|
2nd (South Canterbury) Regiment
The 2nd (South Canterbury) Regiment was a territorial infantry regiment of the New Zealand Military Forces. It was formed in 1911 from various volunteer corps raised during the second half of the nineteenth century. Men from the regiment saw combat in the First World War as part of the Canterbury Infantry Regiment. It was amalgamated with the 1st (Canterbury) Regiment in 1921 to form the 1st Battalion, Canterbury Regiment. History Volunteer corps were first raised in Canterbury in 1859, although it was not until 1866 that the first South Canterbury corps, the Timaru Rifle Volunteers, was formed. The Timaru Rifles, however, did not survive long and were disbanded in 1868. In the same year, the Temuka Volunteer Rifles were raised and it is from this corps that a continuous line of service begins. Over the course of the late 19th century, a number of other South Canterbury volunteer corps were raised. In 1886 the Canterbury based corps were grouped together into the 1st Battalion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Army
, image = New Zealand Army Logo.png , image_size = 175px , caption = , start_date = , country = , branch = , type = Army , role = Land warfare , website = https://www.nzdf.mil.nz/army/ , size = * 4,519 active personnel * 2,065 reserve , command_structure = , garrison = Wellington , garrison_label = , nickname = , patron = , motto = , colours = Red and black , colors_label = , march = , mascot = , equipment = List of equipment of the New Zealand Army , equipment_label = , battles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Officers Of The Canterbury Regiment In Mulheim, Germany, 1919 (21014700313)
An officer is a person who has a position of authority in a hierarchical organization. The term derives from Old French ''oficier'' "officer, official" (early 14c., Modern French ''officier''), from Medieval Latin ''officiarius'' "an officer," from Latin ''officium'' "a service, a duty" the late Latin from ''officiarius'', meaning " official." Examples Ceremonial and other contexts *Officer, and/or Grand Officer, are both a grade, class, or rank of within certain chivalric orders and orders of merit, e.g. Legion of Honour (France), Order of the Holy Sepulchre (Holy See), Order of the British Empire ( UK), Order of Leopold (Belgium) *Great Officer of State *Merchant marine officer or licensed mariner *Officer of arms *Officer in The Salvation Army, and other state decorations Corporations *Bank officer *Corporate officer, a corporate title **Chief executive officer (CEO) ** Chief financial officer (CFO) **Chief operating officer (COO) *Executive officer Education *Chief academi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Regiments Of New Zealand
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''infant''. The individual-soldier term ''infantryma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Official Publications
New Zealand official publications are frequently quoted by their abbreviation; they include those listed below. Past copies of most by year or session are held in bound volumes in major public libraries. AJHR, AtoJs, or Appendix to the Journal of the House of Representatives The Appendix to the Journal of the House of Representatives is published annually or by each sitting of Parliament. It includes annual reports of government departments, and various special reports e.g. reports of commissions or Royal Commissions. Most of the 1860 to 1950 volumes of AJHR have been digitised and are available online aAtoJsOnline NZOYB or New Zealand Official Yearbook Published annually. NZG or New Zealand Gazettes The New Zealand Gazette is published weekly. In the 19th century the New Ulster Gazette, the New Munster Gazette and Gazettes of the various provinces were also published. NZPD or New Zealand Parliamentary Debates The '' New Zealand Parliamentary Debates'' (Hansard) is pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
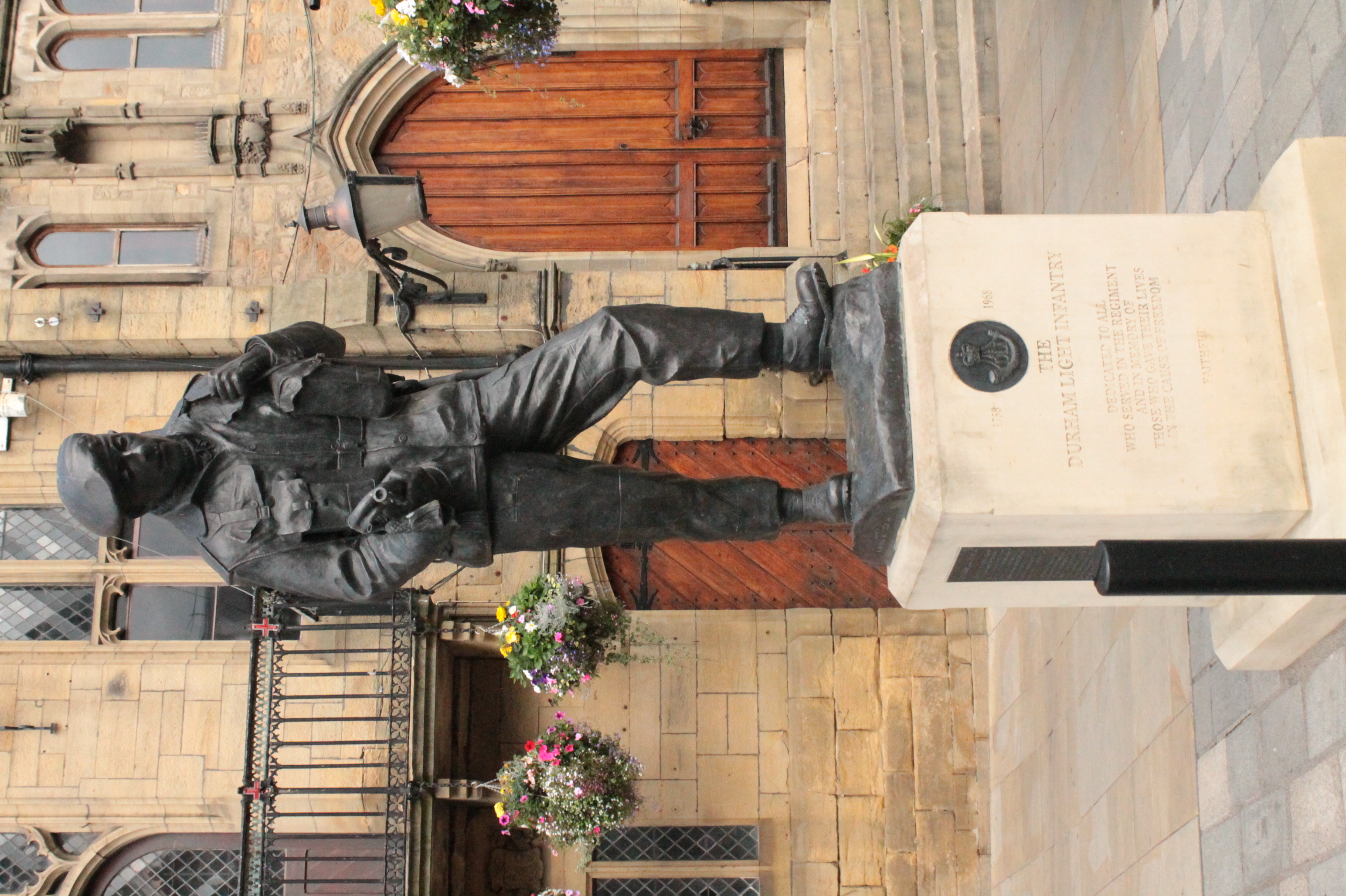
Durham Light Infantry
The Durham Light Infantry (DLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1881 to 1968. It was formed in 1881 under the Childers Reforms by the amalgamation of the 68th (Durham) Regiment of Foot (Light Infantry) and the 106th Regiment of Foot (Bombay Light Infantry) along with the Militia and Volunteers of County Durham. The regiment served notably in the Second Boer War, World War I and World War II, the Korean War and the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation. During times of peace it had duty in India, China, West Germany and Cyprus. In 1968, the regiment was amalgamated with the Somerset and Cornwall Light Infantry, the King's Own Yorkshire Light Infantry and the King's Shropshire Light Infantry to form The Light Infantry, which again amalgamated in 2007 with the Devonshire and Dorset Regiment, the Royal Gloucestershire, Berkshire and Wiltshire Regiment and the Royal Green Jackets to form a new large regiment, The Rifles, which continues the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Gazette
The ''New Zealand Gazette'' ( mi, Te Kāhiti o Aotearoa), commonly referred to as ''Gazette'', is the official newspaper of record (Government gazette) of the New Zealand Government. Published since 1840, it is the longest-running publication in New Zealand. Since 26 October 2017, it has been published online continuously. Special editions are also published twice a year to cover the New Year Honours and Queen's Birthday Honours. History The first issue was published as ''Gazette Extraordinary'' on 30 December 1840. Then it was the ''New Zealand Government Gazette'' from 1841 to 1847. Between 1847 and 1853 it was split into the ''New Zealand Government Gazette, Province of New Ulster'' for New Ulster (the North Island), published in Auckland, and the ''New Zealand Government Gazette, Province of New Munster'' for New Munster (the South Island), published in Wellington Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Days' Offensive
The Hundred Days Offensive (8 August to 11 November 1918) was a series of massive Allied offensives that ended the First World War. Beginning with the Battle of Amiens (8–12 August) on the Western Front, the Allies pushed the Central Powers back, undoing their gains from the German spring offensive. The Germans retreated to the Hindenburg Line, but the Allies broke through the line with a series of victories, starting with the Battle of St Quentin Canal on 29 September. The offensive, together with a revolution breaking out in Germany, led to the Armistice of 11 November 1918 which ended the war with an Allied victory. The term "Hundred Days Offensive" does not refer to a battle or strategy, but rather the rapid series of Allied victories against which the German Army had no reply. Background The German spring offensive of the German Army on the Western Front had begun on 21 March 1918 with Operation Michael and had petered out by July. The Germans had advanced to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Passchendaele
The First Battle of Passchendaele took place on 12 October 1917 during the First World War, in the Ypres Salient in Belgium on the Western Front. The attack was part of the Third Battle of Ypres and was fought west of Passchendaele village. The British had planned to capture the ridges south and east of the city of Ypres as part of a strategy decided by the Allies at conferences in November 1916 and May 1917. Passchendaele lay on the last ridge east of Ypres, from the railway junction at Roulers, which was an important part of the supply system of the German 4th Army. After a dry spell in September, rains began on 3 October and by the Battle of Poelcappelle on 9 October much of the British field artillery opposite Passchendaele was out of action due to rain, mud and German artillery-fire. The remaining guns were either left in old positions and fired at the limit of their range or were operated from any flat ground near wooden roadways or from platforms, many of which were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Broodseinde
The Battle of Broodseinde was fought on 4 October 1917 near Ypres in Belgium, at the east end of the Gheluvelt plateau, by the British Second and Fifth armies against the German 4th Army. The battle was the most successful Allied attack of the Third Battle of Ypres. Using ''bite-and-hold'' tactics, with objectives limited to what could be held against German counter-attacks, the British devastated the German defence, which prompted a crisis among the German commanders and caused a severe loss of morale in the 4th Army. Preparations were made by the Germans for local withdrawals and planning began for a greater withdrawal, which would entail the abandonment by the Germans of the Belgian coast, one of the strategic aims of the Flanders offensive. After the period of unsettled but drier weather in September, heavy rain began again on 4 October and affected the remainder of the campaign, working more to the advantage of the German defenders, being pushed back on to far less dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
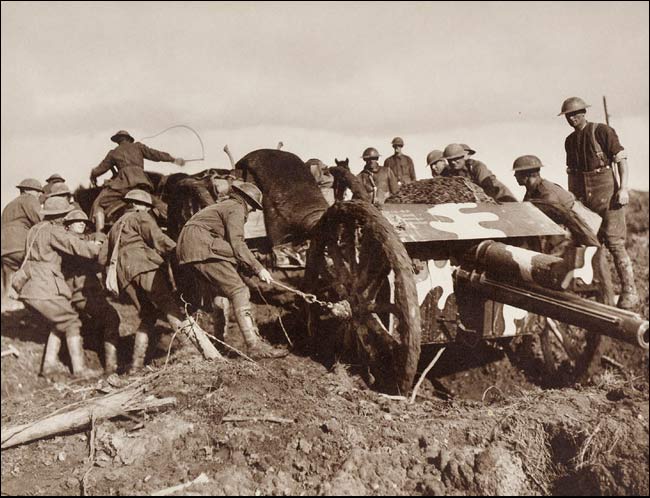
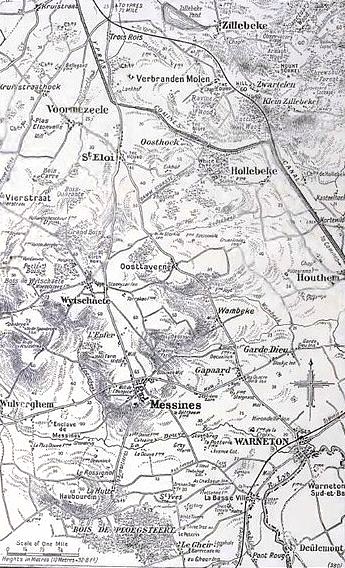
Battle Of Messines (1917)
The Battle of Messines (7–14 June 1917) was an attack by the British Second Army (General Sir Herbert Plumer), on the Western Front, near the village of Messines (now Mesen) in West Flanders, Belgium, during the First World War. The Nivelle Offensive in April and May had failed to achieve its more grandiose aims, had led to the demoralisation of French troops and confounded the Anglo-French strategy for 1917. The attack forced the Germans to move reserves to Flanders from the Arras and Aisne fronts, relieving pressure on the French. The British tactical objective was to capture the German defences on the ridge, which ran from Ploegsteert Wood (Plugstreet to the British) in the south, through Messines and Wytschaete to Mt Sorrel, depriving the German 4th Army of the high ground. The ridge gave commanding views of the British defences and back areas of Ypres to the north, from which the British intended to conduct the Northern Operation, an advance to Passchendaele Ridge an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Somme
The Battle of the Somme (French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place between 1 July and 18 November 1916 on both sides of the upper reaches of the Somme, a river in France. The battle was intended to hasten a victory for the Allies. More than three million men fought in the battle of whom one million were wounded or killed, making it one of the deadliest battles in human history. The French and British had committed themselves to an offensive on the Somme during the Chantilly Conference in December 1915. The Allies agreed upon a strategy of combined offensives against the Central Powers in 1916 by the French, Russian, British and Italian armies, with the Somme offensive as the Franco-British contribution. Initial plans called for the French army to undertake the main part of the Somme offensive, supported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)