|
2,4-Dichloroamphetamine
2,4-Dichloroamphetamine (2,4-DCA) is a psychostimulant of the amphetamine family and a potent serotonergic neurotoxin related to ''para''-chloroamphetamine (PCA; 4-chloroamphetamine). It is also a potent monoamine oxidase inhibitor. See also * 3-Chloroamphetamine (3-CA) * 3,4-Dichloroamphetamine 3,4-Dichloroamphetamine (DCA), is an amphetamine derived drug invented by Eli Lilly in the 1960s, which has a number of pharmacological actions. It acts as a highly potent and selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) and binds to the seroto ... (3,4-DCA) References Chloroarenes Monoamine oxidase inhibitors Monoaminergic neurotoxins Substituted amphetamines Stimulants {{Nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonergic Neurotoxin
A monoamine neurotoxin, or monoaminergic neurotoxin, is a drug that selectively damages or destroys monoaminergic neurons. Monoaminergic neurons are neurons that signal via stimulation by monoamine neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. Examples of monoamine neurotoxins include the serotonergic neurotoxins ''para''-chloroamphetamine (PCA), methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), and 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine (5,7-DHT); the dopaminergic neurotoxins oxidopamine (6-hydroxydopamine), MPTP, and methamphetamine; and the noradrenergic neurotoxins oxidopamine and DSP-4. In the case of serotonergic neurotoxins like MDMA, research suggests that simultaneous induction of serotonin and dopamine release, serotonin depletion, dopamine uptake and metabolism, hyperthermia, oxidative stress and antioxidant depletion, and/or drug metabolites may all be involved in the neurotoxicity. On the other hand, there is evidence that drug metabolites may not be involved. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychostimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or illicitly) as performance-enhancing or recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or '' comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and prescription stimulants" (with "amphetamines" including amphetamine and methamphetamine) the value was 0.7%, and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
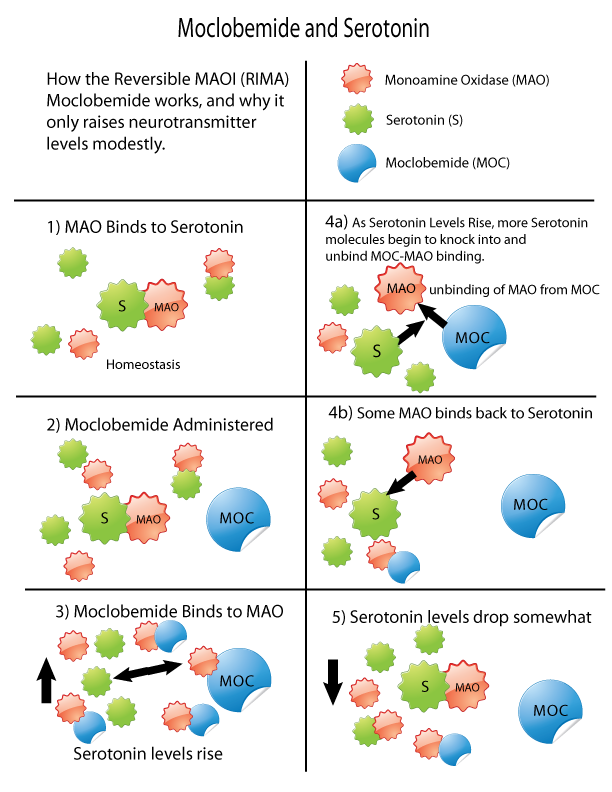
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with ago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychostimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or illicitly) as performance-enhancing or recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or '' comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and prescription stimulants" (with "amphetamines" including amphetamine and methamphetamine) the value was 0.7%, and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituted Amphetamine
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone (diethylpropion), pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP). Some of amphetamine's substituted derivatives occur in nature, for example in the leaves of '' Ephedra'' and khat plants. Amphetamine was first produced at the end of the 19th century. By the 1930s, amphetamine and some of its derivative compounds found use as decongestants in the symptomatic treatment of colds and also occasionally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potency (pharmacology)
In the field of pharmacology Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemi ..., potency is a measure of drug activity expressed in terms of the amount required to produce an effect of given intensity. A highly potent drug (e.g., fentanyl, alprazolam, risperidone, bumetanide, bisoprolol) evokes a given response at low concentrations, while a drug of lower potency ( meperidine, diazepam, ziprasidone, furosemide, metoprolol) evokes the same response only at higher concentrations. Higher potency does not necessarily mean greater effectiveness or more side effects. The IUPHAR has stated that 'potency' is ''"an imprecise term that should always be further defined"'', for instance as EC_, IC_, ED_, LD_ and so on. See also * Reaction inhibitor § Potency References F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with ago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3,4-Dichloroamphetamine
3,4-Dichloroamphetamine (DCA), is an amphetamine derived drug invented by Eli Lilly in the 1960s, which has a number of pharmacological actions. It acts as a highly potent and selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) and binds to the serotonin transporter with high affinity, but also acts as a selective serotonergic neurotoxin in a similar manner to the related para-chloroamphetamine, though with slightly lower potency. It is also a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), as well as a very potent inhibitor of the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase which normally functions to transform noradrenaline into adrenaline in the body. Synthesis The reaction of 3,4-Dichlorobenzyl Chloride 02-47-6(1) with cyanide anion gives 3,4-Dichlorophenylacetonitrile 218-49-3(2). Reaction with sodium methoxide and ethylacetate gives Alpha-Acetoxy-3,4-DichlorobenzeneacetonitrileCID:14318103(3). Removal of the nitrile group in the presence of sulfuric acid gives 3,4-Dichlorophenylacet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |