|
257 Roberts
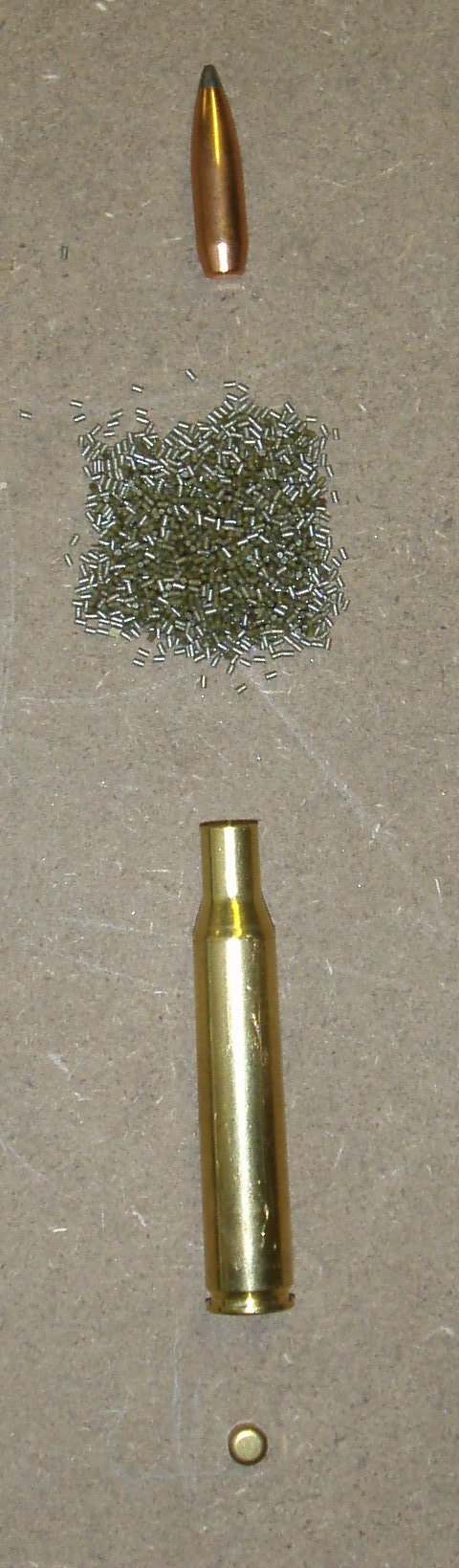
The .257 Roberts, also known as .257 Bob, is a medium-powered .25 caliber rifle cartridge. It has been described as the best compromise between the low recoil and flat trajectory of smaller calibers such as the 5 mm (.22") and 6 mm (.24"), and the higher energy but harder recoil of larger popular hunting calibers, such as the 7 mm (.28") family and the popular 7.62 mm (.30").The .257 Roberts (.257 Roberts +P) by Chuck Hawks (membership required) Nominal bullet diameter of the .257 Roberts is .257 inches. The .257 Roberts uses the same caliber bullets as or the more powerful |
Remington Arms
Remington Arms Company, LLC was an American manufacturer of firearms and ammunition, now broken into two companies, each bearing the Remington name. The firearms manufacturer is ''Remington Arms''. The ammunition business is called ''Remington''. The company which was broken up was called Remington Outdoor Company. Sturm, Ruger & Co. purchased the Marlin Firearms division of the Remington Outdoor Company in 2020. Founded in 1816 by Eliphalet Remington (as E. Remington and Sons) in Ilion, New York, it was one of the oldest gun makers in the US and claimed to be the oldest factory in the US that still made its original product. The company was the largest rifle manufacturer in North America according to 2015 ATF statistics. The company developed or adopted more cartridges than any other gun maker or ammunition manufacturer in the world. History 19th century origins The Remington company was founded in 1816. Eliphalet Remington II (1793–1861) believed he could build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 38 Rifle
The is a bolt-action service rifle that was used by the Empire of Japan predominantly during the Second Sino-Japanese War and Second World War. The design was adopted by the Imperial Japanese Army in 1905 (the 38th year of the Meiji period, hence "Type 38"). Due to a lack of power in its 6.5×50mmSR Arisaka cartridge, it was partially replaced during the war with the Type 99 rifle, but both rifles saw usage until the end of the war. History and development The Imperial Japanese Army introduced the Type 30 rifle in 1897. However, the weapon had numerous shortcomings, which were highlighted by combat experience in the early stages of the Russo-Japanese War. These included bursting cartridges, a poorly designed lock in which excess gunpowder tended to accumulate, burning the face of the shooter, frequent misfires, jamming, difficulty in cleaning, and cartridge extraction. Major Kijiro Nambu undertook a redesign of the Type 30, which was introduced in 1906. Nambu reduced the num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grain (unit)
A grain is a unit of measurement of mass, and in the troy weight, avoirdupois, and apothecaries' systems, equal to exactly milligrams. It is nominally based upon the mass of a single ideal seed of a cereal. From the Bronze Age into the Renaissance, the average masses of wheat and barley grains were part of the legal definitions of units of mass. Expressions such as "thirty-two grains of wheat, taken from the middle of the ear" appear to have been ritualistic formulas, essentially the premodern equivalent of legal boilerplate. Another source states that it was defined such that 252.458 units would balance of distilled water at an ambient air-water pressure and temperature of and respectively. Another book states that Captain Henry Kater, of the British Standards Commission, arrived at this value experimentally. The grain was the legal foundation of traditional English weight systems, and is the only unit that is equal throughout the troy, avoirdupois, and apothecaries' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one one thousandth of a kilogram. Originally defined as of 1795 as "the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to the cube of the hundredth part of a metre melting ice", the defining temperature (~0 °C) was later changed to 4 °C, the temperature of maximum density of water. However, by the late 19th century, there was an effort to make the Base unit (measurement), base unit the kilogram and the gram a derived unit. In 1960, the new International System of Units defined a ''gram'' as one one-thousandth of a kilogram (i.e., one gram is Scientific notation, 1×10−3 kg). The kilogram, as of 2019, is defined by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures from the fixed numerical value of the Planck constant (), which is kg⋅m2⋅s−1. Official SI symbol The only unit symbol for gram that is recognised by the International S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
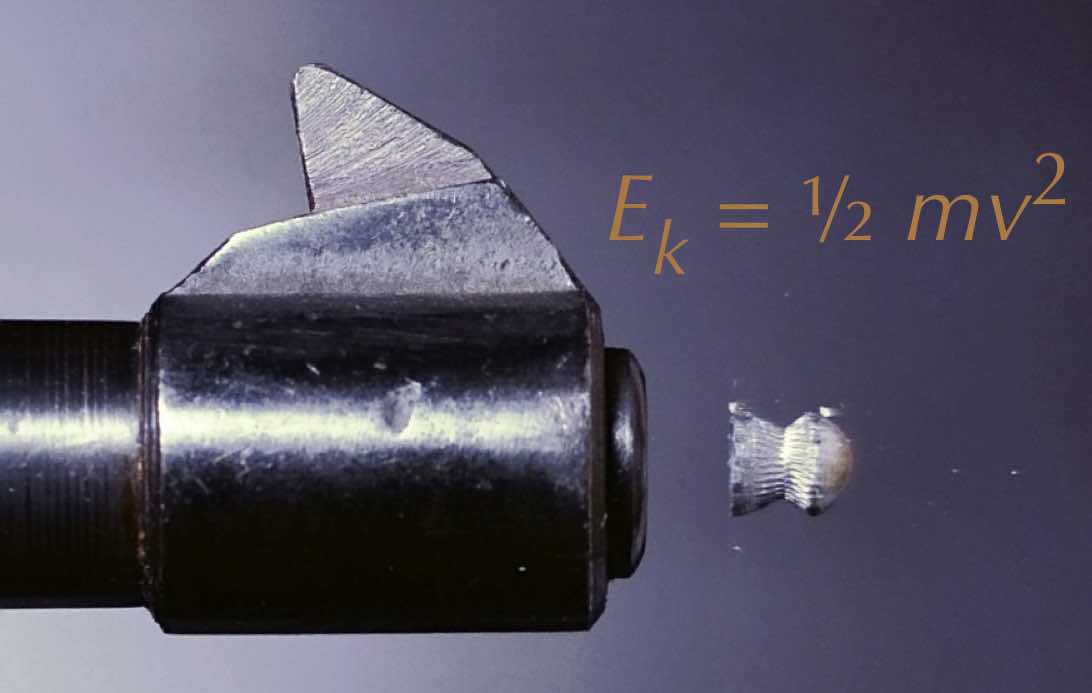
Muzzle Energy
Muzzle energy is the kinetic energy of a bullet as it is expelled from the muzzle of a firearm. Without consideration of factors such as aerodynamics and gravity for the sake of comparison, muzzle energy is used as a rough indication of the destructive potential of a given firearm or cartridge. The heavier the bullet and especially the faster it moves, the higher its muzzle energy and the more damage it will do. Kinetic energy The general formula for the kinetic energy is :E_\mathrm = \frac mv^2 where :''v'' is the velocity of the bullet :''m'' is the mass of the bullet. Although both mass and velocity contribute to the muzzle energy, the muzzle energy is proportional to the mass while proportional to the ''square'' of the velocity. The velocity of the bullet is a more important determinant of muzzle energy. For a constant velocity, if the mass is doubled, the energy is doubled; however, for a constant mass, if the velocity is doubled, the muzzle energy increases ''four'' t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzzle Velocity
Muzzle velocity is the speed of a projectile (bullet, pellet, slug, ball/ shots or shell) with respect to the muzzle at the moment it leaves the end of a gun's barrel (i.e. the muzzle). Firearm muzzle velocities range from approximately to in black powder muskets, to more than in modern rifles with high-velocity cartridges such as the .220 Swift and .204 Ruger, all the way to for tank guns firing kinetic energy penetrator ammunition. To simulate orbital debris impacts on spacecraft, NASA launches projectiles through light-gas guns at speeds up to . Projectile velocity For projectiles in unpowered flight, its velocity is highest at leaving the muzzle and drops off steadily because of air resistance. Projectiles traveling less than the speed of sound (about in dry air at sea level) are ''subsonic'', while those traveling faster are ''supersonic'' and thus can travel a substantial distance and even hit a target before a nearby observer hears the "bang" of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAAMI
The Sporting Arms and Ammunition Manufacturers' Institute (SAAMI, pronounced "Sammy") is an association of American manufacturers of firearms, ammunition, and components. SAAMI is an accredited standards developer that publishes several American National Standards that provide safety, reliability, and interchangeability standards for commercial manufacturers of firearms, ammunition, and components. In addition, SAAMI publishes information on the safe and responsible transportation, storage, and use of those products. History The origins of SAAMI date back to World War I and the Society of American Manufacturers of Small Arms and Ammunition (SAMSAA). In 1913, the US War Department encouraged the firearms and ammunition industry to establish an organization to share new technology and establish common standards for small arms and ammunition. SAMSAA was officially formed in 1918, however became inactive by the early 1920s. By the mid-1920s the United States was still suff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
250-3000 Savage
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has attained significance throughout history in part because typical humans have five digits on each hand. In mathematics 5 is the third smallest prime number, and the second super-prime. It is the first safe prime, the first good prime, the first balanced prime, and the first of three known Wilson primes. Five is the second Fermat prime and the third Mersenne prime exponent, as well as the third Catalan number, and the third Sophie Germain prime. Notably, 5 is equal to the sum of the ''only'' consecutive primes, 2 + 3, and is the only number that is part of more than one pair of twin primes, ( 3, 5) and (5, 7). It is also a sexy prime with the fifth prime number and first prime repunit, 11. Five is the third factorial prime, an alternating factorial, and an Eisenstein prime with no imaginary part and real part of the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varmint Hunting
Varmint hunting or varminting is the practice of hunting vermin — generally small/medium-sized wild mammals or birds — as a means of pest control, rather than as games for food or trophy. The targeted animals are culled because they are considered economically harmful pests to agricultural crops, livestocks or properties; pathogen-carrying hosts/vectors that transmit cross-species/ zoonotic diseases; or for population control as a mean of protecting other vulnerable species and ecosystems. The term "varminter" may refer to a ''varmint hunter'', or describe the hunting equipments (such as a varmint rifle) either specifically designed or coincidentally suitable for the practice of varmint hunting. Varmint hunters may hunt to exterminate a nuisance animal from their own property, to collect a bounty offered by another landowner or the government, or simply as a hobby. Targets of varmint hunting The term ''varmint'' is a US colloquial term for ''vermin'', though it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headstamp
A headstamp is the markings on the bottom of a cartridge case designed for a firearm. It usually tells who manufactured the case. If it is a civilian case it often also tells the caliber: if it is military, the year of manufacture is often added. The headstamp is punched into the base of the cartridge during manufacture. A resource for identifying where the ammunition originated can be found aCartridge Collectors Australia * BB ''Bertram Bullet Co. Pty. Ltd.'' (1986–present) – Seymour, Melbourne, Victoria. Bruce Bertram bought Super Cartridge Co.'s machinery and moved it to Seymour, where he began manufacturing brass cases for handloaders. The "BB" is at 12 o'clock and small kangaroos are positioned counter-clockwise at 3 o'clock and 9 o'clock. Brass is sold in lots of 20-case cartons and can be made to customer's specifications with personalized headstamps. * ICI-ANZ ''Imperial Chemical Industries – Australia / New Zealand'' (1940s – 1980s) – Deer Park, Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handloading
Handloading, or reloading, is the practice of making firearm cartridges by assembling the individual components (case, primer, propellant, and projectile), rather than purchasing mass-assembled, factory-loaded ammunition. The term ''handloading'' is the more general term, and refers generically to the manual assembly of ammunition. ''Reloading'' refers more specifically to handloading using previously fired cases and shells. The terms are often used interchangeably however, as the techniques are largely the same, whether the handloader is using new or recycled components. The differences lie in the initial preparation of cases and shells; new components are generally ready to load, while previously fired components often need additional procedures, such as cleaning, removal of expended primers, or the reshaping and resizing of brass cases. Reasons for handloading Economy, increased performance and accuracy, commercial ammunition shortages, and hobby interests are all co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norma Precision
Norma Precision AB, commonly referred to simply as Norma, is a Swedish manufacturer of firearm ammunition based in Åmotfors, Värmland, just off the Norwegian border. History Norma was started in 1902 by three Norwegian brothers from Nordre Land, Lars Enger (1850-1917), Johan Enger (1852-1925) and Ivar Enger (1863-1942), whose company L.A.Enger & Co acquired an ammunition factory in Raufoss and later moved to Kristiania (modern day Oslo) as Norma Projektilfabrik A/S (Norma projectile factory stock company) a few years earlier in 1895. The name "Norma" has often been confused as a shorthand for Normandy or "Norge" (Norway in Nordic), however the name was actually chosen because Lars, the eldest of the three brothers, was very fond of the Italian opera '' Norma'' by Vincenzo Bellini. The Swedish shooting movement needed a supplier and Norma Projektilfabrik A/S was asked to establish a local presence in Sweden. At this time, Sweden and Norway were in a union. The y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)