th Pursuit Squadron (Reserve) began operations at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). Yields in the low kilotons can devastate cities. A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than 1.2 megatons of TNT (5.0 PJ). Apart from the blast, effects of nuclear weapons include firestorms, extreme heat and ionizing radiation, radioactive nuclear fallout, an electromagnetic pulse, and a radar blackout. The first nuclear weapons were developed by the Allied Manhattan Project during World War II. Their production continues to require a large scientific and industrial complex, primari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okinawa Island
, officially , is the largest of the Okinawa Islands and the Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Islands of Japan in the Kyushu region. It is the smallest and least populated of the five Japanese archipelago, main islands of Japan. The island is approximately long, an average wide, and has an area of . It is roughly south of the main island of Kyushu and the rest of Japan. It is northeast of Taiwan. The total population of Okinawa Island was 1,384,762 in 2009. The greater Naha area has roughly 800,000 residents, while the city itself has about 320,000 people. Naha is the seat of Okinawa Prefecture on the southwestern part of Okinawa Island. Okinawa has a humid subtropical climate. Okinawa has been a strategic location for the United States Armed Forces since the Battle of Okinawa and the end of World War II. The island was formally controlled by the United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands until 1972, with around 26,000 U.S. military personnel stationed on Oki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
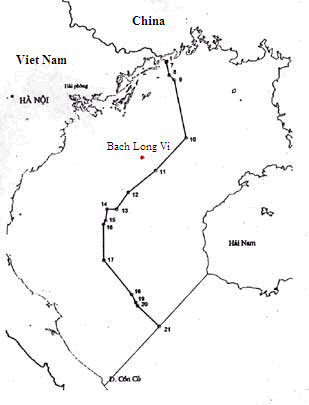
Tonkin Gulf
The Gulf of Tonkin is a gulf at the northwestern portion of the South China Sea, located off the coasts of Tonkin (northern Vietnam) and South China. It has a total surface area of . It is defined in the west and northwest by the northern coastline of Vietnam down to the Cồn Cỏ district, in the north by China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, and to the east by the Leizhou Peninsula and Hainan Island. English sources from the People's Republic of China refer to the Gulf of Tonkin as Beibu Wan. Description and etymology The name ''Tonkin'', written "" in chữ Hán characters and in the Vietnamese alphabet, means "eastern capital", and is the former toponym for Hanoi, the present capital of Vietnam. It is not to be confused with Tokyo, which is also written "" and also means "eastern capital". During the French colonial era, the northern region of today’s Vietnam was called ''Tonkin''. ''Bắc Bộ'' is the native Vietnamese name of Tonkin, which is the nowadays re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hainan Island
Hainan is an island province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally means "South of the Sea". The province has a land area of , of which Hainan Island is and the rest is over 200 islands scattered across three archipelagos: Zhongsha, Xisha and Nansha. It was part of Guangdong from 1950 to 1988, after which it was made a province of its own and was designated as a special economic zone by Deng Xiaoping, as part of the Chinese economic reform program. The Han Chinese population, who compose a majority of the population at 82%, speak a wide variety of languages including Standard Chinese, Hainam Min, Yue Chinese, Cantonese, Hakka Chinese, etc. Indigenous peoples such as the Hlai, a Kra–Dai-speaking ethnic group, are native to the island and compose 15% of the population. Their native languages include the Hlai langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated B-32 Dominator
The Consolidated B-32 Dominator (Consolidated Model 34) was an American heavy strategic bomber built for the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. A B-32 was involved in the last air combat engagement of the war, resulting in the war's last American air combat death. It was developed by Consolidated Aircraft in parallel with the Boeing B-29 Superfortress as a fallback design should the B-29 prove unsuccessful.Jones 1974, p. 106. The B-32 reached units in the Pacific only in mid-May 1945, and subsequently saw only limited combat operations against Japanese targets before the end of the war on 2 September 1945. Most of the extant orders of the B-32 were canceled shortly thereafter and only 118 B-32 airframes of all types were built. Design and development The engineering development of the B-29 had been underway since mid-1938 when, in June 1940, the United States Army Air Corps requested a similar design from the Consolidated Aircraft Company in case of developm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formosa
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The island of Taiwan, formerly known to Westerners as Formosa, has an area of and makes up 99% of the land under ROC control. It lies about across the Taiwan Strait from the southeastern coast of the Mainland China. The East China Sea is to the north of the island, the Philippine Sea to its east, the Luzon Strait directly to its south, and the South China Sea to its southwest. The ROC also controls a number of smaller islands, including the Penghu archipelago in the Taiwan Strait, Kinmen and Matsu in Fuchien near the Mainland coast, as well as Pratas and Taiping in the South China Sea. Geologically, the main island comprises a tilted fault block, characterized by the contrast between the eastern two-thirds, consisting mostly of five rugged mountain ranges running parallel to the east coast, and the flat to gently rolling plains of the western third, where the majority of the population resides. Sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butanol
Butanol (also called butyl alcohol) is a four-carbon alcohol with a formula of C4 H9 OH, which occurs in five isomeric structures (four structural isomers), from a straight-chain primary alcohol to a branched-chain tertiary alcohol; all are a butyl or isobutyl group linked to a hydroxyl group (sometimes represented as BuOH, ''sec''-BuOH, i-BuOH, and ''t''-BuOH). These are 1-butanol, two stereoisomers of ''sec''-butyl alcohol, isobutanol and ''tert''-butyl alcohol. Butanol is primarily used as a solvent and as an intermediate in chemical synthesis, and may be used as a fuel. Biologically produced butanol is called biobutanol, which may be ''n''-butanol or isobutanol. Isomers The unmodified term ''butanol'' usually refers to the straight chain isomer with the alcohol functional group at the terminal carbon, which is also known as 1-butanol. The straight chain isomer with the alcohol at an internal carbon is ''sec''-butyl alcohol or 2-butanol. The branched isomer with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas A-20 Havoc
The Douglas A-20 Havoc (company designation DB-7) is an American light bomber, attack aircraft, Intruder (air combat), night intruder, night fighter, and reconnaissance aircraft of World War II. Designed to meet an Army Air Corps requirement for a bomber, it was ordered by France for their air force before the USAAC decided it would also meet their requirements. French DB-7s were the first to see combat; after the fall of France, the bomber served with the Royal Air Force under the British military aircraft designation systems#Names, service name Boston. From 1941, night fighter and Intruder (air combat), intruder versions were given the service name Havoc. In 1942 USAAF A-20s saw combat in North Africa. It served with several Allies of World War II, Allied air forces, principally the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), the Soviet Air Forces (''VVS''), Soviet Naval Aviation (''AVMF''), and the Royal Air Force (RAF) of the United Kingdom. A total of 7,478 aircraft were built, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtiss P-40 Warhawk
The Curtiss P-40 Warhawk is an American single-engined, single-seat, all-metal fighter-bomber that first flew in 1938. The P-40 design was a modification of the previous Curtiss P-36 Hawk which reduced development time and enabled a rapid entry into production and operational service. The Warhawk was used by most Allies of World War II, Allied powers during World War II, and remained in frontline service until the end of the war. It was the third most-produced American fighter of World War II, after the North American P-51 Mustang and Republic P-47 Thunderbolt; by November 1944, when production of the P-40 ceased, 13,738 had been built,Murphy and McNiece 2009, p. 83. all at Curtiss-Wright Corporation's main production facilities in Buffalo, New York. P-40 Warhawk was the name the United States Army Air Corps gave the plane, and after June 1941, the USAAF adopted the name for all models, making it the official name in the US for all P-40s. The Commonwealth of Nations, British Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American A-36 Apache
The North American A-36 (company designation NA-97, listed in some sources as "Apache" or "Invader", but generally called Mustang) is the Attack aircraft, ground-attack/dive bomber version of the North American P-51 Mustang, from which it could be distinguished by the presence of rectangular, slatted dive brakes above and below the wings. A total of 500 A-36 dive bombers served in the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II, Mediterranean and South-East Asian theatre, Southeast Asia theaters during World War II before being withdrawn from operational use in 1944. The A-36 project was a stopgap measure intended to keep North American Aviation (NAA) assembly lines running during the first half of 1942 despite the US having exhausted its funds earmarked for fighter aircraft. Design and development With the introduction of the North American Mustang Mk I with the Royal Air Force's RAF Army Cooperation Command, Army Co-operation Squadrons in February 1942, the new fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |