|
28th Division (Imperial Japanese Army)
The was an infantry division in the Imperial Japanese Army. Its call sign was the . The 28th Division of the Kwantung Army was formed on 10 July 1940, in Manchukuo capital - Changchun. History The 28th Division was tasked with the defense of the Manchukuo capital, and the neighboring areas of Harbin and Qiqihar under direct control of Kwantung Army. With the start of the Battle of Saipan 15 June 1944, its 36th Infantry Regiment was sent to Saipan, but returned to division soon as Saipan was lost before 36th regiment could arrive. Simultaneously, the 28th Division was reassigned to the 32nd Army in June, 1944 and reassigned to the Ryukyu Islands, specifically to Miyakojima (where it based its headquarters) and Ishigaki archipelago. Its former garrison and some left-over troops were incorporated into 112th division. In the Battle of Okinawa, the 28th Division main positions were never invaded, but were heavily bombed and subject to coastal bombardment. As all higher-ranking off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Korea Treaty of 1910, 1910 to Japanese Instrument of Surrender, 1945, it included the Japanese archipelago, the Kuril Islands, Kurils, Karafuto Prefecture, Karafuto, Korea under Japanese rule, Korea, and Taiwan under Japanese rule, Taiwan. The South Seas Mandate and Foreign concessions in China#List of concessions, concessions such as the Kwantung Leased Territory were ''de jure'' not internal parts of the empire but dependent territories. In the closing stages of World War II, with Japan defeated alongside the rest of the Axis powers, the Japanese Instrument of Surrender, formalized surrender was issued on September 2, 1945, in compliance with the Potsdam Declaration of the Allies of World War II, Allies, and the empire's territory subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Saipan
The Battle of Saipan was an amphibious assault launched by the United States against the Empire of Japan during the Pacific War, Pacific campaign of World War II between 15 June and 9 July 1944. The initial invasion triggered the Battle of the Philippine Sea, which effectively destroyed Japanese Aircraft carrier operations during World War II, carrier-based airpower, and the battle resulted in the American capture of the island. Its occupation put the major cities of the Japanese home islands within the range of B-29 bombers, making them vulnerable to strategic bombing by the United States Army Air Forces. It also precipitated the resignation of Hideki Tōjō, the prime minister of Japan. Saipan was the first objective in Operation Forager, the campaign to occupy the Mariana Islands that got underway at the same time the Allies in World War II, Allies were invading France in Operation Overlord. After a two-day naval bombardment, the U.S. 2nd Marine Division, 4th Marine Division, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Disestablished In 1945
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstruction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Divisions Of Japan
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese World War II Divisions
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japanese studies , sometimes known as Japanology in Europe, is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese language, history, culture, litera ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was Hirohito surrender broadcast, announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally Japanese Instrument of Surrender, signed on 2 September 1945, End of World War II in Asia, ending the war. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) was incapable of conducting major operations and an Operation Downfall, Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and Republic of China (1912–49), China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of Japan in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme War Council (Japan), Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
112th Division (Imperial Japanese Army)
The was an infantry division of the Imperial Japanese Army. Its call sign was the . It was formed 12 July 1944 in Hunchun as a triangular division. The nucleus for the formation was the remnants of the 28th Division been transferred to Miyako-jima. The division was initially assigned to the Third army. Action The garrison of the division was the Jiandao area. As the Soviet invasion of Manchuria has started 9 August 1945, it fought a desperate defensive battle meeting Red Army forces south and west of Hunchun while fighting the against Soviet "113th fortified sector" and 88th Rifle Corps. The division's resistance was described as "heavy", despite the estimate by the 1st Area Army that the 112th was only 35% combat effective. 11 August 1945, a frontal attack by the Soviet armour near Michiang was repulsed. The Hunchun itself was lost to Soviet forces 14 August 1945, after Red Army was forced to send in reinforcements in the form of 386th Rifle Division. Another Sovi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishigaki, Okinawa
is a Cities of Japan, city in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. It includes Ishigaki Island, Ishigaki island and the Senkaku Islands territory. The city is the political, cultural, and economic center of the Yaeyama Islands. New Ishigaki Airport serves the city. As of December 2012, the city has an estimated population of 48,816 and a population density of 213 persons per km2. The total area is 229.00 km2. It is also the location of the Senkaku Islands (see below in the Geography section). History The current city of Ishigaki was founded in 1908 as Yaeyama Village, an amalgamation of the Ishigaki, Ōhama, and Miyara magiri. In 1914 it was renamed to Ishigaki Village, and grew to become Ishigaki Town in 1926. Ishigaki was elevated to city status on July 10, 1947. Historical footnote: One of the first Frenchmen ever to visit Japan, Guillaume Courtet, came ashore at Ishigaki in 1636. Geography The city of Ishigaki covers the entirety of Ishigaki Island (). The island is surrounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
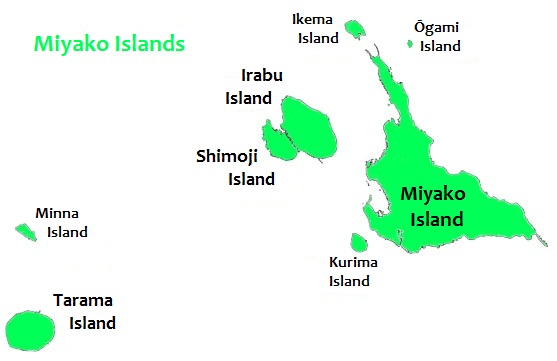
Miyakojima
is the largest and the most populous island among the Miyako Islands of Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Miyako Island is administered as part of the City of Miyako Island, which includes not only Miyako Island, but also five other islands. Geography Miyako Island lies approximately southwest of Okinawa Island. With an area of , Miyako is the fourth-largest island in Okinawa Prefecture. The island is triangular in shape and is composed of limestone. Miyako Island is subject to drought and is frequently struck by typhoons. Miyako Island is well known for its beauty, particularly the , a nationally designated Place of Scenic Beauty at the southeasternmost point of Miyako Island. It is considered by many as one of the most beautiful spots in Japan. Other notable locations include Yonaha Maehama beach, Sunayama beach, Painagama Beach and the sights on Irabu-jima. There are three islands nearby which are connected by bridges to Miyako Island, Irabujima (as of early 2015), , and . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |