|
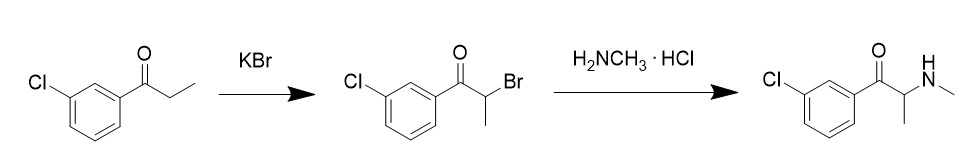
3-chloro-N-cyclopropylcathinone
3-Chloro-''N''-cyclopropylcathinone (3Cl-CpC; code names PAL-433, RTI-6037-39) is a stimulant and hybrid monoamine releasing agent and monoamine reuptake inhibitor of the cathinone family related to bupropion (3-chloro-''N''-''tert''-butylcathinone). It acts specifically as a dual serotonin releasing agent (SRA) and serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI). Its for induction of serotonin release is 1,328nM, whereas its values for monoamine reuptake inhibition are 265 to 533nM for dopamine, 2,150nM for norepinephrine, and 3,180nM for serotonin. The drug produces psychostimulant-like effects in animals, with a slow onset of action and a long duration of action. The activities of the individual enantiomers of 3Cl-CpC, (–)-3Cl-CpC (PAL-1122) and (+)-3Cl-CpC (PAL-1123), have also been reported. 3Cl-CpC was first described in the scientific literature by 2009. It was being investigated by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) as a potential treatment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
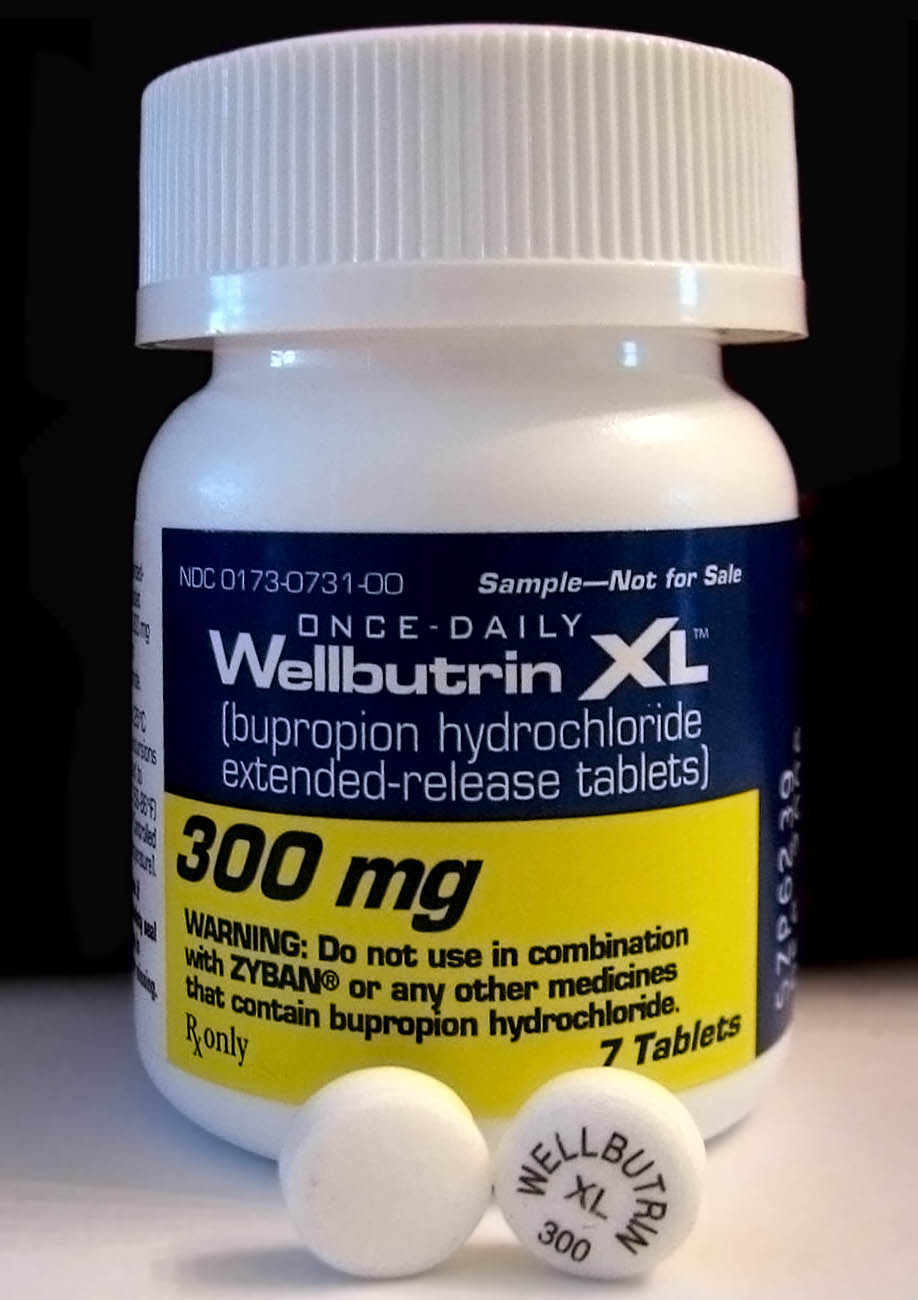
Bupropion
Bupropion, formerly called amfebutamone, and sold under the brand name Wellbutrin among others, is an atypical antidepressant that is indicated in the treatment of major depressive disorder, seasonal affective disorder, and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the cases of "incomplete response" to the first-line selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant. Bupropion has several features that distinguish it from other antidepressants: it does not usually cause sexual dysfunction, it is not associated with weight gain and sleepiness, and it is more effective than SSRIs at improving symptoms of hypersomnia and fatigue. Bupropion, particularly the immediate-release formulation, carries a higher risk of seizure than many other antidepressants, hence caution is recommended in patients with a history of seizure disorder. The medication is taken by mouth. Common adverse effects of bupropion with the greatest difference fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulant
Stimulants (also known as central nervous system stimulants, or psychostimulants, or colloquially as uppers) are a class of drugs that increase alertness. They are used for various purposes, such as enhancing attention, motivation, cognition, Mood disorder, mood, and physical activity, physical performance. Some stimulants occur naturally, while others are exclusively synthetic. Common stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine, methylphenidate, and modafinil. Stimulants may be subject to varying forms of regulation, or outright prohibition, depending on jurisdiction. Stimulants increase activity in the sympathetic nervous system, either directly or indirectly. Prototypical stimulants increase synaptic concentrations of neurotransmitter, excitatory neurotransmitters, particularly norepinephrine and dopamine (e.g., methylphenidate). Other stimulants work by binding to the Receptor (biochemistry), receptors of excitatory neurotransmitters (e.g., nicotine) or by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duration Of Action
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for example, infection). Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are the main branches of pharmacology, being itself a topic of biology interested in the study of the interactions of both endogenous and exogenous chemical substances with living organisms. In particular, pharmacodynamics is the study of how a drug affects an organism, whereas pharmacokinetics is the study of how the organism affects the drug. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects. Pharmacodynamics is sometimes abbreviated as PD and pharmacokinetics as PK, especially in combined reference (for example, when speaking of PK/PD models). Pharmacodynamics places particular emphasis on dose–response relationships, that is, the relationships between drug con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Drugs
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopropyl Compounds
A cyclopropyl group is a chemical structure derived from cyclopropane; it is typically produced in a cyclopropanation reaction. The group has an empirical formula of C3H5 and chemical bonds from each of the three carbons to both of the other two. Structure and bonding Due to the unfavoured bond angles (60°), cyclopropyl groups are highly strained. Two orbital models were proposed to describe the bonding situation. The Coulson-Moffit model uses bent bonds. The C-C bonds are formed by overlap of two sp-hybrid orbitals. To adapt to the small bond angle, there is some rehybridization resulting in sp~5-hybrids for the ring bonds and sp~2 for the C-H bonds. This model resembles the banana bond model for C=C double bonds (τ bonds). Alternatively the structure can be explained with the Walsh model. Here the two sp-hybrids forming the ring bond are separated into one sp2-hybrid and one pure p-orbital. This corresponds to the π bond description of C=C double bonds. Cyclopropyl grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathinones
Substituted cathinones, or simply cathinones, which include some stimulants and Empathogen-entactogen, entactogens, are chemical derivative, derivatives of cathinone. They feature a substituted phenethylamine, phenethylamine core with an alkyl functional group, group attached to the alpha and beta carbon, alpha carbon, and a ketone group attached to the alpha and beta carbon, beta carbon, along with additional Substitution reaction, substitutions. Cathinone occurs naturally in the plant khat whose leaves are chewed as a recreational drug. Substituted cathinones act as monoamine releasing agents and/or monoamine reuptake inhibitors, including of norepinephrine, dopamine, and/or serotonin. In contrast to substituted amphetamines, most substituted cathinones do not act as agonists of the human trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1). This may potentiate their stimulating and drug addiction, addictive effects. In addition, β-keto-substituted phenethylamines, such as βk-2C-B, app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Chloromethcathinone
3-Chloromethcathinone (3-CMC), also known as clophedrone, is a synthetic substance belonging to the Substituted cathinone, cathinone class of Psychoactive drug, psychoactive compounds. It is very similar in structure to other methcathinone derivatives such as 3-MMC and 4-CMC. Unlike cathinone, which occurs naturally in the khat plant Catha edulis, 3-CMC is not found in nature and is solely produced through chemical synthesis. First detected in 2014, 3-CMC gained attention for its Stimulant, stimulating effects that are described to be similar to the effects of mephedrone and, to a lesser extent, those of MDMA and cocaine. 3-CMC has been sold online as a designer drug mainly in European countries such as Germany, Poland, the Netherlands, and Sweden. It is a controlled substance in many countries. Use Recreational The perceived effects are said to resemble those of 3-MMC, users report reduced effects and a shorter duration in comparison. Effects include stimulation, euphoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Chlorocathinone
3-Chlorocathinone (3-CC) is a psychostimulant drug of the cathinone family. It is the analogue of the antidepressant and norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) bupropion in which the ''N''- ''tert''-butyl group has been removed. The drug is also the analogue of the stimulant 3-chloromethcathinone (3-CMC; clophedrone) in which the ''N''-methyl group has been removed. 3-CC is a potent serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). Its values for induction of monoamine release are 64nM for dopamine, 105nM for norepinephrine, and 567nM for serotonin in rat brain synaptosomes. Hence, 3-CC shows almost 10-fold preference for induction of dopamine release over serotonin release and around 1.5-fold preference for induction of dopamine release over norepinephrine release. The drug was encountered as a novel designer and recreational drug Recreational drug use is the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness, ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocaine Dependence
Cocaine dependence is a neurological disorder that is characterized by withdrawal symptoms upon cessation from cocaine use. It also often coincides with cocaine addiction which is a biopsychosocial disorder characterized by persistent use of cocaine and/or crack despite substantial harm and adverse consequences. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed., abbreviated DSM-5), classifies problematic cocaine use as a stimulant use disorder. The International Classification of Diseases (11th rev., abbreviated ICD-11), includes "Cocaine dependence" as a classification (diagnosis) under "Disorders due to use of cocaine". The use of cocaine creates euphoria and high amounts of energy. If taken in large doses, it is possible to cause mood swings, paranoia, insomnia, psychosis, high blood pressure, a fast heart rate, panic attacks, seizures that are extremely difficult to control, cognitive impairments and drastic changes in personality. Cocaine overdose may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulant Dependence
Stimulant use disorder is a type of substance use disorder where the use of stimulants caused clinically significant impairment or distress. It is defined in the DSM-5 as "the continued use of amphetamine-type substances, cocaine, or other stimulants leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, from mild to severe". These psychoactive drugs, known as stimulants, are among the most widely used drugs in the world today, although not all stimulants can induce addiction. Definition A psychoactive drug, such as a stimulant, is a chemical or substance that affects one's behavior, mind, and body. A stimulant can be smoked, injected, snorted, taken in pill form, chewed, and even ingested in the form of a drink. Synthetic stimulants are becoming increasingly popular as users attempt to alter the chemicals in drugs to create different reactions, and ultimately steer clear of jail time, legal penalties, and detection in drug screening efforts. If a substance is used over a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |