|
2023 Jishishan Earthquake
On 18 December 2023 at around 23:59:30 CST, an earthquake with a magnitude of 5.9–6.2 struck Jishishan County, in Gansu Province, China. The shallow thrust faulting earthquake struck a densely populated area on the border between the provinces of Gansu and Qinghai. One hundred and fifty-one people died and 982 others were injured. This made it China's deadliest earthquake since the 2014 Ludian earthquake. Tectonic setting The Jishi Shan range lies in the easternmost segment of the Qilian Mountains that form part of the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. The plateau is a thickened zone of continental crust formed as a result of the ongoing collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. The plateau continues to be pushed northwards, while spreading laterally, causing the development of a combination of large left-lateral strike-slip faults and zone of thrust faulting. The NNW–SSE trending Jishi Shan range is bounded on both sides by faults that sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Standard Time
The time in China follows a single standard UTC offset, time offset of UTC+08:00 (eight hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time), even though the country spans almost five geographical time zones. The official national standard time is called ''Beijing Time'' (BJT, ) domestically and ''China Standard Time'' (CST) internationally. Daylight saving time has not been observed since 1991. China Standard Time (UTC+8) is consistent across Mainland China, Hong Kong Time, Hong Kong, Macau Standard Time, Macau, Time in Taiwan, Taiwan, Philippine Standard Time, Philippines, Singapore Standard Time, Singapore, Time in Brunei, Brunei, Time in Mongolia, Mongolia, etc. History In the 1870s, the Shanghai Xujiahui Observatory was constructed by a French Catholic missionary. In 1880s officials in Shanghai French Concession started to provide a time announcement service using the Shanghai Mean Solar Time provided by the aforementioned observatory for ships into and out of Shanghai. By the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
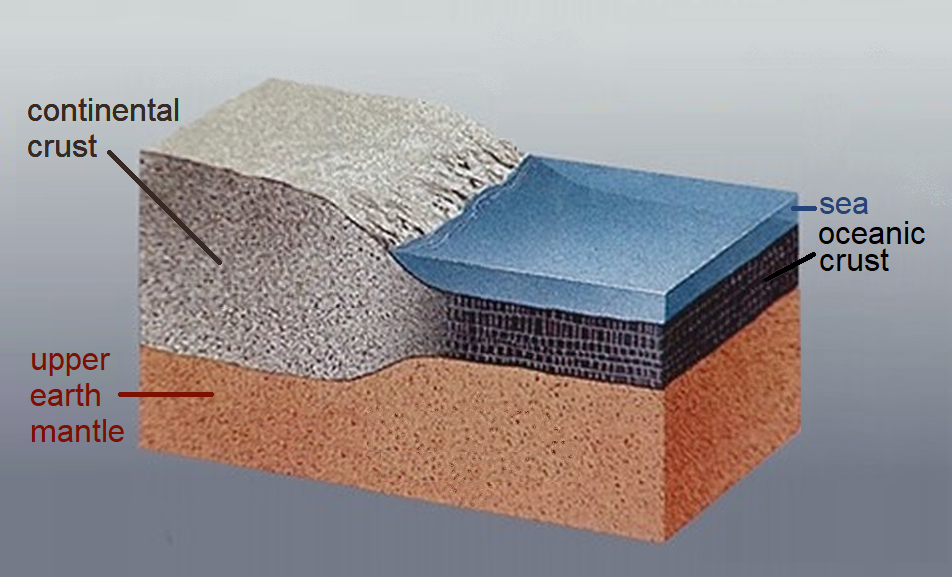
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNSS Applications
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers, using the GPS, GLONASS, Galileo or BeiDou system, are used in many applications. The first systems were developed in the 20th century, mainly to help military personnel find their way, but location awareness soon found many civilian applications. Navigation *Automobiles can be equipped with GNSS receivers at the factory or as aftermarket equipment. Units often display moving maps and information about location, speed, direction, and nearby streets and points of interest. *Air navigation systems usually have a moving map display and are often connected to the autopilot for en-route navigation. Cockpit-mounted GNSS receivers and glass cockpits are appearing in general aviation aircraft of all sizes, using technologies such as SBAS or DGPS to increase accuracy. Many are certified for instrument flight rules navigation, and some can also be used for final approach and landing operations as in Joint precision approach and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lajia
Lajia () is a Bronze Age archaeological site in the upper reaches of the Yellow River, on the border between the Chinese provinces of Gansu and Qinghai. As at other sites of the Qijia culture (c. 2300–1500 BCE), the people of Lajia had an agricultural economy based primarily on millet cultivation and sheep herding. They also kept pigs for use in ritual activities, including making oracle bones, and experimented with a high temperature-fired pottery described as proto-porcelain. The world's oldest known noodles were discovered at the site in 2005. A natural disaster that buried the site and killed many of its inhabitants in around 1920 BCE, but archaeologists continue to debate the exact cause of the catastrophe. Background Lajia is associated with the Qijia culture, an archaeological culture of northwestern China dated to the late Neolithic and early Bronze Age periods (c. 2300–1500 BCE). Excavations at the site have unearthed various Qijia artifacts, including pottery, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jishi Gorge Outburst Flood
The Jishi Gorge outburst flood was a natural disaster that occurred around 1920 BC in China. The water flow during the eruption was one of the largest fresh water flows to occur in our geologic epoch (Holocene) and caused large widespread flooding around the Yellow River, affecting everyone living in the river basin. The flood outbreak was triggered by the bursting of a dam caused by landslides after an earthquake. The flood is suggested to possibly be the disaster that gave rise to the Gun-Yu flood myth, which preceded the establishment of the Xia dynasty. The Lajia archaeological site, downstream of the Jishi Gorge, was first destroyed by the earthquake and later covered by sediments from the flood eruption. The course The Jishi Gorge (球石峡) leads the Yellow River from the river area around Xunhua in the west through the Jishi Mountain and further east to the river area around the Guanting Basin. An earthquake triggered landslides and rock avalanches that dammed the Yellow R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
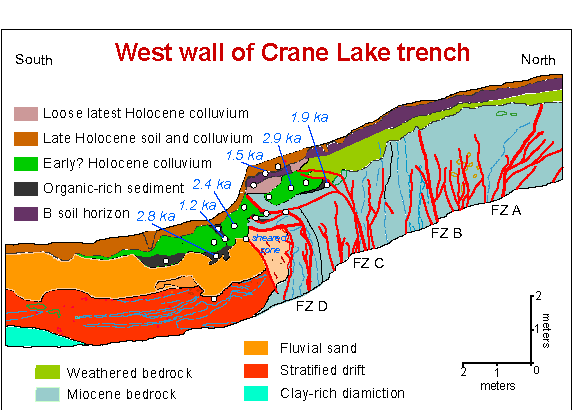
Paleoseismology
Paleoseismology looks at geologic sediments and rocks, for signs of ancient earthquakes. It is used to supplement seismic monitoring, for the calculation of seismic hazard. Paleoseismology is usually restricted to geologic regimes that have undergone continuous sediment creation for the last few thousand years, such as swamps, lakes, river beds and shorelines. In this typical example, a trench is dug in an active sedimentation regime. Evidence of thrust faulting can be seen in the walls of the trench. It becomes a matter of deducting the relative age of each fault, by cross-cutting patterns. The faults can be dated in absolute terms, if there is dateable carbon, or human artifacts. Many notable discoveries have been made using the techniques of paleoseismology. For example, there is a common misconception that having many smaller earthquakes can somehow 'relieve' a major fault such as the San Andreas Fault, and reduce the chance of a major earthquake. It is now known ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinling
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major east–west mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Yellow River systems, providing a natural boundary between North and South China and support a huge variety of plant and wildlife, some of which is found nowhere else on earth. To the north is the densely populated Wei River valley, an ancient center of Chinese civilization. To the south is the Han River valley. To the west is the line of mountains along the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. To the east are the lower Funiu and Dabie Shan which rise out of the coastal plain. The northern side of the range is prone to hot weather, however the physical barrier of the mountains mean that the land to the North has a semi-arid climate, with the lack of rich, fertile landscape that can not support a wealth of wildlife. The mountains also acte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riyue Mountain
Riyue Mountain (), known in Tibetan as Nyima Dawa La, is actually a mountain pass situated in Huangyuan County, Xining, Qinghai Province, China. The mountain pass is above sea level and separates the Qinghai Lake endorheic basin from the Huangshui River basin, a tributary of the Yellow River. The Daotang River () flows west from the pass into Qinghai Lake. The pass separates Qinghai Province into a pastoral zone in the west and an agricultural zone in the east. The mountain pass is currently crossed by China National Highway 214 that follows the ancient trade route into Tibet.Dorje (1999), pp. 535-536. Legend The Nyima Dawa La (pass) was made famous due to its association with the Han-Chinese Princess Wencheng when she was en route to marry Tibetan King Songtsen Gampo in the 7th century. She is said to have looked in a magic mirror here with a sun-moon design which was supposed to show her family in Chang'an Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpression
In geology, transpression is a type of strike-slip deformation that deviates from simple shear because of a simultaneous component of shortening perpendicular to the fault plane. This movement ends up resulting in oblique shear. It is generally very unlikely that a deforming body will experience "pure" shortening or "pure" strike-slip. The relative amounts of shortening and strike-slip can be expressed in the convergence angle alpha which ranges from zero (ideal strike-slip) to 90 degrees (ideal convergence). During shortening, unless material is lost, transpression produces vertical thickening in the crust. Transpression that occurs on a regional scale along plate boundaries is characterized by oblique convergence. More locally, transpression occurs within restraining bends in strike-slip fault zones. Transpressional structures Transpressional shear zones are characterized by an association of structures that suggest zone-normal shortening and zone-parallel shearing. Commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephonic or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. The GPS project was started by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1973. The first prototype spacecraft wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike-slip Fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A '' fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |