|
242 Deaths
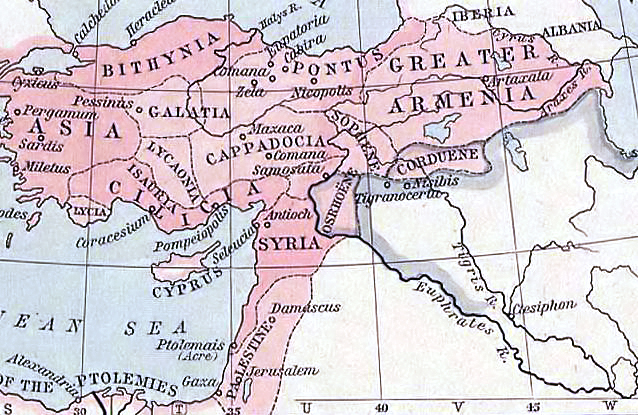
Year 242 ( CCXLII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Gratus and Lepidus (or, less frequently, year 995 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 242 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Gordian III begins a campaign against King Shapur I, and leads victories at Antioch, Carrhae, Nisibis, and Resaina. * Gordian III evacuates the Cimmerian cities in the Bosphorus (Crimea), as the territory is now controlled by the Goths. Persia * Shapur I makes a pre-emptive attack on Antioch to drive out the Romans. Gordian's father-in-law, Timesitheus, leads a Roman army to defeat the Sassanids at Carrhae and Nisibis. * King Ardashir I, founder of the Sassanid Empire, dies after a 30-year reign. He is succeeded by his son and co-ruler Shapur I. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinar Of Shapur I, Circa AD 244-252
The dinar () is the name of the principal currency unit in several countries near the Mediterranean Sea, with a more widespread historical use. The English word "dinar" is the transliteration of the Arabic دينار (''dīnār''), which was borrowed via the Syriac ''dīnarā'' from the Latin ''dēnārius''. The modern gold dinar is a projected bullion gold coin, and is not issued as an official currency by any state. History The modern dinar's historical antecedents are the gold dinar and the silver dirham, the main coin of the medieval Islamic empires, first issued in AH 77 (696–697 AD) (Late Antiquity) by Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan. The word "dinar" derives from the Latin word " ''dēnārius''," a silver coin of ancient Rome, which was first minted about c. 211 BC. The Kushan Empire introduced a gold coin known as the ''dīnāra'' in India in the 1st century AD; the Gupta Empire and its successors up to the 6th century adopted the coin. The 8th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is now Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania. From here they conducted raids into Roman territory, and large numbers of them joined the Roman military. These early Goths lived in the regions where archaeologists find the Chernyakhov culture, which flourished throughout this region during the 3rd and 4th centuries. In the late 4th century, the lands of the Goths in present-day Ukraine were overwhelmed by a significant westward movement of Alans and Huns from the east. Large numbers of Goths subsequently concentrated upon the Roman border at the Lower Danube, seeking refuge inside the Roman Empire. After they entered the Empire, violence broke out, and Goth-led forces inflicted a devastating defeat upon the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Wei
Wei () was one of the major Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic states in China during the Three Kingdoms period. The state was established in 220 by Cao Pi based upon the foundations laid by his father Cao Cao during the end of the Han dynasty. Its capital was initially located at Xuchang, and was later moved to Luoyang. The name ''Wei'' first became associated with Cao Cao when he was named the Duke of Wei by the Eastern Han government in 213, and became the name of the state when Cao Pi proclaimed himself emperor in 220. Historians often add the prefix "Cao" to distinguish it from other Chinese states known as ''Wei (other), Wei''. The authority of the ruling Cao family dramatically weakened following the deposition and execution of Cao Shuang, a regent for the dynasty's third emperor Cao Fang. Beginning in 249, another regent in Sima Yi gradually consolidated state authority for himself and his relatives, with the last Wei emperors largely being puppet ruler, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Hui (Prince Of Dongping)
Cao Hui (died February or March 242) was an imperial prince of the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period of China. Life Cao Hui was a son of Cao Cao, a warlord who rose to prominence towards the end of the Han dynasty and laid the foundation for the Cao Wei state. His mother was Consort Song (宋姬), a concubine of Cao Cao. He was designated as the heir of his uncle, Cao Yu (曹玉), because the latter had no son to succeed him when he died.(東平靈王徽,奉叔公朗陵哀侯玉後。) ''Sanguozhi'' vol. 20. In 217, Cao Hui was enfeoffed as the "Marquis of Licheng" (歷城侯) by Emperor Xian, the figurehead emperor of the Han dynasty. In 220, following Cao Cao's death, Cao Hui's half-brother Cao Pi usurped the throne from Emperor Xian, ended the Han dynasty, and established the Cao Wei state with himself as the new emperor. The following year, Cao Pi enfeoffed Cao Hui as a duke. In 222, Cao Pi elevated Cao Hui from the status of a duke to a prince under the title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonius Saccas
Ammonius Saccas (; ; 175 AD243 AD) was a Hellenistic Platonist self-taught philosopher from Alexandria, generally regarded as the precursor of Neoplatonism or one of its founders. He is mainly known as the teacher of Plotinus, whom he taught from 232 to 243. He was undoubtedly the most significant influence on Plotinus in his development of Neoplatonism, although little is known about his own philosophical views. Later Christian writers stated that Ammonius was a Christian, but it is now generally assumed that there was a different Ammonius of Alexandria who wrote biblical texts. Life The origins and meaning of Ammonius' cognomen, "Sakkas", are disputed. Many scholars have interpreted it as indicating he was a porter in his youth, a view supported in antiquity by Byzantine bishop Theodoret. Others have asserted that this is a misreading of "Sakkas" for "sakkophoros" (porter). Some others have connected the cognomen with the " Śākyas", an ancient ruling clan of India, claimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saloninus
Publius Licinius Cornelius Saloninus Valerianus (died 260), typically just called Saloninus, was a young Roman nobleman who briefly became emperor in 260. The grandson of Valerian I, Saloninus was appointed ''caesar'' (heir) in 258 in an attempt to shore up the Licinial line of succession during the Crisis of the Third Century. During his time in power, Saloninus administered the German marches out of Cologne. Nevertheless, Saloninus soon became embroiled in a dispute with future Gallic emperor Postumus over war spoils. In 260, Saloninus' troops acclaimed him ''augustus'' (emperor) in an unsuccessful bid for political legitimacy; Postumus killed Saloninus shortly thereafter. Early life Saloninus' father was the later emperor Gallienus, his mother Cornelia Salonina, a Greek from Bithynia. In 258 Saloninus was appointed '' Caesar'' by his father (just like his older brother Valerian II, who had died around 258) and sent to Gaul to make sure his father's authority was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecumenical Patriarch Of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople () is the List of ecumenical patriarchs of Constantinople, archbishop of Constantinople and (first among equals) among the heads of the several autocephalous churches that comprise the Eastern Orthodox Church. The ecumenical patriarch is regarded as the representative and spiritual leader of the Eastern Orthodox Christians worldwide. The term ''ecumenical'' in the title is a historical reference to the Ecumene, a Greek designation for the civilised world, i.e. the Roman Empire, and it stems from Canon 28 of the Council of Chalcedon. The patriarch's Episcopal see, see, the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, is one of the most enduring institutions in the world and has had a prominent part in world history. The ecumenical patriarchs in ancient times helped in the spread of Christianity and the resolution of various doctrinal disputes. In the Middle Ages, they played a major role in the affairs of the Eastern Orthodox Church, as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugenius I Of Byzantium
Eugenius I of Byzantium (; died ) was the bishop of Byzantium from around 240 until his death in . Notes and references 242 deaths Bishops of Byzantium 3rd-century Romans Year of birth unknown {{Byzantine-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Of Byzantium
Titus of Byzantium (Greek: Τῖτος; died 272) was Bishop of Byzantium from 242 to 272. He is venerated in the Eastern Orthodox Church The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ... on the 4 June. Notes and references {{Authority control 272 deaths Year of birth unknown Bishops of Byzantium 3rd-century Romans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late antiquity.Norman A. Stillman ''The Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardashir I
Ardashir I (), also known as Ardashir the Unifier (180–242 AD), was the founder of the Sasanian Empire, the last empire of ancient Iran. He was also Ardashir V of the Kings of Persis, until he founded the new empire. After defeating the last Parthian Empire, Parthian King of Kings, shahanshah Artabanus IV of Parthia, Artabanus IV on the Battle of Hormozdgan, Hormozdgan plain in 224, he overthrew the Parthian Empire, Arsacid dynasty and established the Sasanian dynasty. Afterwards, Ardashir called himself ''shahanshah'' and began conquering the land that he called ''Iran (word), Eranshahr'', the realm of the Arya (Iran), Iranians. There are various historical reports about Ardashir's lineage and ancestry. According to al-Tabari's ''History of the Prophets and Kings'', Ardashir was son of Papak, son of Sasan. Another narrative recorded in Kar-Namag i Ardashir i Pabagan, ''Kar-Namag i Ardashir i Pabagan'' and Ferdowsi, Ferdowsi's ''Shahnameh'' states that Ardashir was born from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nusaybin
Nusaybin () is a municipality and district of Mardin Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,079 km2, and its population is 115,586 (2022). The city is populated by Kurds of different tribal affiliation. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli by the Syria–Turkey border. The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla escarpment at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River (), the ancient Mygdonius (). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire and is recorded in Akkadian inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire, in the Hellenistic period the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty after the conquests of Alexander the Great. A part of first the Roman Republic and then the Roman Empire, the city (; ) was mainly Syriac-speaking, and control of it was contested between the Kingdom of Armenia, the Romans, and the Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |