|
27 Lyncis
27 Lyncis is a single star in the northern constellation of Lynx. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.78. This object is located around 250 light years away from the Sun, as determine from parallax measurements. It is moving further from the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of +11 km/s. This is an ordinary A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A2 V, which indicates it is generating energy through hydrogen fusion at its core. It is 157 million years old and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 183. The star has 2.24 times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 65 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 10,014 K. X-ray emission Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays. Several types of astrophysical objects emit X-rays. They includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynx (constellation)
Lynx is a constellation named after lynx, the animal, usually observed in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere. The constellation was introduced in the late 17th century by Johannes Hevelius. It is a faint constellation, with its brightest stars forming a zigzag line. The orange giant Alpha Lyncis is the brightest star in the constellation, and the semiregular variable star Y Lyncis is a target for amateur astronomy, amateur astronomers. Six star systems have been found to contain exoplanet, planets. Those of 6 Lyncis and HD 75898 were discovered by the Doppler spectroscopy, Doppler method; those of XO-2 (star), XO-2, XO-4, XO-5 and WASP-13 were observed as they Methods of detecting extrasolar planets#Transit method, passed in front of the host star. Within the constellation's borders lie NGC 2419, an unusually remote globular cluster; the galaxy NGC 2770, which has hosted three recent Type Ib and Ic supernovae, Type Ib supernovae; the distant quasar APM 08279+5255, whose light is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Of The Sun
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. More precisely, the mass of the Sun is The solar mass is about times the mass of Earth (), or times the mass of Jupiter (). History of measurement The value of the gravitational constant was first derived from measurements that were made by Henry Cavendish in 1798 with a torsion balance. The value he obtained differs by only 1% from the modern value, but was not as precise. The diurnal parallax of the Sun was accurately measured during the transits of Venus in 1761 and 1769, yielding a value of (9 arcseconds, compared to the present value of ). From the value of the diurnal parallax, one can determine the distance to the Sun from the geometry of Earth. The first known estimate of the solar mass was by Isaac N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Draper Catalogue Objects
Henry may refer to: People and fictional characters * Henry (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters * Henry (surname) * Henry, a stage name of François-Louis Henry (1786–1855), French baritone Arts and entertainment * Henry (2011 film), ''Henry'' (2011 film), a Canadian short film * Henry (2015 film), ''Henry'' (2015 film), a virtual reality film * ''Henry: Portrait of a Serial Killer'', a 1986 American crime film * Henry (comics), ''Henry'' (comics), an American comic strip created in 1932 by Carl Anderson * "Henry", a song by New Riders of the Purple Sage Places Antarctica * Henry Bay, Wilkes Land Australia *Henry River (New South Wales) *Henry River (Western Australia) Canada * Henry Lake (Vancouver Island), British Columbia * Henry Lake (Halifax County), Nova Scotia * Henry Lake (District of Chester), Nova Scotia New Zealand * Lake Henry (New Zealand) * Henry River (New Zealand) United States * Henry, Illinois * Henry, Indiana * Henry, Nebras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flamsteed Objects
John Flamsteed (19 August 1646 – 31 December 1719) was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, ''Catalogus Britannicus'', and a star atlas called '' Atlas Coelestis'', both published posthumously. He also made the first recorded observations of Uranus, although he mistakenly catalogued it as a star, and he laid the foundation stone for the Royal Greenwich Observatory. Life Flamsteed was born in Denby, Derbyshire, England, the only son of Stephen Flamsteed and his first wife, Mary Spadman. He was educated at the free school of Derby and at Derby School, in St Peter's Churchyard, Derby, near where his father carried on a malting business. At that time, most masters of the school were Puritans. Flamsteed had a solid knowledge of Latin, essential for reading the scientific literature of the day, and a love of history, leaving the school in May 1662.Birks, John L. (1999) ''John Flamsteed, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durchmusterung Objects
In astronomy, Durchmusterung or Bonner Durchmusterung (BD) is an astrometric star catalogue of the whole sky, published by the Bonn Observatory in Germany from 1859 to 1863, with an extension published in Bonn in 1886. The name comes from ('run-through examination'), a German word used for a systematic survey of objects or data. The term has sometimes been used for other astronomical surveys, including not only stars, but also the search for other celestial objects. Special tasks include celestial scanning in electromagnetic spectrum, electromagnetic wavelengths shorter or longer than visible light waves. Original catalog The Bonner Durchmusterung (abbreviated BD), was initiated by Friedrich Wilhelm Argelander, Friedrich Argelander and using observations largely carried out by his assistants, which resulted in a catalogue of the positions and apparent magnitudes of 342,198 stars down to approximate apparent magnitude 9.5 and covering the sky from 90°N to 2°S declination. The cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-type Main-sequence Stars
A type or type A may refer to: Science * A-type asteroid, a type of relatively uncommon inner-belt asteroids * A type blood, a type in the ABO blood group system * A-type inclusion, a type of cell inclusion * A-type potassium channel, a type of voltage-gated potassium channel * A type proanthocyanidin, a specific type of flavonoids * A-type star, a class of stars * Type A climate, a type in the Köppen climate classification * Type A flu, a type of influenza virus * Type A evaluation of uncertainty, an uncertainty in measurement that can be inferred, for example, from repeated measurement * Type A personality, a personality type in the Type A and Type B personality theory * Hemophilia type A, a type of haemophilia * A-type granite a type of granite rock * Adenosine receptor Technology * Type A Dolby Noise Reduction, a type of Dolby noise-reduction system * Type A plug (see also NEMA connector) * Type A submarine, a class of submarines in the Imperial Japanese Navy which served during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
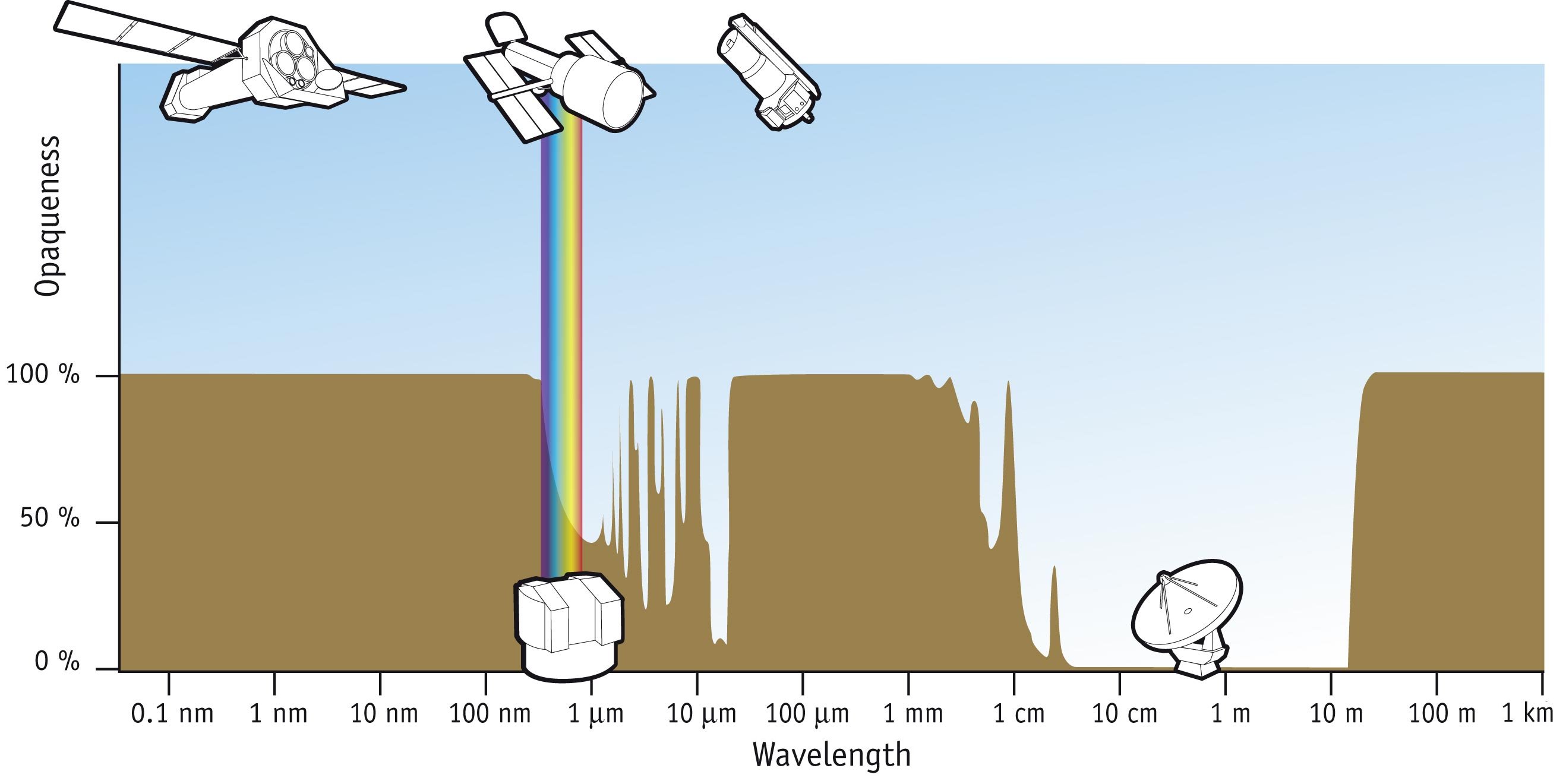
X-ray Astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by Balloon-borne telescope, balloons, sounding rockets, and X-ray astronomy satellite, satellites. X-ray astronomy uses a type of space telescope that can see x-ray radiation which standard optical telescopes, such as the Mauna Kea Observatories, cannot. X-ray generation, X-ray emission is expected from astronomical objects that contain extremely hot gases at temperatures from about a million kelvin (K) to hundreds of millions of kelvin (MK). Moreover, the maintenance of the E-layer of ionized gas high in the Earth's thermosphere also suggested a strong extraterrestrial source of X-rays. Although theory predicted that the Sun and the stars would be prominent X-ray sources, there was no way to verify this because Earth's atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature when the body's emissivity curve (as a function of wavelength) is not known. When the star's or planet's net emissivity in the relevant wavelength band is less than unity (less than that of a black body), the actual temperature of the body will be higher than the effective temperature. The net emissivity may be low due to surface or atmospheric properties, such as the greenhouse effect. Star The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per ''surface area'' () as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law . Notice that the total ( bolometric) luminosity of a star is then , where is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered. A photosphere is the region of a luminous object, usually a star, that is transparent to photons of certain wavelengths. Stars, except neutron stars, have no solid or liquid surface. Therefore, the photosphere is typically used to describe the Sun's or another star's visual surface. Etymology The term ''photosphere'' is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos'', ''photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it being a spherical surface that is perceived to emit light. Temperature The surface of a star is defined to have a temperature given by the effective temperature in the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Various stars have photospheres of vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun's Luminosity
The solar luminosity () is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal solar luminosity is defined by the International Astronomical Union to be . This corresponds almost exactly to a bolometric absolute magnitude of +4.74. The Sun is a weakly variable star, and its actual luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle (sunspot cycle) that causes a quasi-periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Other variations over the last 200–300 years are thought to be much smaller than this. Determination Solar luminosity is related to solar irradiance (the solar constant). Slow changes in the axial tilt of the planet and the shape of its orbit cause cyclical changes to the solar irradiance. The result is orbital forcing that causes the Milankovitch cycles, which determine Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projected Rotational Velocity
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface. The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge due to centrifugal force. As stars are not solid bodies, they can also undergo differential rotation. Thus the equator of the star can rotate at a different angular velocity than the higher latitudes. These differences in the rate of rotation within a star may have a significant role in the generation of a stellar magnetic field. In its turn, the magnetic field of a star interacts with the stellar wind. As the wind moves away from the star its angular speed decreases. The magnetic field of the star interacts with the wind, which applies a drag to the stellar rotation. As a result, angular momentum is transferred from the star to the wind, and over time this gradually slows the star's rate of rotation. Measurement Unless a sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and traces of heavier elements. Its stellar mass, total mass mainly determines it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |