|
2019 Redefinition Of The SI Base Units
In 2019, four of the seven SI base units specified in the International System of Quantities were redefined in terms of natural physical constants, rather than human artefacts such as the standard kilogram. Effective 20 May 2019, the 144th anniversary of the Metre Convention, the kilogram, ampere, kelvin, and mole are defined by setting exact numerical values, when expressed in SI units, for the Planck constant ('), the elementary electric charge ('), the Boltzmann constant (), and the Avogadro constant (), respectively. The second, metre, and candela had previously been redefined using physical constants. The four new definitions aimed to improve the SI without changing the value of any units, ensuring continuity with existing measurements. In November 2018, the 26th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) unanimously approved these changes, The conference ran from 13–16 November and the vote on the redefinition was scheduled for the last day. Kazakhsta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Relations In The New SI
Unit may refer to: General measurement * Unit of measurement, a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law **International System of Units (SI), modern form of the metric system **English units, historical units of measurement used in England up to 1824 **Unit of length Science and technology Physical sciences * Natural unit, a physical unit of measurement * Geological unit or rock unit, a volume of identifiable rock or ice * Astronomical unit, a unit of length roughly between the Earth and the Sun Chemistry and medicine * Equivalent (chemistry), a unit of measurement used in chemistry and biology * Unit, a vessel or section of a chemical plant * Blood unit, a measurement in blood transfusion * Enzyme unit, a measurement of active enzyme in a sample * International unit, a unit of measurement for nutrients and drugs Mathematics * Unit number, the number 1 * Unit, identity element * Unit (ring theory), an element that is inverti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Constant
A physical constant, sometimes fundamental physical constant or universal constant, is a physical quantity that cannot be explained by a theory and therefore must be measured experimentally. It is distinct from a mathematical constant, which has a fixed numerical value, but does not directly involve any physical measurement. There are many physical constants in science, some of the most widely recognized being the speed of light in vacuum ''c'', the gravitational constant ''G'', the Planck constant ''h'', the electric constant ''ε''0, and the elementary charge ''e''. Physical constants can take many dimensional forms: the speed of light signifies a maximum speed for any object and its dimension is length divided by time; while the proton-to-electron mass ratio is dimensionless. The term "fundamental physical constant" is sometimes used to refer to universal-but-dimensioned physical constants such as those mentioned above. Increasingly, however, physicists reserve the expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Constituent Assembly (France)
The National Constituent Assembly () was a constituent assembly in the Kingdom of France formed from the National Assembly (French Revolution), National Assembly on 9 July 1789 during the first stages of the French Revolution. It dissolved on 30 September 1791 and was succeeded by the Legislative Assembly (France), Legislative Assembly. Background Estates-General The Estates General of 1789, ''(Etats Généraux)'' made up of representatives of the three estates, which had not been convened since 1614, met on 5 May 1789. The Estates-General reached a deadlock in its deliberations by 6 May. The representatives of the Third Estate attempted to make the whole body more effective and so met separately from 11 May as the ''Communes''. On 12 June, the ''Communes'' invited the other Estates to join them: some members of the Estates of the realm#First Estate, First Estate did so the following day. On 17 June 1789, the ''Communes'' approved s:Motion of Abbé Sieyès, the motion made by Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton (unit)
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u, respectively) is a unit of mass defined as of the mass of an Bound state, unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and invariant mass, at rest. It is a Non-SI units mentioned in the SI, non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. The word "unified" emphasizes that the definition was accepted by both IUPAP and IUPAC. The atomic mass constant, denoted , is defined identically. Expressed in terms of , the atomic mass of carbon-12: . Its value in International System of Units, SI units is an experimentally determined quantity. The 2022 CODATA recommended value of the atomic mass constant expressed in the SI base unit kilogram is:This value serves as a Conversion of units, conversion factor of mass from daltons to kilograms, which can easily be converted to Gram, grams and other metric units of mass. The 2019 revision of the SI redefined the kilogram by fixing the value of the Planck constant (), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
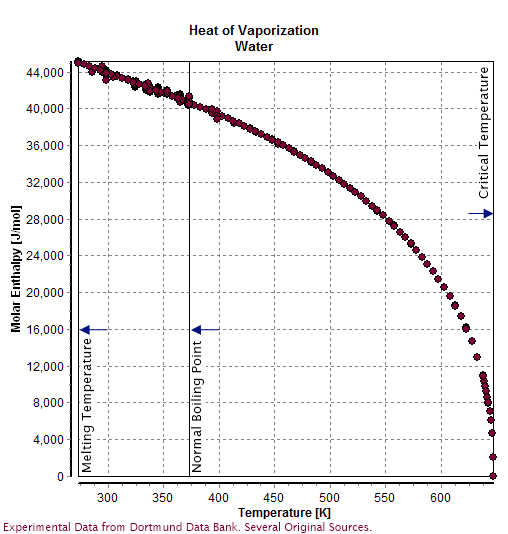
Triple Point Of Water
Water () is a polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, which is nearly colorless apart from an inherent hint of blue. It is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" and the "solvent of life". It is the most abundant substance on the surface of Earth and the only common substance to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas on Earth's surface. It is also the third most abundant molecule in the universe (behind molecular hydrogen and carbon monoxide). Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids, thus dissolving them. Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties, such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form, a relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar mass, and a high heat capacity. Water is amphote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric System
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules governing the metric system have changed over time, the modern definition, the International System of Units (SI), defines the metric prefixes and seven base units: metre (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), Mole (unit), mole (mol), and candela (cd). An SI derived unit is a named combination of base units such as hertz (cycles per second), Newton (unit), newton (kg⋅m/s2), and tesla (unit), tesla (1 kg⋅s−2⋅A−1) and in the case of Celsius a shifted scale from Kelvin. Certain units have been Non-SI units mentioned in the SI#Units officially accepted for use with the SI, officially accepted for use with the SI. Some of these are decimalised, like the litre and electronvolt, and are considered "metric". Others, like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherent System
A coherent system of units is a system of units of measurement used to express physical quantities that are defined in such a way that the equations relating the numerical values expressed in the units of the system have exactly the same form, including numerical factors, as the corresponding equations directly relating the quantities. It is a system in which every quantity has a unique unit, or one that does not use conversion factors. A coherent derived unit is a SI derived unit, derived unit that, for a given system of quantities and for a chosen set of Base unit (measurement), base units, is a product of powers of base units, with the proportionality factor being one. If a system of quantities has equations that relate quantities and the associated system of units has corresponding base units, with only one unit for each base quantity, then it is coherent if and only if every derived unit of the system is coherent. The concept of coherence was developed in the mid-nineteenth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of second. The speed of light is invariant (physics), the same for all observers, no matter their relative velocity. It is the upper limit for the speed at which Information#Physics_and_determinacy, information, matter, or energy can travel through Space#Relativity, space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Much starlight viewed on Earth is from the distant past, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When Data communication, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krypton-86
There are 34 known isotopes of krypton (36Kr) with atomic mass numbers from 67 to 103. Naturally occurring krypton is made of five stable isotopes and one () which is slightly radioactive with an extremely long half-life, plus traces of radioisotopes that are produced by cosmic rays in the atmosphere. List of isotopes , -id=Krypton-67 , rowspan=2, 67Kr , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 36 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 31 , rowspan=2, 66.98331(46)# , rowspan=2, 7.4(29) ms , β+? (63%) , 67Br , rowspan=2, 3/2-# , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , - , 2p (37%) , 65Se , -id=Krypton-68 , rowspan=3, 68Kr , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 36 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 32 , rowspan=3, 67.97249(54)# , rowspan=3, 21.6(33) ms , β+, p (>90%) , 67Se , rowspan=3, 0+ , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , - , β+? (98.7%) , 70Br , rowspan=2, 0+ , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , - , β+, p (<1.3%) , 69Se , -id=Krypton-71 , row ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves), phase'' on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The multiplicative inverse, inverse of the wavelength is called the ''spatial frequency''. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (''λ''). For a modulated wave, ''wavelength'' may refer to the carrier wavelength of the signal. The term ''wavelength'' may also apply to the repeating envelope (mathematics), envelope of modulated waves or waves formed by Interference (wave propagation), interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed phase velocity, wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prototype Metre
During the French Revolution, the traditional units of measure were to be replaced by consistent measures based on natural phenomena. As a base unit of length, scientists had favoured the seconds pendulum (a pendulum with a half-period of one second) one century earlier, but this was rejected as it had been discovered that this length varied from place to place with local gravity. A new unit of length, the ''metre'' was introduced – defined as one ten-millionth of the shortest distance from the North Pole to the equator passing through Paris, assuming an Earth flattening of . Following the arc measurement of Delambre and Méchain, the historical French official standard of the metre was made available in the form of the , a platinum bar held in Paris. During the mid nineteenth century, following the American Revolution and independence of Latin America, the metre gained adoption in Americas, particularly in scientific usage, and it was officially established as an inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |