|
3-APBT
3-APBT (former developmental code name SKF-6678), also known as 3-(2-aminopropyl)benzo �hiophene, is a monoamine releasing agent and serotonin receptor agonist of the benzothiophene group. It is an analogue of α-methyltryptamine (AMT) in which the indole ring has been replaced with a benzothiophene ring. The drug acts as a potent and well-balanced serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). It is also a full agonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors, including of the serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors. 3-APBT produces the head-twitch response, a behavioral proxy of psychedelic effects, in rodents. It does not stimulate locomotor activity in rodents, suggesting that it does not possess stimulant-type effects. The drug has been reported be a weak monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), specifically of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) ( = 16,200nM). 3-APBT was developed by Smith, Kline & French (SKF) as a potential pharmaceutical drug in the late 1950s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituted Benzothiophene
The substituted benzothiophenes are a class of chemical compounds based on benzothiophene. They are closely related to the substituted benzofurans, substituted tryptamines, and to other chemical groups such as the substituted benzodioxoles (or methylenedioxyphenyl compounds). Substituted benzothiophenes include the (2-aminopropyl)benzo �hiophenes (APBTs) 2-APBT, 3-APBT (SKF-6678), 4-APBT, 5-APBT, 5-MAPBT, 6-APBT, 6-MAPBT, and 7-APBT. These drugs have been found to act as serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agents (SNDRAs) and, in some cases, as potent serotonin 5-HT2 receptor agonists, analogously to the entactogen MDMA. They do not produce hyperlocomotion in rodents, suggesting that they lack psychostimulant effects. However, those acting as serotonin 5-HT2 receptor agonists have been found to induce the head-twitch response, a behavioral proxy of psychedelic effects, in rodents. These findings suggest that substituted benzothiophenes may have entactogenic and/or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Releasing Agent
A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters. MRAs work by reversing the direction of the monoamine transporters (MATs), including the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and/or dopamine transporter (DAT), causing them to promote efflux of non-vesicular cytoplasmic monoamine neurotransmitter rather than reuptake of synaptic monoamine neurotransmitter. Many, but not all MRAs, also reverse the direction of the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), thereby additionally resulting in efflux of vesicular monoamine neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-APBT
2-APBT is a monoamine releasing agent (MRA) of the benzothiophene family. It acts specifically as a fairly well-balanced serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA), with values of 8.9nM for serotonin, 21.6nM for norepinephrine, and 38.6nM for dopamine in rat brain synaptosomes. 2-APBT was first described in the scientific literature Scientific literature encompasses a vast body of academic papers that spans various disciplines within the natural and social sciences. It primarily consists of academic papers that present original empirical research and theoretical ... by 2020. See also * 3-APBT References External links 2-APBT - Isomer Design Amines Benzothiophenes Designer drugs Entactogens {{Psychoactive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine Releasing Agent
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA), also known as a triple releasing agent (TRA), is a type of drug which induces the release of serotonin, norepinephrine/epinephrine, and dopamine in the brain and body. SNDRAs produce euphoriant, entactogen, and psychostimulant effects, and are almost exclusively encountered as recreational drugs. A closely related type of drug is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI). Examples of SNDRAs Examples of SNDRAs include specific amphetamines such as MDMA, MDA, 4-methylamphetamine, methamphetamine (in high doses), certain substituted benzofurans such as 5-APB and 6-APB, naphthylisopropylamine; cathinones such as mephedrone and methylone; tryptamines such as αMT and αET; along with agents of other chemical classes such as 4,4'-DMAR, and 5-IAI.Bruce E. Blough, Richard Rothman, Antonio Landavazo, Kevin M. Page, Ann Marie Decker. Phenylmorpholines and analogues thereof. US Patent 2013/0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2A Receptor
The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor, 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and functions as a GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a cell surface receptor that activates multiple intracellular signalling cascades. Like all 5-HT2 receptors, the 5-HT2A receptor is coupled to the Gq protein, Gq/G11 signaling pathway. It is the primary excitatory receptor subtype among the serotonin-responsive GPCRs. The 5-HT2A receptor was initially noted for its central role as the primary target of serotonergic psychedelic drugs such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms. It later regained research prominence when found to mediate, at least in part, the effects of many antipsychotic drugs, particularly atypical antipsychotic, atypical antipsychotics. Downregulation of post-synaptic 5-HT2A receptors is an adaptive response triggered by chronic administration of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and atypical antipsychotics. Elevated 5-HT2A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positional Isomer
In chemistry, a structural isomer (or constitutional isomer in the IUPAC nomenclature) of a compound is a compound that contains the same number and type of atoms, but with a different connectivity (i.e. arrangement of bonds) between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept. For example, butanol , methyl propyl ether , and diethyl ether have the same molecular formula but are three distinct structural isomers. The concept applies also to polyatomic ions with the same total charge. A classical example is the cyanate ion and the fulminate ion . It is also extended to ionic compounds, so that (for example) ammonium cyanate and urea are considered structural isomers,William F. Bynum, E. Janet Browne, Roy Porter (2014)''Dictionary of the History of Science'' page 218. and so are methylammonium formate and ammonium acetate . Structural isomerism is the most radical type of isomerism. It is opposed to stereoisomerism, in which the atoms and bonding s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmaceutical Drug
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are classified in many ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the medical prescription) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Medicines may be classified by mode of action, route of administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines. Drug discovery and drug development are complex and expensive endeavors undertaken by pharmaceutical companies, academic scientists, and governments. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith, Kline & French
Smith, Kline & French (SKF) was an American pharmaceutical company that is now a part of the British group GSK plc. History In 1830, John K. Smith opened a drugstore in Philadelphia, and his younger brother, George, joined him in 1841 to form John K Smith & Co. In 1865, Mahlon Kline joined the company, as a bookkeeper. In 1875, he took on additional responsibilities as a salesman and added many new and large accounts, as a reward the company, Mahlon K Smith and Company, was renamed into Smith, Kline and Company. In 1891, Smith, Kline and Company acquired French, Richards and Company, founded in 1844 by Clayton French and William Richards, which provided the company with a greater portfolio of consumer brands. The combined business became the ''Smith, Kline and French Company''. In 1932, SKF chemist Gordon Alles was awarded a patent for amphetamine. In 1968, the company acquired Recherche et Industrie Thérapeutiques in Belgium. SmithKline acquired Allergan in 1982, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase A
Monoamine oxidase A, also known as MAO-A, is an enzyme ( E.C. 1.4.3.4) that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOA'' gene. This gene is one of two neighboring gene family members that encode mitochondrial enzymes which catalyze the oxidative deamination of amines, such as norepinephrine, serotonin and tyramine. A mutation of this gene results in Brunner syndrome. This gene has also been associated with a variety of other psychiatric disorders, including antisocial behavior. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed. Structures Gene Monoamine oxidase A, also known as MAO-A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOA'' gene. The promoter of ''MAOA'' contains conserved binding sites for Sp1, GATA2, and TBP. This gene is adjacent to a related gene ('' MAOB'') on the opposite strand of the X chromosome. In humans, there is a 30-base repeat sequence repeated several different numbers of times in the promoter re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
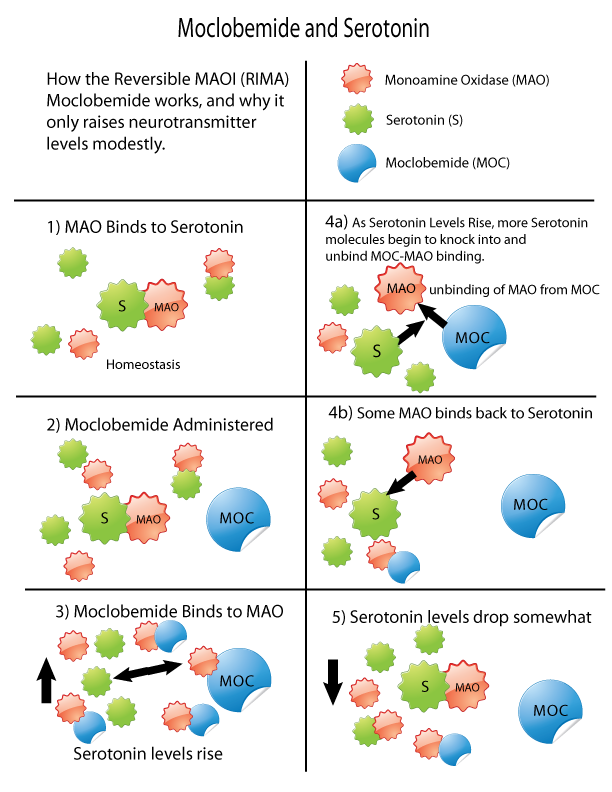
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a drug class, class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that binding selectivity, selectively and Enzyme inhibitor#Reversible inhibitors, reversibly enzyme inhibitor, inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the medication, treatment of major depressive disorder, depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulant
Stimulants (also known as central nervous system stimulants, or psychostimulants, or colloquially as uppers) are a class of drugs that increase alertness. They are used for various purposes, such as enhancing attention, motivation, cognition, Mood disorder, mood, and physical activity, physical performance. Some stimulants occur naturally, while others are exclusively synthetic. Common stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine, methylphenidate, and modafinil. Stimulants may be subject to varying forms of regulation, or outright prohibition, depending on jurisdiction. Stimulants increase activity in the sympathetic nervous system, either directly or indirectly. Prototypical stimulants increase synaptic concentrations of neurotransmitter, excitatory neurotransmitters, particularly norepinephrine and dopamine (e.g., methylphenidate). Other stimulants work by binding to the Receptor (biochemistry), receptors of excitatory neurotransmitters (e.g., nicotine) or by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperlocomotion
Locomotor activity is a measure of animal behavior which is employed in scientific research. Hyperlocomotion, also known as locomotor hyperactivity, hyperactivity, or increased locomotor activity, is an effect of certain drugs in animals in which locomotor activity (locomotion) is increased. It is induced by certain drugs like psychostimulants and NMDA receptor antagonists and is reversed by certain other drugs like antipsychotics and certain antidepressants. Stimulation of locomotor activity is thought to be mediated by increased signaling in the nucleus accumbens, a major brain area involved in behavioral activation and motivated behavior. Hypolocomotion, also known as locomotor hypoactivity, hypoactivity, and decreased locomotor activity, is an effect of certain drugs in animals in which locomotor activity is decreased. It is a characteristic effect of many sedative agents and general anesthetics. Antipsychotics, which are dopamine receptor antagonists, and many serotonerg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |