|
1st Cavalry Division (United Kingdom)
The 1st Cavalry Division was a regular Division of the British Army during the First World War where it fought on the Western Front. During the Second World War it was a first line formation, formed from Yeomanry Regiments. It fought in the Middle East before being converted to the 10th Armoured Division. Napoleonic Wars During the Peninsular War, Wellington organized his cavalry into The Cavalry Division from June 1809 under Major-General Sir William Payne. This performed a purely administrative, rather than tactical, role; the normal tactical headquarters were provided by brigades commanding two, later usually three, regiments. On 3 June 1810, Payne returned home and his second-in-command, Major-General Stapleton Cotton, took command. Cotton was to remain in command thereafter and effectively acted as Wellington's chief of cavalry. On 19 June 1811, the cavalry was reorganized as two divisions and The Cavalry Division was redesignated as 1st Cavalry Division with the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive government specifically or only to the monarch and their Viceroy, direct representatives. The term can be used to refer to the rule of law; or to the functions of executive (government), executive (the Crown-King-in-Council, in-council), legislative (the Crown-in-parliament), and judicial (the Crown on the bench) governance and the civil service. The concept of the Crown as a corporation sole developed first in the Kingdom of England as a separation of the physical crown and property of the kingdom from the person and personal property of the monarch. It spread through English and later British colonisation and developed into an imperial crown, which rooted it in the legal lexicon of all 15 Commonwealth realms, their various dependencies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Ypres
The Second Battle of Ypres was fought from 22 April – 25 May 1915, during the First World War, for control of the tactically-important high ground to the east and the south of the Flanders, Flemish town of Ypres, in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the previous autumn. The Second Battle of Ypres was the first mass use by Germany of Chemical weapon, poison gas on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front. Background The Germans, German chemist Walther Nernst, who in 1914 was a volunteer driver, proposed to Colonel Max Bauer, the German general staff officer responsible for liaison with scientists, that they could empty the opposing trenches by a surprise attack with tear gas. Observing a field test of this idea, the chemist Fritz Haber instead proposed using heavier-than-air chlorine gas. The German commander Erich von Falkenhayn agreed to try the new weapon but intended to use it in a diversionary attack by the 4th Army (German Empire), 4t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve personnel and 4,697 "other personnel", for a total of 108,413. The British Army traces back to 1707 and the Acts of Union 1707, formation of the united Kingdom of Great Britain which joined the Kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland into a Political union, single state and, with that, united the English Army and the Scots Army as the British Army. The Parliament of England, English Bill of Rights 1689 and Convention of the Estates, Scottish Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the Charles III, monarch as their commander-in-chief. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence (United Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Allenby, 1st Viscount Allenby
Field Marshal Edmund Henry Hynman Allenby, 1st Viscount Allenby, (23 April 1861 – 14 May 1936) was a senior British Army officer and imperial governor. He fought in the Second Boer War and also in World War I, in which he led the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign against the Ottoman Empire in the conquest of Palestine. The British succeeded in capturing Beersheba, Jaffa, and Jerusalem from October to December 1917. His forces occupied the Jordan Valley during the summer of 1918, then went on to capture northern Palestine and defeat the Ottoman Yildirim Army Group's Eighth Army at the Battle of Megiddo, forcing the Fourth and Seventh Army to retreat towards Damascus. Subsequently, the EEF Pursuit by Desert Mounted Corps captured Damascus and advanced into northern Syria. During this pursuit, he commanded T. E. Lawrence (''"Lawrence of Arabia"''), whose campaign with Faisal's Arab Sherifial Forces assiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria–Lebanon Campaign
The Syria–Lebanon campaign, also known as Operation Exporter, was the invasion of Syria and Lebanon (then controlled by Vichy France, a vassal state of Nazi Germany) in June and July 1941 by British Empire forces, during the Second World War. On 1 April 1941, after the Iraqi coup d'état, Iraq was controlled by Iraqi nationalists led by Rashid Ali al-Gaylani, who appealed for Italian and German support. The Anglo-Iraqi War (2–31 May 1941) led to the overthrow of the Ali regime and the installation of a pro-British government. During this conflict, Admiral François Darlan allowed German aircraft to use Vichy airfields in Syria for attacks against the British in Iraq. The British invaded Syria and Lebanon in June to prevent the Axis powers from using the Syrian Republic and French Lebanon as bases for attacks on Egypt, during an invasion scare in the aftermath of the Axis victories in the Battle of Greece (6–30 April 1941) and the Battle of Crete (20 May – 1 June) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Iraqi War
The Anglo-Iraqi War was a British-led Allies of World War II, Allied military campaign during the Second World War against the Kingdom of Iraq, then ruled by Rashid Ali al-Gaylani who had seized power in the 1941 Iraqi coup d'état with assistance from Germany and Italy. The campaign resulted in the downfall of Gaylani's government, the re-occupation of Iraq by the British, and the return to power of the Regent of Iraq, Prince 'Abd al-Ilah, a British ally. Mandatory Iraq had been governed by the British since 1921. Prior to Iraq's nominal independence in 1932, Britain concluded the Anglo-Iraqi Treaty of 1930, which was opposed by Iraqi nationalism, Iraqi nationalists, including Rashid Ali al-Gaylani. Although Iraq was considered a Neutral powers during World War II, neutral power under Regent of Iraq, Regent Abd al-Ilah, it had a pro-British government. In April 1941, Iraqi nationalists organized the Golden Square coup, with assistance from Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy (1922� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Final Advance In Picardy
Final, Finals or The Final may refer to: *Final examination or finals, a test given at the end of a course of study or training *Final (competition), the last or championship round of a sporting competition, match, game, or other contest which decides a winner for an event ** Another term for playoffs, describing a sequence of contests taking place after a regular season or round-robin tournament, culminating in a final by the first definition. Art and entertainment * ''Finals'' (comics), a four-issue comic book mini-series * ''The Finals'', a first-person shooter game Film * ''Final'' (film), a science fiction film * ''The Final'' (film), a thriller film * ''Finals'' (film), a 2019 Malayalam sports drama film Music *Final, a tone of the Gregorian mode *Final (band), an English electronic musical group *''Final (Vol. 1)'', 2021 album by Enrique Iglesias **''Final (Vol. 2)'', 2024 album by Enrique Iglesias * ''The Final'' (album), by Wham! *"The Final", a song by Dir en grey on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
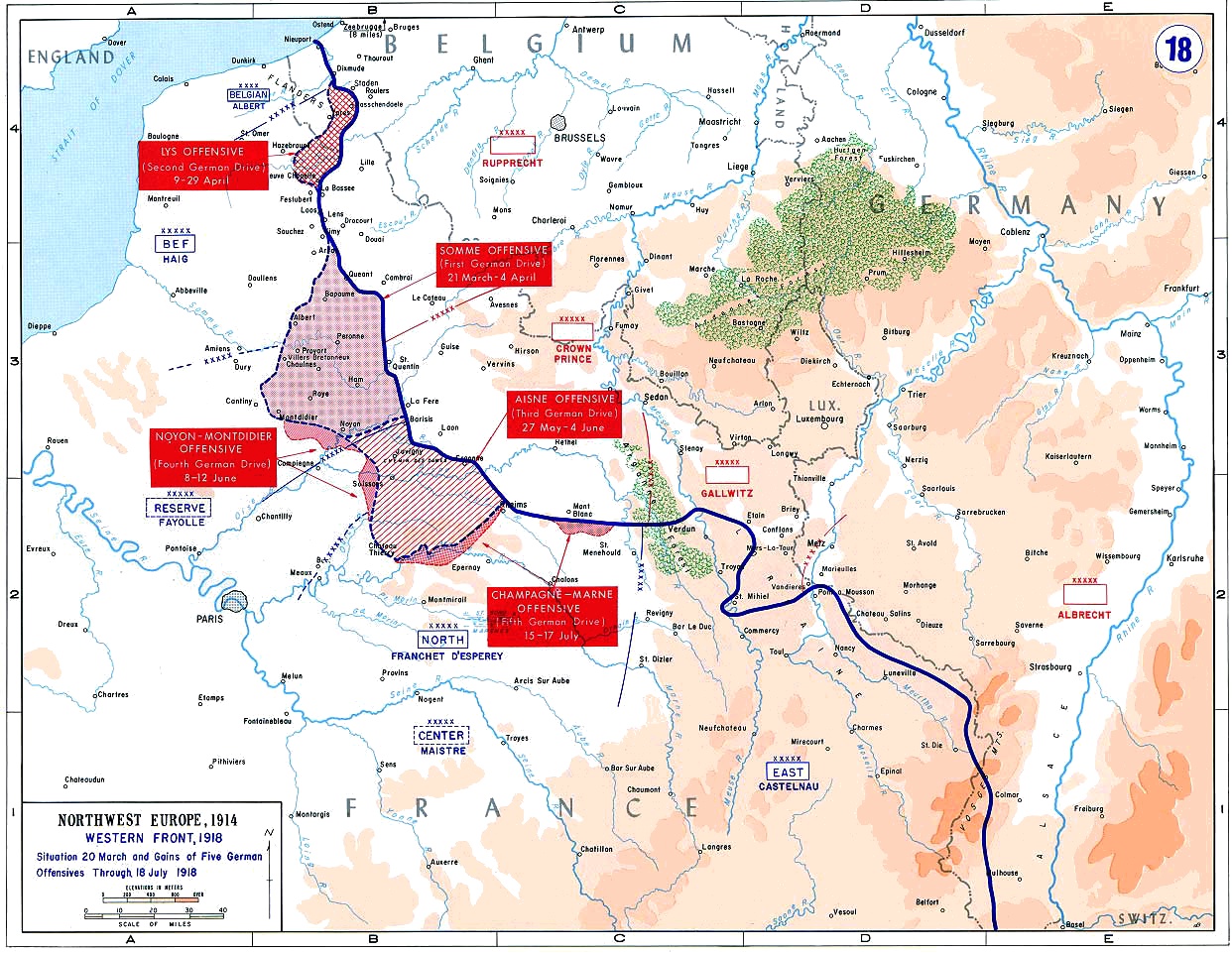
Hindenburg Line
The Hindenburg Line (, Siegfried Position) was a German Defense line, defensive position built during the winter of 1916–1917 on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front in France during the First World War. The line ran from Arras to Laffaux, near Soissons on the Aisne River, Aisne. In 1916, the Battle of Verdun and the Battle of the Somme left the German western armies () exhausted and on the Eastern Front (World War I), Eastern Front, the Brusilov Offensive had inflicted huge losses on the Austro-Hungarian armies and forced the Germans to take over more of the front. The declaration of war by Romania during World War I, Romania had placed additional strain on the German army and war economy. The Hindenburg Line, built behind the Noyon Salient (territory), Salient, was to replace the old front line as a precaution against a resumption of the Battle of the Somme in 1917. By devastating the intervening ground, the Germans could delay a spring offensive in 1917. A shorte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of The Somme
The Second Battle of the Somme of 1918 was fought during the First World War on the Western Front from late August to early September, in the basin of the River Somme. It was part of a series of successful counter-offensives in response to the German Spring Offensive, after a pause for redeployment and supply. The most significant feature of the two 1918 Somme battles was that with the failure of the first 1918 Somme Battle (not to be confused with the 1916 Battle of the Somme) having halted what had begun as a large German offensive, the second formed the central part of the Allies' advance to the Armistice of 11 November. Battle On August 15, British field marshal Douglas Haig refused demands from Supreme Allied Commander Marshal Ferdinand Foch to continue the Amiens offensive, as that attack was faltering as the troops outran their supplies and artillery, and German reserves were being moved to the sector. Instead, Haig began to plan for an offensive at Alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Amiens (1918)
The Battle of Amiens, also known as the Third Battle of Picardy was the opening phase of the Allies of World War I, Allied offensive which began on 8 August 1918, later known as the Hundred Days Offensive, which ultimately led to the end of World War I. Allied forces advanced over on the first day, one of the greatest advances of the war, with Gen Henry Rawlinson, 1st Baron Rawlinson, Henry Rawlinson's British Fourth Army, with nine of its 19 Division (military), divisions supplied by the fast-moving Australian Corps of Lt General John Monash and Canadian Corps of Lt General Arthur Currie, and Gen Marie Eugène Debeney's French First Army playing a decisive role. The battle is also notable for its effects on both sides' morale and the large number of surrender (military), surrendering German Empire, German forces. This led Erich Ludendorff to later describe the first day of the battle as "the black day of the German Army". Amiens was one of the first major battles involving arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Michael
Operation Michael () was a major German military offensive during World War I that began the German spring offensive on 21 March 1918. It was launched from the Hindenburg Line, in the vicinity of Saint-Quentin, France. Its goal was to break through the Allied (Entente) lines and advance in a north-westerly direction to seize the Channel Ports, which supplied the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), and to drive the BEF into the sea. Two days later General Erich Ludendorff, the chief of the German General Staff, adjusted his plan and pushed for an offensive due west, along the whole of the British front north of the River Somme. This was designed to first separate the French and British Armies before continuing with the original concept of pushing the BEF into the sea. The offensive ended at Villers-Bretonneux, to the east of the Allied communications centre at Amiens, where the Allies managed to halt the German advance; the German Army had suffered many casualties and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |