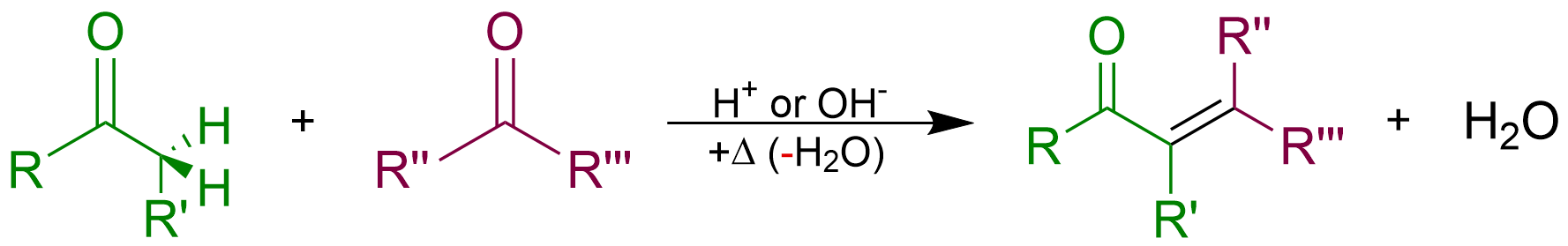|
2-ethylhexanol
2-Ethylhexanol (abbreviated 2-EH) is an organic compound with formula CHO. It is a branched, eight-carbon chiral alcohol. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. It is produced on a large scale (>2,000,000,000 kg/y) for use in numerous applications such as solvents, flavors, and fragrances and especially as a precursor for production of other chemicals such as emollients and plasticizers. It is encountered in plants, fruits, and wines. The odor has been reported as "heavy, earthy, and slightly floral" for the R enantiomer and "a light, sweet floral fragrance" for the S enantiomer. Properties and applications The branching in 2-ethylhexanol inhibits crystallization. Esters of 2-ethylhexanol are similarly affected, which together with low volatility, is the basis of applications in the production of plasticizers and lubricants, where its presence helps reduce viscosity and lower freezing points. Because 2-ethylhexanol is a fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylheptyl Alcohol
2-Propylheptanol (2PH) is a colourless waxy or oily solid. Production 2-Propylheptanol is an oxo alcohol, meaning that it is produced from the hydroformylation ("oxo synthesis") of C4 alkenes followed by hydrogenation of the resulting aldehyde. The production route is similar to that for 2-Ethylhexanol 2-Ethylhexanol (abbreviated 2-EH) is an organic compound with formula CHO. It is a branched, eight-carbon chiral alcohol. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. It is produced on a large scale .... Applications Such compounds enjoy many applications, including as raw materials for plasticizers, resins, processing solvents, and precursors to detergents. Heat stabilizers manufactured for PVC compounds use similar high boiling and high molecular weight oxo-alcohols, which enhance product performance. A further application area of this C10 alcohol is for the manufacture of oleate- and palmitate-based materials used by the cosmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Ethylhexanoic Acid
2-Ethylhexanoic acid is the organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)3CH(C2H5)CO2H. It is a carboxylic acid that is widely used to prepare lipophilic metal derivatives that are soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. 2-Ethylhexanoic acid is a colorless viscous oil. It is supplied as a racemic mixture. Production 2-Ethylhexanoic acid is produced industrially from propylene, which is hydroformylated to give butyraldehyde. Aldol condensation of the aldehyde gives 2-ethylhexenal, which is hydrogenated to 2-ethylhexanal. Oxidation of this aldehyde gives the carboxylic acid. Metal ethylhexanoates 2-Ethylhexanoic acid forms compounds with metal cations that have stoichiometry as metal acetates. These ethylhexanoate complexes are used in organic and industrial chemical synthesis. They function as catalysts in polymerizations as well as for oxidation reactions as "oil drying agents." They are highly soluble in nonpolar solvents. These metal complexes are often described as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Methylheptane
3-Methylheptane is a branched alkane isomeric to octane. Its structural formula is CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH2CH2CH3. It has one stereocenter. Its refractive index In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, o ... is 1.398 (20 °C, D). References External linksNon-stereospecific oxidation of DL-3-methylheptane by aPseudomonas {{DEFAULTSORT:Methylheptane, 3- Alkanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Methylhexane
2-Methylhexane ( C7 H16, also known as isoheptane, ethylisobutylmethane) is an isomer of heptane. It is structurally a hexane molecule with a methyl group attached to its second carbon atom. It exists in most commercially available heptane merchandises as an impurity but is usually not considered as impurity in terms of reactions since it has very similar physical and chemical properties when compared to n-heptane (straight-chained heptane). Being an alkane, 2-methylhexane is insoluble in water, but is soluble in many organic solvents, such as alcohols and ether. However, 2-methylhexane is more commonly considered as a solvent itself. Therefore, even though it is present in many commercially available heptane products, it is not considered as a destructive impurity, as heptane is usually used as a solvent. Nevertheless, by concise processes of distillation and refining, it is possible to separate 2-methylhexane from n-heptane. Within a group of isomers, those with more branches ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate, diethylhexyl phthalate, diisooctyl phthalate, DEHP; incorrectly — dioctyl phthalate, DIOP) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO2C8H17)2. DEHP is the most common member of the class of phthalates, which are used as plasticizers. It is the diester of phthalic acid and the branched-chain 2-ethylhexanol. This colorless viscous liquid is soluble in oil, but not in water. Production Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate is produced commercially by the reaction of excess 2-ethylhexanol with phthalic anhydride in the presence of an acid catalyst such as sulfuric acid or ''para''-toluenesulfonic acid. It was first produced in commercial quantities in Japan around 1933 and in the United States in 1939. : As 2-ethylhexanol is produced as a racemic mixture, DEHP consists of the (''R'',''R'')- and (''S'',''S'')- diasteromers, and the ''meso''-isomer. : Use Due to its suitable properties and the low cost, DEHP is widely used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Methylheptane
2-Methylheptane is a branched alkane isomeric to octane. Its structural formula The structural formula of a chemical compound is a graphic representation of the molecular structure (determined by structural chemistry methods), showing how the atoms are possibly arranged in the real three-dimensional space. The chemical bond ... is (CH3)2CH(CH2)4CH3. References External links *Chemical and physical properties table {{DEFAULTSORT:Methylheptane, 2- Alkanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valnoctamide
Valnoctamide (INN, USAN) has been used in France as a sedative-hypnotic since 1964. It is a structural isomer of valpromide, a valproic acid prodrug; unlike valpromide, however, valnoctamide is not transformed into its homologous acid, valnoctic acid, ''in vivo''. Indications In addition to being a sedative, valnoctamide has been investigated for use in epilepsy. It was studied for neuropathic pain in 2005 by Winkler et al., with good results: it had minimal effects on motor coordination and alertness at effective doses, and appeared to be equally effective as gabapentin. RH Belmaker, Yuly Bersudsky and Alex Mishory started a clinical trial of valnoctamide for prophylaxis of mania in lieu of the much more teratogenic valproic acid or its salts. Side effects The side effects of valnoctamide are mostly minor and include somnolence and the slight motor impairments mentioned above. Interactions Valnoctamide is known to increase through inhibition of epoxide hydrolase the serum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldol Condensation
An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which two carbonyl moieties (of aldehydes or ketones) react to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone (an aldol reaction), and this is then followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone. The overall reaction is as follows (where the Rs can be H): Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis and biochemistry as ways to form carbon–carbon bonds. In its usual form, it involves the nucleophilic addition of a ketone enolate to an aldehyde to form a β-hydroxy ketone, or "aldol" (aldehyde + alcohol), a structural unit found in many naturally occurring molecules and pharmaceuticals. The term ''aldol condensation'' is also commonly used, especially in biochemistry, to refer to just the first (addition) stage of the process—the aldol reaction itself—as catalyzed by aldolases. However, this is formally an addition reaction rather than a condensation reaction because it does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
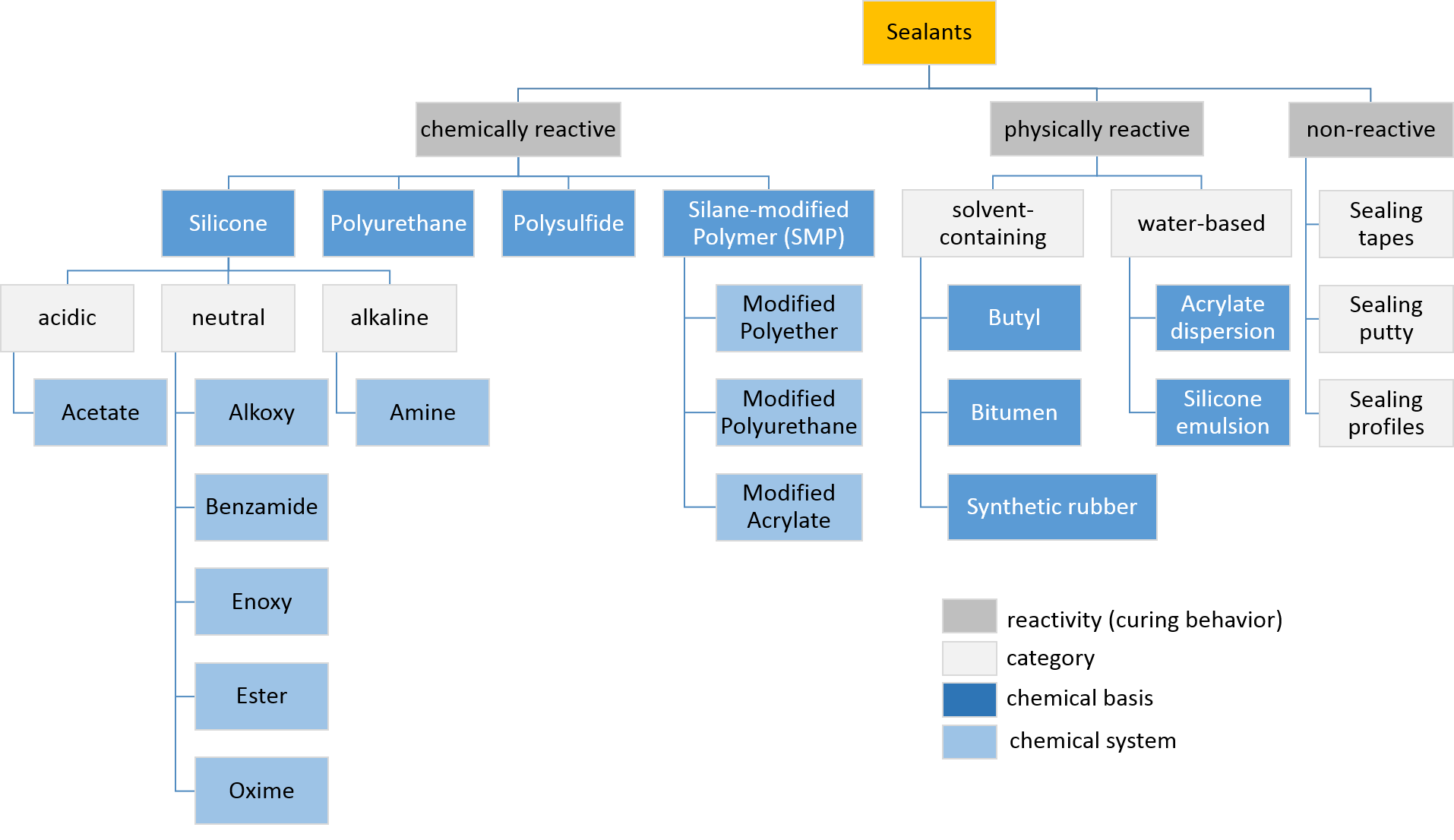
Sealant
Sealant is a substance used to block the passage of fluids through openings in materials, a type of mechanical seal. In building construction ''sealant'' is sometimes synonymous with ''caulking'' and also serve the purposes of blocking dust, sound and heat transmission. Sealants may be weak or strong, flexible or rigid, permanent or temporary. Sealants are not adhesives but some have adhesive qualities and are called ''adhesive-sealants'' or ''structural sealants''. History Sealants were first used in prehistory in the broadest sense as mud, grass and reeds to seal dwellings from the weather such as the daub in wattle and daub and thatching. Natural sealants and adhesive-sealants included plant resins such as pine pitch and birch pitch, bitumen, wax, tar, natural gum, clay (mud) mortar, lime mortar, lead, blood and egg. In the 17th century glazing putty was first used to seal window glass made with linseed oil and chalk, later other drying oils were also used to make oil-based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimellitic Acid
Trimellitic acid (benzene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H3(СООН)3. Like the other isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid, trimellitic acid is a colorless solid. It is prepared by oxidation of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene. Isomers * Hemimellitic acid (benzene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid) * Trimesic acid (benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid) See also * Trimellitic anhydride chloride * Trimellitic anhydride * Plasticizer#Trimellitates * Mellitic acid Mellitic acid, also called graphitic acid or benzenehexacarboxylic acid, is an acid first discovered in 1799 by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in the mineral mellite (honeystone), which is the aluminium salt of the acid. It crystallizes in fine silky ... References Tricarboxylic acids Benzoic acids {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. Powder coatings. Paints and lacquers are coatings that mostly have dual uses of protecting the substrate and being decorative, although some artists paints are only for decoration, and the paint on large industrial pipes is for preventing corrosion and identification e.g. blue for process water, red for fire-fighting control etc. Functional coatings may be applied to change the surface properties of the substrate, such as adhesion, wettability, corrosion resistance, or wear resistance. In other cases, e.g. semiconductor device fabrication (where the substrate is a wafer), the coating adds a completely new property, such as a magnetic response or electrical conductivity, and forms an essential part of the finished product. A major consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions . Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali that decomposes proteins at ordinary ambient temperatures and may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water, and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound. As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water and acidic hydrochloric acid to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students. Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the manufacture of pulp and paper, textiles, drinking water, soaps and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

2.jpg)