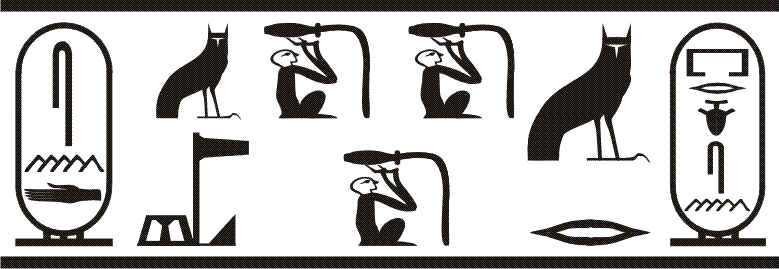
|
2nd Dynasty
The Second Dynasty of ancient Egypt (or Dynasty II, – ) is the latter of the two dynasties of the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt, Egyptian Archaic Period, when the seat of government was centred at Thinis. It is most known for its last ruler, Khasekhemwy, but is otherwise one of the most obscure periods in History of ancient Egypt, Egyptian history. Though archaeological evidence of the time is very scant, contrasting data from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First and Third Dynasty of Egypt, Third Dynasties indicates important institutional and economic developments during the Second Dynasty. Rulers For the first three pharaohs, sources are fairly close in agreement and the order is supported by an inscription on the statuette of Hetepdief, who served in the mortuary cults of these three kings. But the identity of the next few rulers is unclear. Surviving sources might be giving the Horus name or the Nebty name and the birth names of these rulers. They may also be entirely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nynetjer
Nynetjer (also known as Ninetjer and Banetjer) is the Horus name of the third pharaoh of the Second Dynasty of Egypt during the Early Dynastic Period. Archaeologically, Nynetjer is the best attested king of the entire dynasty. Direct evidence shows that he succeeded Raneb on the throne. What happened after him is much less clear as historical sources and archaeological evidences point to some breakdown or partition of the state. Nynetjer's reign is difficult to date precisely, with most experts proposing that he flourished some time during the late to the early . Estimating the duration of his rule is equally difficult and Egyptologists have proposed from 43 to 50 years of reign for him. Attestations Archaeologically, Nynetjer is the best attested of the kings of the early second dynasty. His name appears in inscriptions on stone vessels and clay sealings in large numbers from his tomb at Sakkara. A large number of artifacts bearing his name were also found in the tomb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senedj
Senedj (also known as Sened and Sethenes) was an early Egyptian king (pharaoh), who may have ruled during the 2nd Dynasty. His historical standing remains uncertain. His name is included in the kinglists of the Ramesside era, although it is written in different ways: While the Abydos King List imitates the archaic form, the Royal Canon of Turin and the Saqqara King List form the name with the hieroglyphic sign of a plucked goose. It is unknown how long Senedj ruled over Egypt. The Royal Canon of Turin credits him with 70 years of rulership, the ancient Egyptian historian Manetho states that ''Séthenes'' (as he calls Senedj) ruled for 41 years. Name sources The possibly only known contemporary inscription from Senedj's reign was found in 1909 by Egyptologist Uvo Hölscher, who assisted the excavations at the Khephren- and Menkaura temple at Giza. Hölscher found a small, thin-walled and polished diorite shard, which once belonged to a flat bowl. At the left breakline an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekhemib-Perenmaat
Sekhemib-Perenma'at (or simply Sekhemib), is the Horus name of an early Egyptian king who ruled during the 2nd Dynasty. Similar to his predecessor, successor or co-ruler Seth-Peribsen, Sekhemib is contemporarily well attested in archaeological records, but he does not appear in any posthumous document. The exact length of his reign is unknown and his burial site has yet to be found. Name sources Sekhemib's name is known from seal impressions and from inscriptions on vessels made of alabaster and breccia. They were found in the entrance of Peribsen's tomb at Abydos, in the underground galleries beneath the step pyramid of (3rd Dynasty) king Djoser at Sakkara and on one excavation site at Elephantine.Toby A. H. Wilkinson: ''Early Dynastic Egypt''. Routledge, London und New York 1999, , page 90–91.William Matthew Flinders Petrie & Francis Llewellyn Griffith: ''The royal tombs of the first dynasty''. Volume II., Trübner & Co., London, 1900, page 7, 14, 19, 20 & 48.Pierre Lacau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ') is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was known as ''mḥw'' which means "north". Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into a number of regions or nomes () – '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abydos King List
The Abydos King List, also known as the Abydos Table or the Abydos Tablet, is a list of the names of 76 kings of ancient Egypt, found on a wall of the Temple of Seti I at Abydos, Egypt. It consists of three rows of 38 cartouches (borders enclosing the name of a king) in each row. The upper two rows contain names of the kings, while the third row merely repeats Seti I's throne name and nomen. Besides providing the order of the Old Kingdom kings, it is the sole source to date of the names of many of the kings of the Seventh and Eighth Dynasties, so the list is valued greatly for that reason. This list omits the names of many earlier pharaohs. The bulk of these appear to have been left out because although they claimed royal titles and rule over all Egypt, their actual authority was limited to only part of the country. This category includes all the rulers of the Ninth and Tenth Dynasties, the early rulers of the Eleventh Dynasty ( Mentuhotep I, Intef I, Intef II, and In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saqqara Tablet
The Saqqara Tablet, also known as the Saqqara King List or the Saqqara Table, now in the Egyptian Museum, is an ancient stone engraving surviving from the Ramesside Period of Egypt which features a list of pharaohs. It was found in 1861 in Saqqara, in the tomb of Tjuneroy (or Tjenry), an official ("chief lector priest" and "Overseer of Works on All Royal Monuments") of the pharaoh Ramesses II. The inscription lists fifty-eight kings, from Anedjib ( First Dynasty) to Ramesses II (Nineteenth Dynasty), in reverse chronological order. The names (each surrounded by a border known as a cartouche), of which only forty-seven survive, are badly damaged. As with other Egyptian king lists, the Saqqara Tablet omits certain kings and entire dynasties. The list counts backward from Ramesses II to the mid-point of the First Dynasty, except for the Eleventh and Twelfth Dynasties, which are reversed. A well known photograph of the king list was published in 1865. Detailed and high resolution i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turin King List
The Turin King List, also known as the Turin Royal Canon, is an ancient Egyptian hieratic papyrus thought to date from the reign of Pharaoh Ramesses II (r. 1279–1213 BC), now in the Museo Egizio (Egyptian Museum) in Turin. The papyrus is the most extensive list available of kings compiled by the ancient Egyptians, and is the basis for most Egyptian chronology before the reign of Ramesses II. The list includes the names of 138 kings. Other sources say that there were originally 223 names of kings in the document, of which 126 have survived (sometimes only partially). 97 names have been lost. Creation and use The papyrus is believed to date from the reign of Ramesses II, during the middle of the New Kingdom, or the 19th Dynasty. The beginning and ending of the list are now lost; there is no introduction, and the list does not continue after the 19th Dynasty. The composition may thus have occurred at any subsequent time, from the reign of Ramesses II to as late as the 20th Dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abydos KL 02-04 N12
Abydos may refer to: *Abydos, a progressive metal side project of German singer Andy Kuntz *Abydos (Hellespont), an ancient city in Mysia, Asia Minor * Abydos (''Stargate''), name of a fictional planet in the ''Stargate'' science fiction universe *Abydos, Egypt, a city in ancient Egypt *Abydos Station, a pastoral lease and cattle station in Western Australia See also *Abidu Abidu (, also Romanized as Ābīdū) is a village in Gughar Rural District, in the Central District of Baft County, Kerman Province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in We ..., a village in Iran * Abidos, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, in southwestern France {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadjenes
Wadjenes (ancient Egyptian ''Wadj-nes'', which means "fresh of tongue"), also known as Wadjlas, Ougotlas and Tlas, was an early Egyptian king who may have ruled during the 2nd Dynasty. Since the name form "Wadjenes" is not contemporarily attested as the name of a king, but frequently appears in Ramesside kinglists, Egyptologists to this day are trying to connect Wadjenes with contemporary Horus-kings. Name sources The king's name "Wadjenes" is attested only in the Ramesside kinglists, where he is always presented as the immediate successor of king Nynetjer and as the predecessor of king Senedj. The same goes for the Royal Canon of Turin, where the entry for his name is damaged so only the years of rulership are preserved.Walter Bryan Emery: ''Ägypten. Geschichte und Kultur der Frühzeit.'' Fourier-Verlag, Wiesbaden 1964, , page 275. Whilst all kinglists match each other regarding the chronological position of Wadjenes, Egyptologists are uncertain as to the origin of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weneg (pharaoh)
Weneg (or Uneg), also known as Weneg-Nebty, is the throne name of an Early Dynastic Period of Egypt, early Egyptian king, who ruled during the Second Dynasty of Egypt, Second Dynasty. Although his chronological position is clear to Egyptologists, it is unclear for how long King Weneg ruled. It is also unclear as to which of the archaeology, archaeologically identified Horus-kings corresponds to Weneg. Name sources and contradictions The name "Weneg" is generally accepted to be a ''nebti''- or throne name, introduced by the crest of the Two Ladies (the goddesses Nekhbet and Wadjet) and the sedge-and-bee (hieroglyph), bee-crest. Weneg's name appears in black ink inscriptions on alabaster fragments and in inscriptions on schist-vessels. Seventeen vessels bearing his name have been preserved; eleven of them were found in the underground galleries beneath the step pyramid of king Djoser at Sakkara. Egyptologists such as Wolfgang Helck and Francesco Tiradritti point out that all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manetho
Manetho (; ''Manéthōn'', ''gen''.: Μανέθωνος, ''fl''. 290–260 BCE) was an Egyptian priest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom who lived in the early third century BCE, at the very beginning of the Hellenistic period. Little is certain about his life. He is known today as the author of a history of Egypt in Greek called the '' Aegyptiaca'' (''History of Egypt''), written during the reign of Ptolemy I Soter or Ptolemy II Philadelphus (285–246 BCE). None of Manetho’s original texts have survived; they are lost literary works, known only from fragments transmitted by later authors of classical and late antiquity. The remaining fragments of the ''Aegyptiaca'' continue to be a singular resource for delineating Egyptian chronology, more than two millennia since its composition. Until the decipherment of Ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century CE, Manetho's fragments were an essential source for understanding Egyptian history. His work remains of unique importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |